-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
RNAseq Data
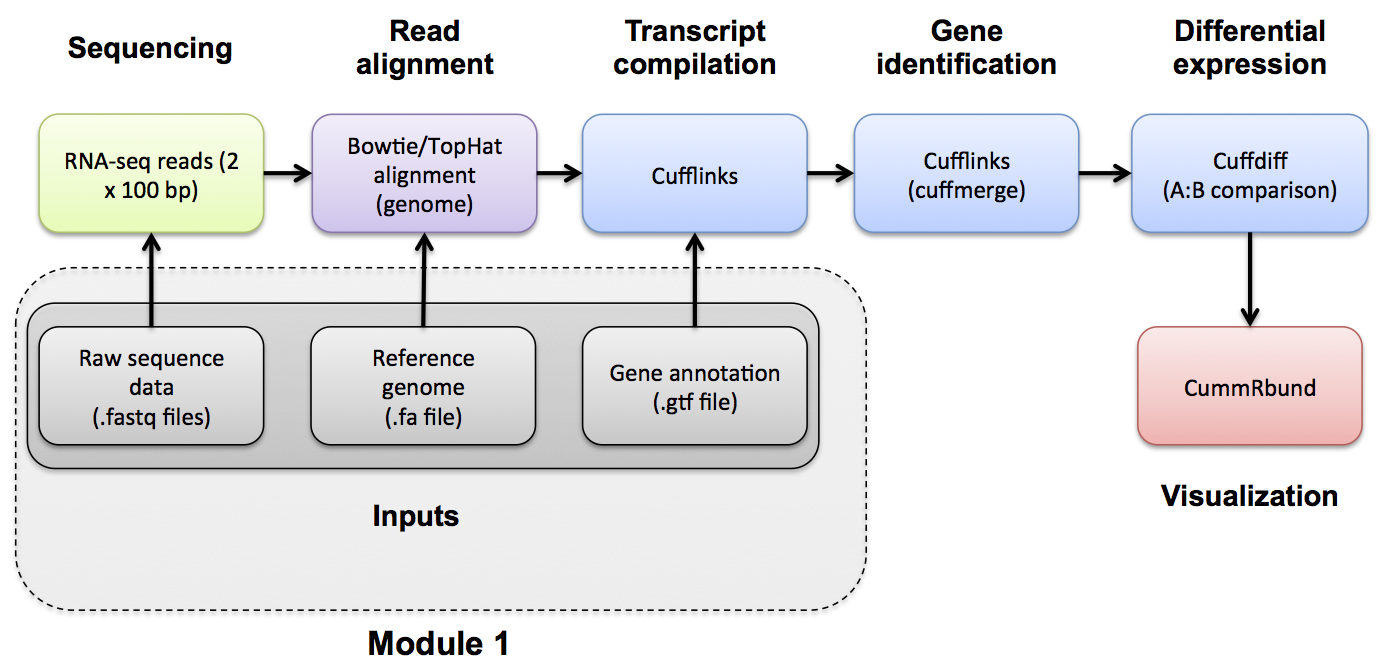
#1-v. RNA-seq Data
The test data consists of two commercially available RNA samples: Universal Human Reference (UHR) and Human Brain Reference (HBR). The UHR is total RNA isolated from a diverse set of 10 cancer cell lines. The HBR is total RNA isolated from the brains of 23 Caucasians, male and female, of varying age but mostly 60-80 years old.
In addition, a spike-in control was used. Specifically we added an aliquot of the ERCC ExFold RNA Spike-In Control Mixes to each sample. The spike-in consists of 92 transcripts that are present in known concentrations across a wide abundance range (from very few copies to many copies). This range allows us to test the degree to which the RNA-seq assay (including all laboratory and analysis steps) accurately reflects the relative abundance of transcript species within a sample. There are two 'mixes' of these transcripts to allow an assessment of differential expression output between samples if you put one mix in each of your two comparisons. In our case, Mix1 was added to the UHR sample, and Mix2 was added to the HBR sample. We also have 3 complete experimental replicates for each sample. This allows us to assess the technical variability of our overall process of producing RNA-seq data in the lab.
For all libraries we prepared low-throughput (Set A) TruSeq Stranded Total RNA Sample Prep Kit libraries with Ribo-Zero Gold to remove both cytoplasmic and mitochondrial rRNA. Triplicate, indexed libraries were made starting with 100ng Agilent/Strategene Universal Human Reference total RNA and 100ng Ambion Human Brain Reference total RNA. The Universal Human Reference replicates received 2 ul of 1:1000 ERCC Mix 1. The Human Brain Reference replicates received 1:1000 ERCC Mix 2. The libraries were quantified with KAPA Library Quantification qPCR and adjusted to the appropriate concentration for sequencing. The triplicate, indexed libraries were then pooled prior to sequencing. Each pool of three replicate libraries were sequenced across 2 lanes of a HiSeq 2000 using paired-end sequence chemistry with 100bp read lengths.
So to summarize we have:
- UHR + ERCC Spike-In Mix1, Replicate 1
- UHR + ERCC Spike-In Mix1, Replicate 2
- UHR + ERCC Spike-In Mix1, Replicate 3
- HBR + ERCC Spike-In Mix2, Replicate 1
- HBR + ERCC Spike-In Mix2, Replicate 2
- HBR + ERCC Spike-In Mix2, Replicate 3
Each data set has a corresponding pair of FastQ files (read 1 and read 2 of paired end reads).
The reads are paired-end 101-mers generated on an Illumina HiSeq instrument.
The test data has been pre-filtered for reads that appear to map to chromosome 22. Lets get that raw input data onto our cloud instance.
cd $RNA_HOME/
mkdir -p data
cd data
Make a copy of the test data
wget http://genome.wustl.edu/pub/rnaseq/data/brain_vs_uhr_w_ercc/downsampled_5pc_chr22/HBR_UHR_ERCC_ds_5pc.tar
Unpack the test data. You should see 6 sets of paired end fastq files. One for each of our sample replicates above. We have 6 pairs (12 files) because in fastq format, read 1 and read 2 of a each read pair (fragment) are stored in separate files.
tar -xvf HBR_UHR_ERCC_ds_5pc.tar
ls
Enter the data directory and view the first two read records of a file (in fastq format each read corresponds to 4 lines of data)
zcat UHR_Rep1_ERCC-Mix1_Build37-ErccTranscripts-chr22.read1.fastq.gz | head -n 8
Identify the following components of each read: read name, read sequence, and quality string
How many reads are there in the first library? Decompress file on the fly with 'zcat', pipe into 'grep', search for the read name prefix and pipe into 'wc' to do a word count ('-l' gives lines)
zcat UHR_Rep1_ERCC-Mix1_Build37-ErccTranscripts-chr22.read1.fastq.gz | grep -P "^\@HWI" | wc -l
##PRACTICAL EXERCISE 2
Assignment: Download an additional dataset and unpack it. This data will be used in future practical exercises.
- Hint: Do this in a separate working directory called ‘practice’ and create sub-directories for organization (data, alignments, etc).
- In this exercise you will download an archive of publicly available read data in FASTQ format from here: http://genome.wustl.edu/pub/rnaseq/data/alignment_practical.tar
Solution: When you are ready you can check your approach against the Solutions
| Previous Section | This Section | Next Section | |:-----------------------------:|:----------------------------:|:-----------------------------------:| | Indexing | Data | Data QC |
##Note: The current version of this tutorial is now at www.rnaseq.wiki
Table of Contents
Module 0: Authors | Citation | Syntax | Intro to AWS | Log into AWS | Unix | Environment | Resources
Module 1: Installation | Reference Genomes | Annotations | Indexing | Data | Data QC
Module 2: Adapter Trim | Alignment | IGV | Alignment Visualization | Alignment QC
Module 3: Expression | Differential Expression | DE Visualization
Module 4: Ref Guided | De novo | Merging | Differential Splicing | Splicing Visualization
Module 5: Kallisto
Appendix: Abbreviations | Lectures | Practical Exercise Solutions | Integrated Assignment | Proposed Improvements | AWS Setup