-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Computer Vision Overview
The FTC control system software has built-in support for two computer vision technologies:
-
Vuforia - Vuforia is PTC's augmented reality technology. Teams can use Vuforia to identify two-dimensional (2D) image targets and use these targets as reference points for autonomous navigation.
- Each season, FIRST provides 2D image tagets that can be used as navigational reference points.
- If Vuforia recognizes an image target, it provides very accurate information about the robot's location relative to the target.
- A robot can use this information to navigate autonomously on the field.
- Special Vuforia image targets, known as VuMarks, can also be used to encode hidden game information on the field.
-
TensorFlow Lite - TensorFlow Lite is a lightweight version of Google's TensorFlow machine learning technology that is designed to run on mobile devices such as an Android smartphone.
- Each season FIRST creates a TensorFlow inference model that can be used to "look" for specific game elements.
- If TensorFlow recognizes an object, it returns location info about the identified object.
- A robot can use this location information to navigate to the recognized object.
- Note that in the FTC control system, the TensorFlow software uses the Vuforia software to "grab" images from the camera while it is looking for or tracking game elements.
- TensorFlow only uses Vuforia to get the camera images.
- TensorFlow does all its own object detection and tracking independently, without any other help from Vuforia.
- Very efficient with a fast detection rate (estimated 15 to 20 detections per second).
- Provides accurate, relative location of robot to target in field coordinates.
- Only looks for 2D image targets.
- Image targets must have a large amount of detail and uniqueness in order to be accurate and useful.
- Vuforia must see the image target clearly in order to calculate location to the target.

Vuforia provides accurate location info, but requires a clear view of the image target.
- TensorFlow learns how to recognize target objects, not just specific images.
- Recognizes objects in spite of different backgrounds.
- Recognizes objects in varied lighting conditions.
- Recognizes objects even when objects are oriented in different positions.
- TensorFlow can be taught how to distinguish between similar looking (but still distinct) objects, such as a Stone and a Skystone from the 2019-2020 challenge.
- TensorFlow is computationally intensive and has a low detection rate (an estimated 1 to 2 detections per second).
- If TensorFlow recognizes an object in its field of view, it only returns location information on where the target object is within its field of view.
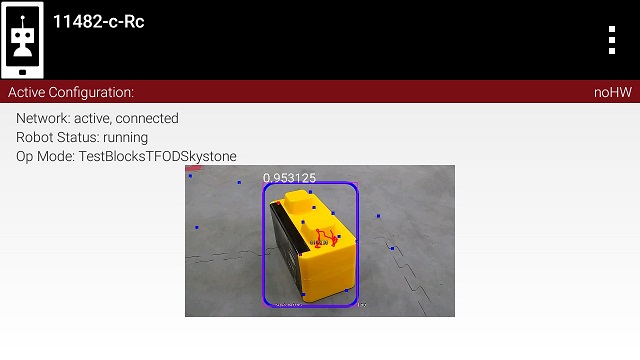
TensorFlow can recognize actual objects (and not just 2D image targets).

TensorFlow can be taught to distinguish between similar looking objects.
The choice of whether to use TensorFlow Lite or Vuforia will be influenced by factors such as distance-to-target, lighting, accuracy required, camera placement and etc..
In the 2019-2020 challenge, the Skystone game element can be identified and tracked using either technology. Vuforia requires that the 2D image target on the face of the Skystone be visible for detection and tracking. TensorFlow can also recognize Stones in the 2019-2020 challenge in addition to the Skystone elements. Either can be used to identify and track Skystones during a match.
