This is a tutorial explaining how to use Apache Zeppelin notebook to interact with Apache Cassandra NoSQL database through Apache Spark or directly through Cassandra CQL language.
Apache Spark is web-based notebook that enables interactive data analytics. Zeppelin interpreter concept allows any language/data-processing-backend to be plugged into Zeppelin. Currently Zeppelin supports many interpreters such as Scala(with Apache Spark), Python(with Apache Spark), SparkSQL, Hive, Markdown, CQL Cassandra, and Shell. More details can be found here https://zeppelin.incubator.apache.org/
Apache Spark is a fast and general engine for big data processing, with built-in modules for streaming, SQL, machine learning and graph processing. More details can be found here http://spark.apache.org. It will be used for Cassandra data processing needs (ETL, transformations, analytics ...).
DataStax have developed a Spark Cassandra Connector to be able to read and write Cassandra data from Spark API. The Spark Cassandra Connector lets you expose Cassandra tables as Spark RDDs (or DataFrames), write Spark RDDs (or DataFrames) to Cassandra tables, and execute arbitrary CQL queries in your Spark applications.
Useful links:
- The Spark Cassandra Connector github repository
- Getting started with Apache Spark and Cassandra
- Free training on DataStax Enterprise Analytics with Apache Spark
The Cassandra Query Language (CQL) is the primary language for communicating with the Cassandra database. Documentation on CQL usage:
The Cassandra CQL Interpreter for Apache Zeppelin is written by my colleague Duy Hai Doan @doanduyhai
CQL Interpreter documentation for Apache Zeppelin 0.5.5
1 - Apache Cassandra and Apache Spark
First you need to install a Cassandra cluster and a Spark cluster connected with the DataStax Spark Cassandra connector. A very simple way to do that is to use DataStax Enterprise (DSE), it’s free for development or test and it contains Apache Cassandra and Apache Spark already linked.
You can download DataStax Enterprise from https://academy.datastax.com/downloads and find installation instructions here http://docs.datastax.com/en/getting_started/doc/getting_started/installDSE.html.
After the installation, start your DSE Cassandra cluster (it can be a single node) with Spark enable with the command line dse cassandra -k.
2 - Apache Zeppelin
-
Clone Zeppelin repository from https://github.com/apache/incubator-zeppelin
git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-zeppelin -
Compile with the cassandra-spark connector
Select your version depending of your DataStax Enterprise (DSE) or Apache Spark version installed. For example for DSE 4.8 or Spark 1.4
mvn clean package -Pcassandra-spark-1.4 -DskipTests
3 - Link between Zeppelin and Spark
You have the choice to use Spark embedded within Zeppelin (automatically installed) or your own deployed Spark cluster (with DSE or in standalone). For this last option you may need to tune the $ZEPPELINE_HOME/conf/zeppelin-env.sh file to change the MASTER parameter. By default it is set to spark://127.0.0.1:7077
4 - Start Zeppelin
$ZEPPELIN_HOME\bin\zeppelin-daemon.sh start
Zeppelin must then be available at http://localhost:8080/
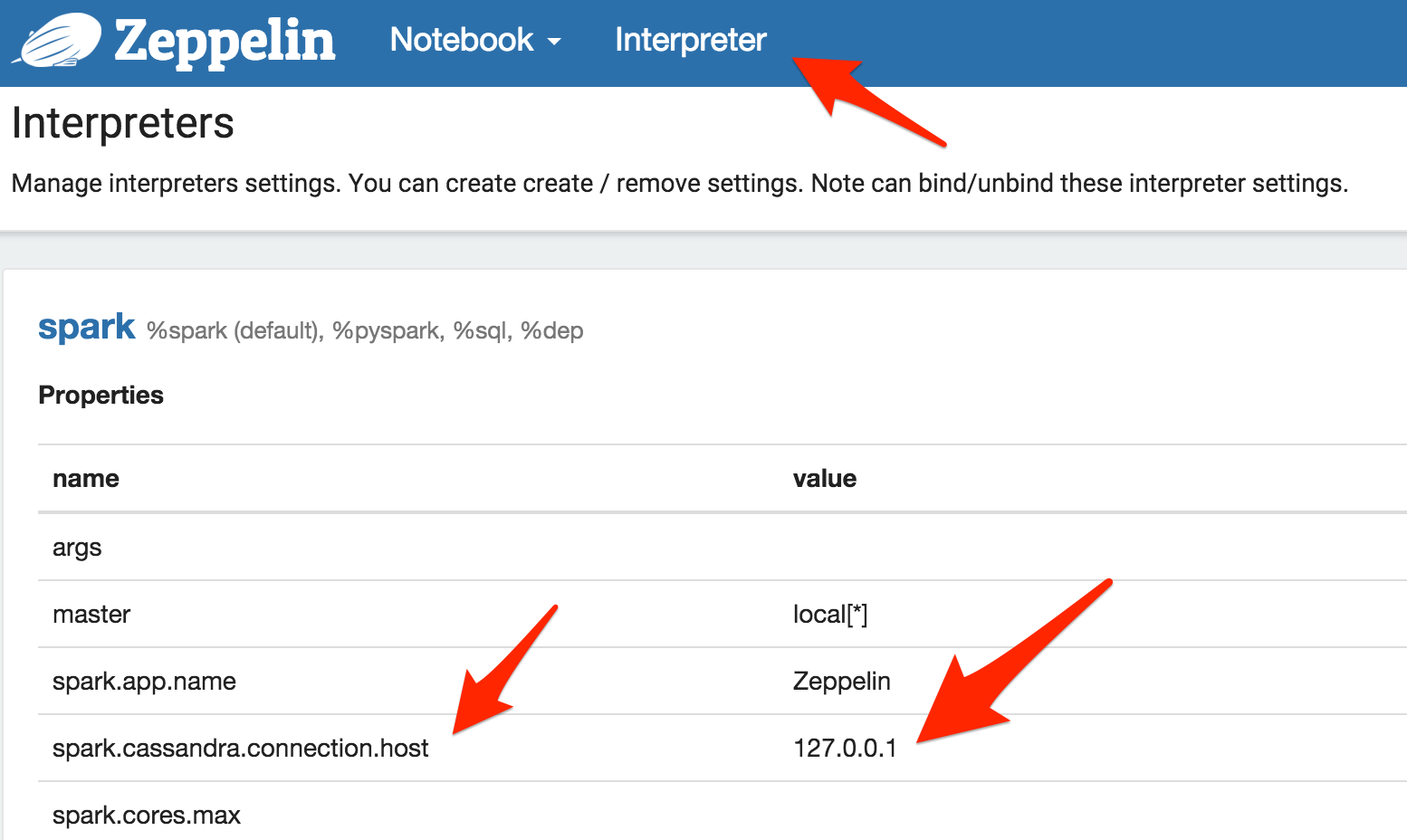
5 - Add the property spark.cassandra.connection.host with value 127.0.0.1 (or IP of one of your Cassandra cluster node) to the Spark connector interpreter
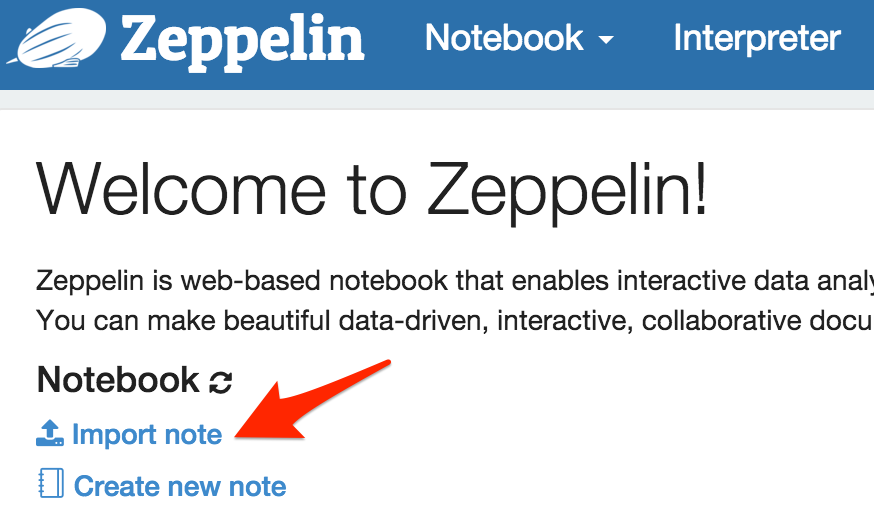
6 - Download and import in Zeppelin the demonstration note found at https://raw.githubusercontent.com/victorcouste/zeppelin-spark-cassandra-demo/master/Demo_Zeppelin_Spark_Cassandra.json
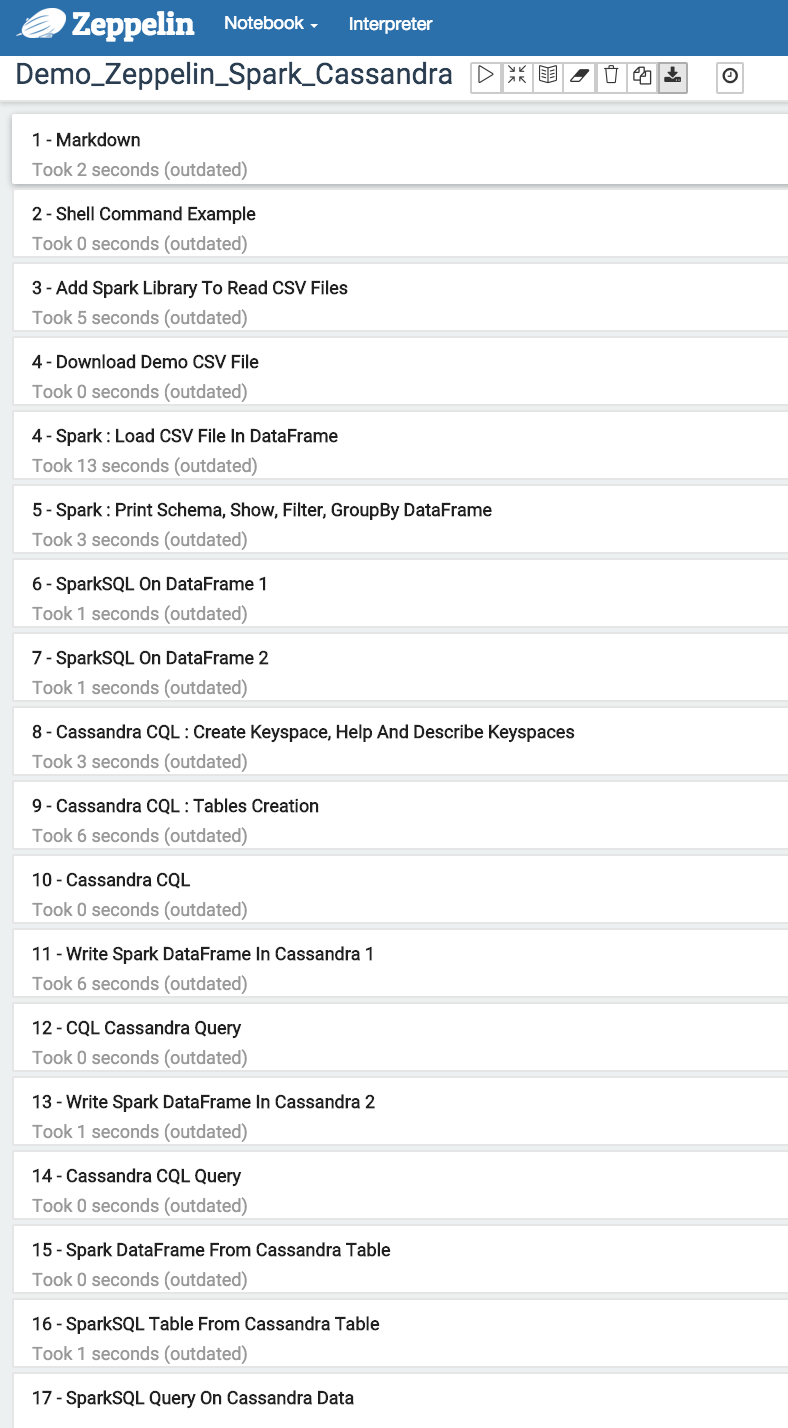
7 - Follow paragraphs of Demo_Zeppelin_Spark_Cassandra note and have fun!
8 - Notes on paragraphs
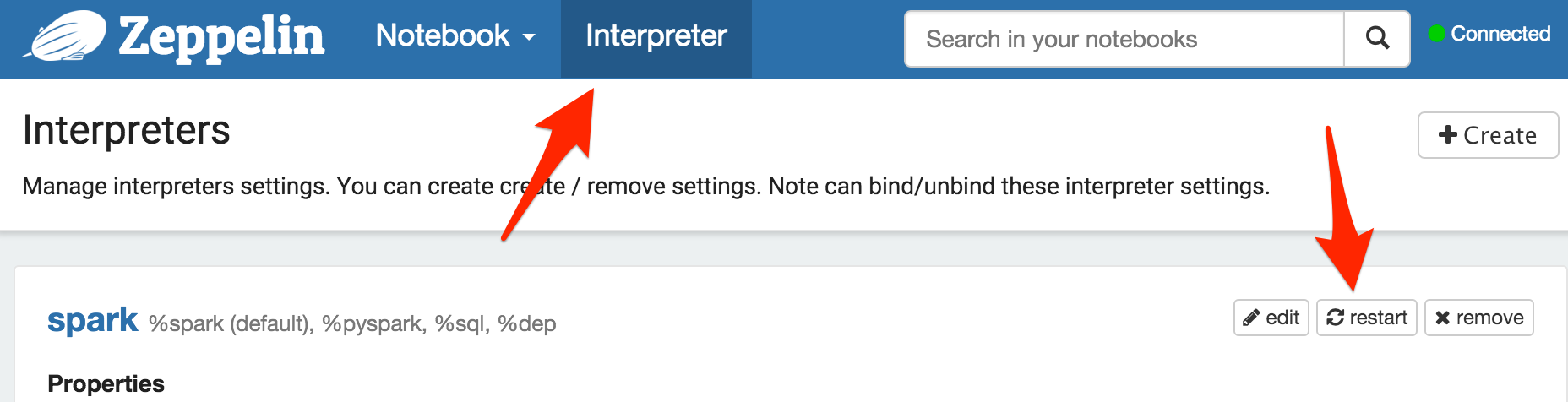
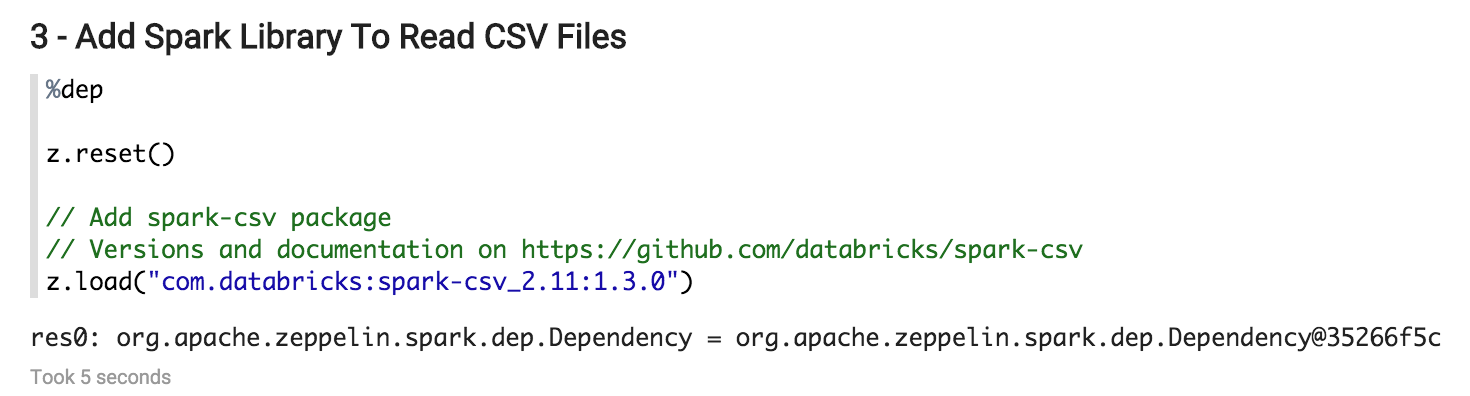
In the paragraph 3, just after running it, you will have to restart the Spark interpreter. Then the error message must disappear if you re-run the paragraph 3.
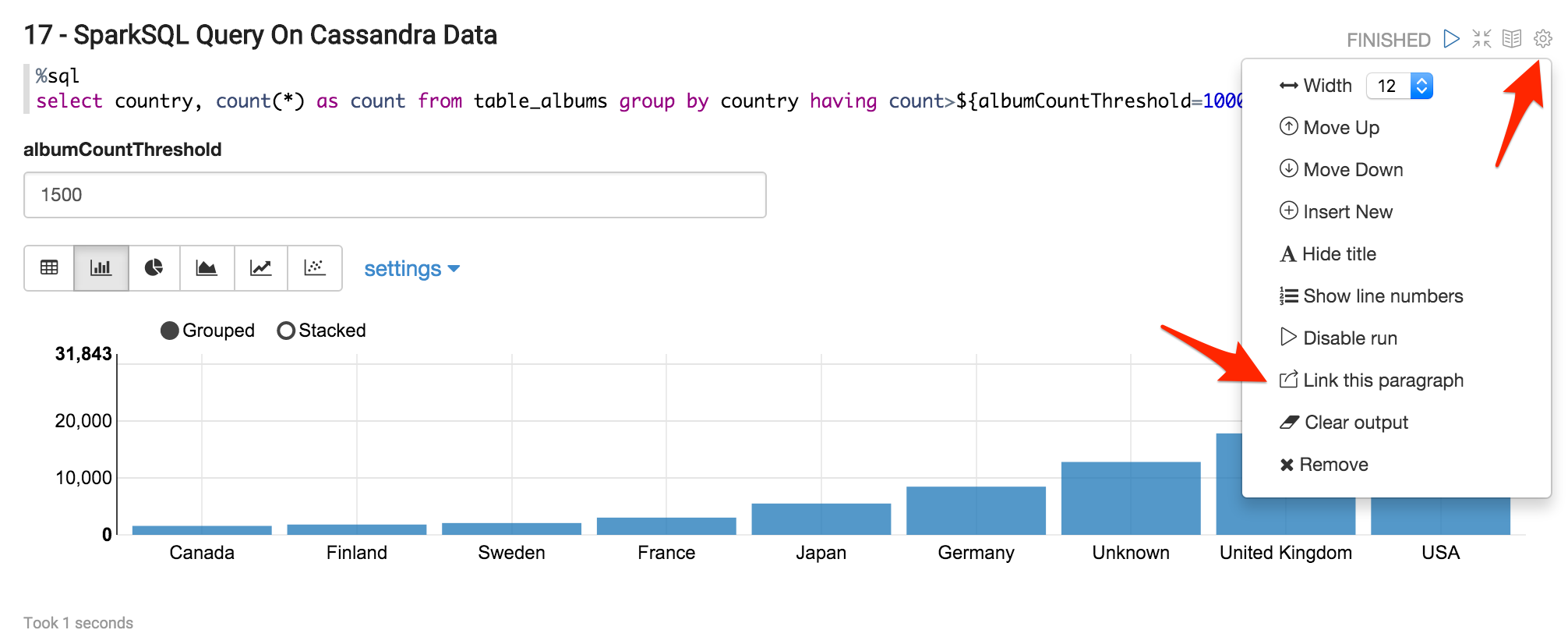
In the last paragraph 17, you can finally create a dashboard that can be embedded in a Website iFrame. Click on “Link this paragraph” and you will get in a new window the URL of the dashboard.