-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 24
Extrapolation and Calibration Modes
dmvdostem has two primary "modes":
- Extrapolation Mode
- Calibration Mode
Using calibration mode, you can view the program's progress in real time, you can pause and resume the program, and edit some program options and parameters.
Extrapolation mode does not provide these capabilities, and should be slightly more efficient. Extrapolation mode should be used for any large scale runs or productions runs.
Running the model without --cal-mode will result in an extrapolation run. During an extrapolation run, there are no .json files produced by the model, and you cannot pause the simulation. The model should run faster in extrapolation mode and consume fewer resources because the json files do not have to be written to the file system at the end of each timestep.
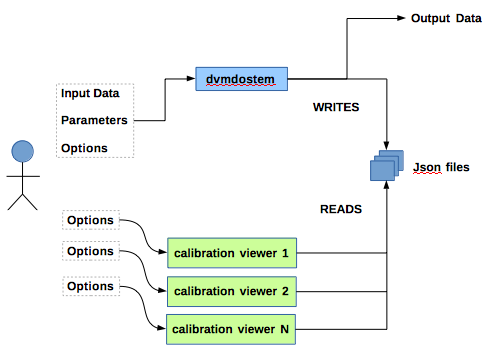
The calibration interface to dvmdostem provides a way to dynamically view the
progress of a dvmdostem simulation in the eq run stage as well as pause
the simulation and modify certain run-time variables before resuming the
simulation.
The calibration interface relies on two primary components:
- Control of the simulation is handled on the "C++ side".
- Visualization of the simulation is handled on the "Python side".
The linkage between these two components is done
with json files that are stored in your /tmp/ directory. Provided in the
project's' calibration/ directory are a set of scripts for visualizing the
progress of the simulation. The progress of the simulation is being recorded in
the json files in your /tmp/ directory.
Why write files to
/tmp/and not some location within the project directory? The volume of files produced is not insignificant. Writing to/tmp/means that the operating system will eventually clean up the files if we forget to delete them.
The arrangement is depicted in the image below.
Right now our calibration viewer consists of the calibration-viewer.py python
script in the calibration/ directory. This is an "Expanding Window" plot which
refers to the fact that the x-axis of the plot will adjust its range to accommodate
the .json that the script finds in the /tmp/ directory. There is much more
info about the script available with the --help flag:
$ ./calibration/calibration-viewer.py
usage: calibration-viewer.py [-h] [--pft {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}]
[--suite {VegSoil,Fire,Soil,NCycle,Environment,Vegetation}]
[--list-suites] [--tar-cmtname | --tar-cmtnum ]
[--list-caltargets] [-l LOGLEVEL] [--static]
[--save-name SAVE_NAME]
[--save-format SAVE_FORMAT] [--no-show]
[--from-archive FROM_ARCHIVE] [--monthly]