In this repository, you can find basic encryption algorithms implemented in JavaScript, Ruby and Python
Caesar cipher (or Vigenere cipher) (Wiki)
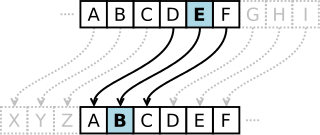
In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher, the shift cipher, Caesar's code or Caesar shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence.
The encryption step performed by a Caesar cipher is often incorporated as part of more complex schemes, such as the Vigenère cipher, and still has modern application in the ROT13 system. As with all single-alphabet substitution ciphers, the Caesar cipher is easily broken and in modern practice offers essentially no communication security.
The action of a Caesar cipher is to replace each plaintext letter with a different one a fixed number of places down the alphabet. The cipher illustrated here uses a left shift of three, so that (for example) each occurrence of E in the plaintext becomes B in the ciphertext.
The encryption can also be represented using modular arithmetic by first transforming the letters into numbers, according to the scheme, A = 0, B = 1,..., Z = 25. Encryption of a letter x by a shift n can be described mathematically as,
Decryption is performed similarly,
(There are different definitions for the modulo operation. In the above, the result is in the range 0...25. I.e., if x+n or x-n are not in the range 0...25, we have to subtract or add 26.)
The replacement remains the same throughout the message, so the cipher is classed as a type of monoalphabetic substitution, as opposed to polyalphabetic substitution.
XOR cipher (Wiki)
In cryptography, the simple XOR cipher is a type of additive cipher,[1] an encryption algorithm that operates according to the principles, where ⊕ denotes the exclusive disjunction (XOR) operation. This operation is sometimes called modulus 2 addition (or subtraction, which is identical). With this logic, a string of text can be encrypted by applying the bitwise XOR operator to every character using a given key. To decrypt the output, merely reapplying the XOR function with the key will remove the cipher.
| A | B | Output |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Feistel cipher (Wiki)
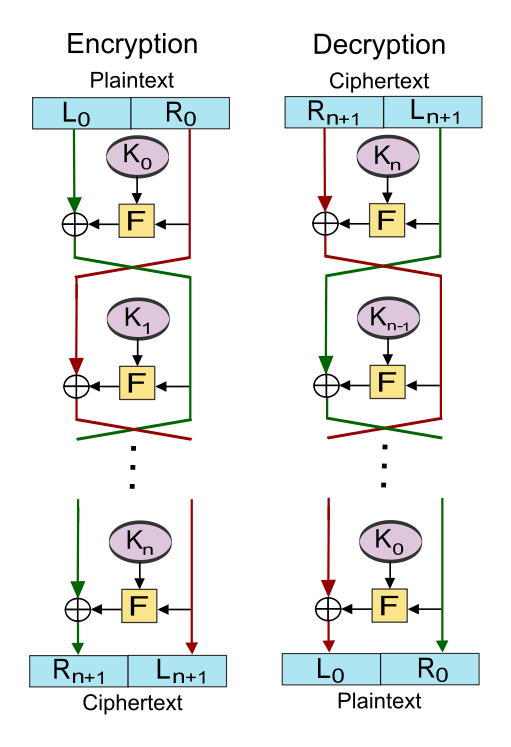
In cryptography, a Feistel cipher is a symmetric structure used in the construction of block ciphers, named after the German-born physicist and cryptographer Horst Feistel who did pioneering research while working for IBM (USA); it is also commonly known as a Feistel network. A large proportion of block ciphers use the scheme, including the Data Encryption Standard (DES). The Feistel structure has the advantage that encryption and decryption operations are very similar, even identical in some cases, requiring only a reversal of the key schedule. Therefore, the size of the code or circuitry required to implement such a cipher is nearly halved.
A Feistel network is an iterated cipher with an internal function called a round function.
Clone the repo and run this commands on cloned folder Gulp'll complie scripts
$ git clone https://github.com/stepanzin/Information-security.git
$ cd Information-security
$ npm i
$ gulp