A mealy Machine Style Finite State Machine in GO
The mainTest.go serves as an example:
mainTest.go is program used to calculate the even/odd number of 1s in a binary string.
For example:
- "1011" has odd number of 1s
- "1001" has even number of 1s
- "110111" has odd number of 1s
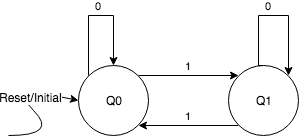
The FSM for the problem would be as follows:
package main
import (
"fmt"
mealy "github.com/evnix/mealy-fsm/mealy"
)
func onTransition(previousState string, currentState string, input string) {
fmt.Println("previous state: "+previousState, "input: "+input, "current state: "+currentState)
}
func main() {
st := mealy.CreateStateTransitionTable()
st.AddRule("Q0", "0", "Q0", onTransition)
st.AddRule("Q0", "1", "Q1", onTransition)
st.AddRule("Q1", "1", "Q0", onTransition)
st.AddRule("Q1", "0", "Q1", onTransition)
st.SetInitialState("Q0")
ipString := "10110011"
for i := 0; i < len(ipString); i++ {
nextState := st.GetNextState(string(ipString[i]))
st.SetState(nextState, string(ipString[i]))
}
if st.GetCurrentState() == "Q0" {
fmt.Println("There are Even number of 1s")
} else {
fmt.Println("There are Odd number of 1s")
}
}The libray itself is completely text based and any unknown state will likely cause an error. So if you get a pointer/reference error, it means the machine is trying to move to an unknown state.