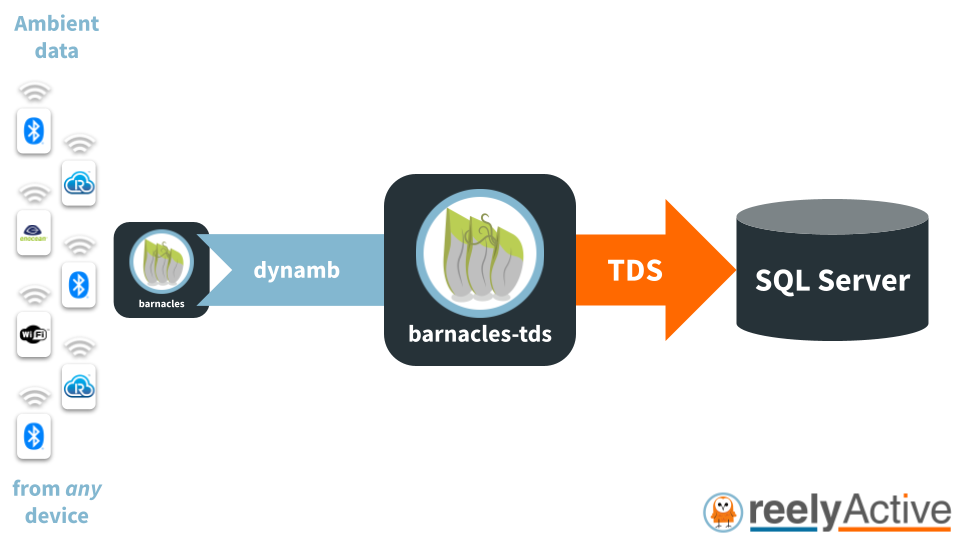
barnacles-tds writes IoT data to a SQL Server database using TDS (Tabular Data Stream).
barnacles-tds ingests a real-time stream of raddec and dynamb objects from barnacles which it writes to the specified SQL Server database as JSON. It couples seamlessly with reelyActive's Pareto Anywhere open source IoT middleware.
barnacles-tds is a lightweight Node.js package that can run on resource-constrained edge devices as well as on powerful cloud servers and anything in between.
A common application of barnacles-tds is to write IoT data from pareto-anywhere to a SQL Server database. Simply follow our Create a Pareto Anywhere startup script tutorial using the script below:
#!/usr/bin/env node
const ParetoAnywhere = require('../lib/paretoanywhere.js');
let pa = new ParetoAnywhere();
// Edit the options to match your SQL Server configuration
const BARNACLES_TDS_OPTIONS = {
config: {
server: 'localhost',
authentication: {
type: 'default',
options: {
userName: 'admin',
password: 'admin',
},
},
options: {
encrypt: false,
database: 'pareto-anywhere',
},
},
raddecTable: 'raddec',
raddecColumn: 'raddec',
dynambTable: 'dynamb',
dynambColumn: 'dynamb',
eventsToStore: { dynamb: {} },
};
// ----- Exit gracefully if the optional dependency is not found -----
let BarnaclesTDS;
try {
BarnaclesTDS = require('barnacles-tds');
} catch (err) {
console.log('This script requires barnacles-tds. Install with:');
console.log('\r\n "npm install barnacles-tds"\r\n');
return console.log('and then run this script again.');
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------------
pa.barnacles.addInterface(BarnaclesTDS, BARNACLES_TDS_OPTIONS);Use the following query to setup the table that will store the dynamb messages.
The column name can be changed if desired, and is configurable through the options.
CREATE TABLE dynamb (
_storeId int NOT NULL IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
dynamb VARCHAR(8000) NOT NULL,
)
Use the following query to setup the table that will store the raddec messages.
The column name can be changed if desired, and is configurable through the options.
CREATE TABLE raddec (
_storeId int NOT NULL IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
raddec VARCHAR(8000) NOT NULL,
)
barnacles-tds supports the following options:
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| config | { /_ See below _/ } | See Tedious Connection config |
| raddecTable | "raddec" | Name of table in which to store raddecs |
| raddecColumn | "raddec" | Name of column in which to store raddec |
| dynambTable | "dynamb" | Name of table in which to store dynambs |
| dynambColumn | "dynamb" | Name of column in which to store dynamb |
| eventsToStore | { dynamb: {} } | See event-specific properties below |
For raddec events, all raddec toFlattened() options are supported. The default is { includePackets: false }. A filters property is also supported, which observes the properties of a raddec-filter.
The default config is as follows:
{
server: "localhost",
authentication: {
type: "default",
options: { userName: "admin", password: "admin" }
},
options: {
encrypt: false,
database: "pareto-anywhere"
}
}
It is possible to test barnacles-tds with simulated raddec and dynamb events by running the following command:
npm run simulator
The following environment variables can optionally be set
| ENVIRONMENT VARIABLE | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| INTERVAL_MILLISECONDS | 5000 | Milliseconds between starting to emit events |
| NUMBER_OF_DYNAMB_EVENTS | 1 | Number of dynamb events to emit each interval |
| NUMBER_OF_RADDEC_EVENTS | 1 | Number of raddec events to emit each interval |
To load test sending events to a database, the NUMBER_OF_DYNAMB_EVENTS and NUMBER_OF_RADDEC_EVENTS environment variables can be set to control the number of events sent every interval. For example:
NUMBER_OF_DYNAMB_EVENTS=250 NUMBER_OF_RADDEC_EVENTS=100 npm run simulator
Each simulated event will be unique, with an intervalCount and deviceNumber used to identify when the event was sent.
The intervalCount identifies which batch the event was created in. The count will reset each time the script is run. For dynamb events, the intervalCount will be stored in the txCount property. For raddec events, the intervalCount will be stored in the numberOfDecodings property.
dynamb events will contain the deviceNumber in the deviceId, and raddec events will contain the deviceNumber in the transmitterId. It will be stored in the last two bytes of the id. For example, the id ff690000030f contains 030f as the last two bytes, which is the number 783. This means that it was the 783rd event sent during one interval. The deviceIds will reset for each interval.
Using the combined values of the intervalCount and deviceID can help identify when an event was sent, useful for debugging.
NOTE: If the number of events is too high, or the interval too quick, then the events will become backlogged in the tdsRequestQueue, and won't end up getting sent to the database. On a laptop with a local instance of SQL Server, it was found that 350 events every 1000 milliseconds was about the maximum before events became backlogged.
Discover how to contribute to this open source project which upholds a standard code of conduct.
Consult our security policy for best practices using this open source software and to report vulnerabilities.
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2024 reelyActive
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.