-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
multiinstrument_example
includes main-level program
MULTI-INSTRUMENT EXAMPLE
This script demonstrates reading Cassini RADAR SAR, VIMS and ISS images and projecting them onto an orthographical map for display as a RGB composite.
The SAR data file used, BIFQI22N068_D045_T003S01_V02.IMG, is too large (202 MB) to include with the OMINAS distribution. This script will look for the file under ~/ominas_data/sar/, and if not found, will download it from PDS<http://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/data/cassini/cassini_orbiter/CORADR_0045/DATA/BIDR/BIFQI22N068_D045_T003S01_V02.ZIP>, then unzip it.
Setup: The instrument detectors, translators and transforms must contain the RADAR, ISS and VIMS definitions, as is included in demo/data/instrument_detectors.tab, demo/data/translators.tab, and demo/data/transforms.tab. The PDS detector and io functions must also be set up in the corresponding tables, as is in config/tab/filetype_detectors.tab and config/tab/io.tab.
This example requires SPICE/Icy to have been setup. It can be run just by doing:
.run multiinstrument_exampleFrom within an OMINAS IDL session.
Troubleshooting: This example uses ISS, VIMS and RADAR data, so each of these 3 might independently fail. If this example fails, it may be helpful to try first running the 3 individual instrument's example scripts first: jupiter_example.pro (ISS), vims_example.pro and radar_example.pro, to see which instruments work in your setup and which do not.
Read and display SAR file
Download the Cassini RADAR SAR image and unzip it, if needed:
;Download the SAR file, if needed ldir='~/ominas_data/sar' spawn,'eval echo '+ldir,res ldir=res img=ldir+path_sep()+'BIFQI22N068_D045_T003S01_V02.IMG' if ~file_test(img,/read) then begin print,'SAR file needed for the demo not found. Downloading it from PDS...' p=pp_wget('http://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/data/cassini/cassini_orbiter/CORADR_0045/DATA/BIDR/BIFQI22N068_D045_T003S01_V02.ZIP',localdir=ldir) p.geturl print,'ZIP file downloaded, decompressing it...' file_unzip,ldir+path_sep()+'CORADR_0045/DATA/BIDR/BIFQI22N068_D045_T003S01_V02.ZIP',/verbose endif ;Read the file dd=dat_read(img)Saturate the data to make the image better looking, since this is just for display purposes:
da=dat_data(dd) dat_set_data,dd,0>da<1d0Show it a 1/20 resolution:
tvim,0d0>da<1d0,zoom=0.05,/order,/new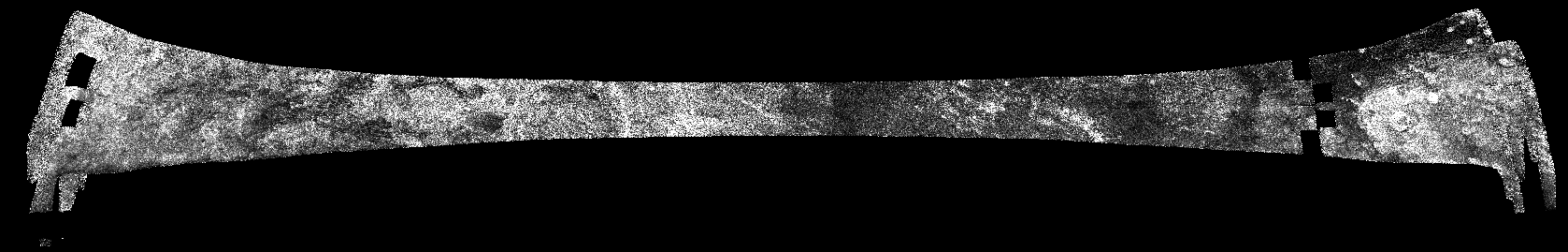
Read and display VIMS and ISS files
Set up a hash containing the file names and precomputed pointing offsets:
hdxy=hash() hdxy['data/CM_1503358311_1_ir_eg.cub']=[5d0,-1d0] hdxy['data/W1477456695_6.IMG']=[0d0,0d0] files=getenv('OMINAS_DIR')+'/demo/data/'+(hdxy.keys()).toarray() nv = n_elements(files) ddv = dat_read(files) sb=bytarr(nv) for i=0,nv-1 do sb[i]=strmatch(files[i],'*.IMG')Create an array of global descriptors and populate it:
gdv = replicate({cd:obj_new(), gbx:obj_new(), dkx:obj_new(), sund:obj_new()}, nv) for i=0, nv-1 do gdv[i].cd = pg_get_cameras(ddv[i]) for i=0, nv-1 do gdv[i].gbx = pg_get_planets(ddv[i], od=gdv[i].cd, name='TITAN') for i=0, nv-1 do gdv[i].sund = pg_get_stars(ddv[i], od=gdv[i].cd, name='SUN')Apply the pointing shifts and compute the limbs:
dxy = dblarr(2,nv) limb_psv=objarr(nv) for i=0, nv-1 do dxy[*,i] = hdxy[file_basename(files[i])] for i=0, nv-1 do pg_repoint, dxy[*,i], 0d, gd=gdv[i] for i=0, nv-1 do limb_psv[i] = pg_limb(gd=gdv[i])Display the VIMS and ISS images:
band=70 for i=0,1 do begin zoom=sb[i] ? 1 : 8 offset=sb[i] ? [200d0,200d0] : [-15,-10] sband=sb[i] ? 0 : band tvim, (dat_data(ddv[i]))[*,*,sband], $ zoom=zoom,/order, /new,offset=offset,$ xsize=600,ysize=600 pg_draw, limb_psv[i] endfor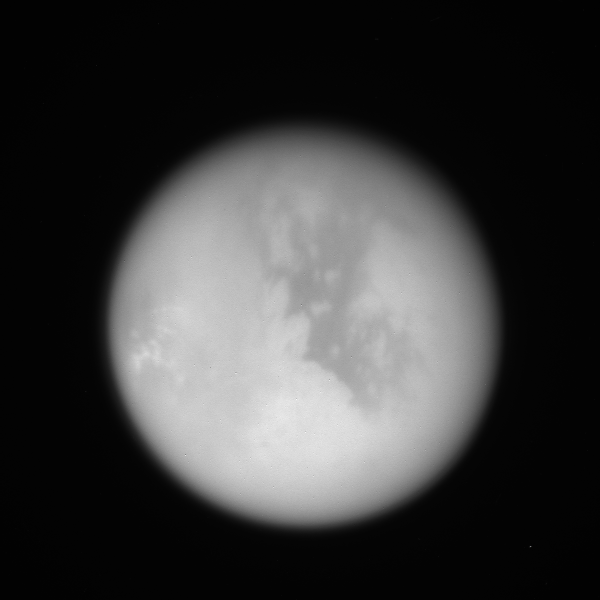
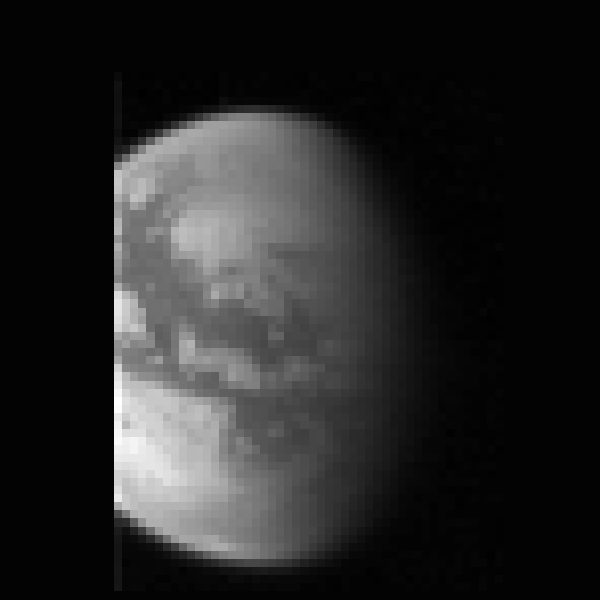

Correct the illumination with a Lambertian function:
dd_phtv = objarr(nv) for i=0, nv-1 do dd_phtv[i] = pg_photom(ddv[i], gd=gdv[i], refl_fn='pht_lamb', $ refl_parm=[0.9d], outline=limb_psv[i])Map images
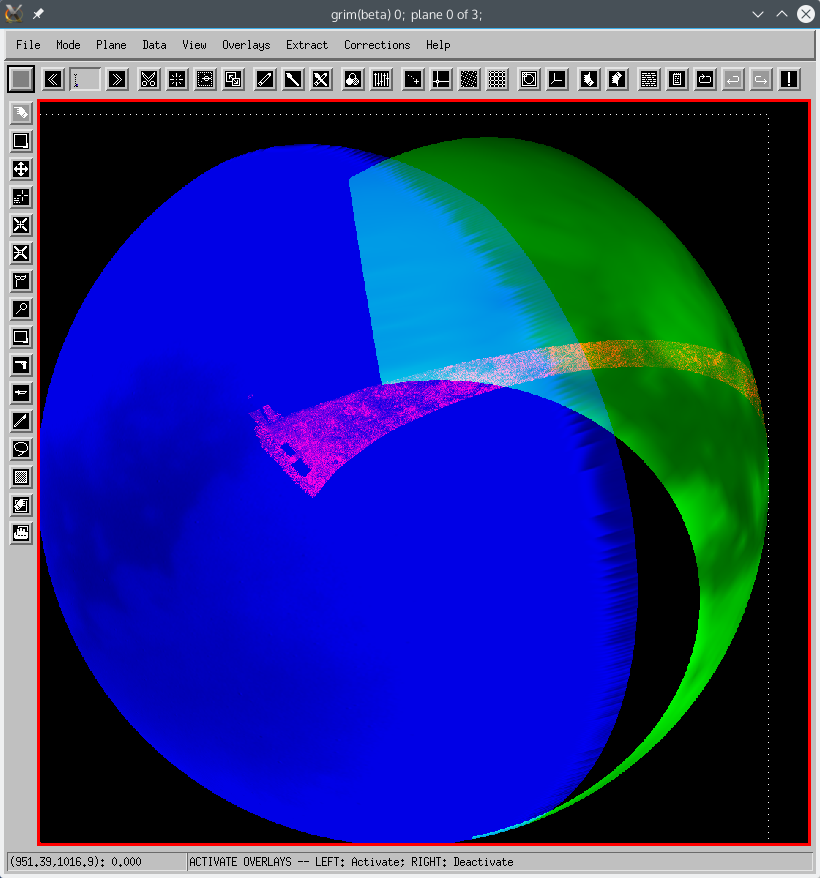
SAR data is provided in PDS as a map on the target, in an oblique rectangular projection, shown above. To use it, first we need to obtain the proper map descriptor from the data object:
mdr=pg_get_maps(dd)Now we will display it in an orthogonal projection. First we define it:
map_xsize = 1000 map_ysize = 1000Create the new map descriptor:
mdp= pg_get_maps(/over, $ name='TITAN',$ type='ORTHOGRAPHIC', $ size=[map_xsize,map_ysize], $ origin=[map_xsize,map_ysize]/2, $ center=[0d0,-0.6d0*!dpi])Now, do the projection of all 3 images:
for i=0,nv-1 do dat_set_data,dd_phtv[i],(dat_data(dd_phtv[i]))[*,*,sb[i] ? 0 : band] dd_mapv = objarr(nv) for i=0, nv-1 do dd_mapv[i] = pg_map(dd_phtv[i], md=mdp, gd=gdv[i], aux=['EMM']) dd_map=pg_map(dd,md=mdp,cd=mdr,pc_xsize=500,pc_ysize=500)Renormalize the data for display, so that all 3 are in the 0-1 range:
mds=[dd_map,dd_mapv] for i=0,2 do begin mdd=dat_data(mds[i]) mddr=minmax(mdd) dat_set_data,mds[i],(mdd-mddr[0])/(mddr[1]-mddr[0]) endforVisualize the result as 3 planes in grim:
grim,mds,cd=replicate(mdp,3),/new;,overlays=['planet_grid']