- Geolocation Options
- Activity Recognition Options
- HTTP & Persistence Options
- Geofencing Options
- Application Options
⚡ Events
🔹 Methods
- Philosophy of Operation
- Geofencing
- HTTP Features
- Android Headless Mode
- Location Data Schema
- Debugging
The following Options can all be provided to the plugin's #ready method:
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 50,
.
.
.
}, function(state) {
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation configured and ready');
if (!state.enabled) { // <-- current state provided to callback
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
}
});
// Use #setConfig if you need to change options after you've executed #configure
BackgroundGeolocation.setConfig({
desiredAccuracy: 10,
distanceFilter: 10
}, function() {
console.log('set config success');
}, function() {
console.log('failed to setConfig');
});| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
desiredAccuracy |
Integer |
0 |
Specify the desired-accuracy of the geolocation system with 1 of 4 values, 0, 10, 100, 1000 where 0 means HIGHEST POWER, HIGHEST ACCURACY and 1000 means LOWEST POWER, LOWEST ACCURACY |
distanceFilter |
Integer |
10 |
The minimum distance (measured in meters) a device must move horizontally before an update event is generated. |
disableElasticity |
Boolean |
false |
Set true to disable automatic speed-based #distanceFilter elasticity. eg: When device is moving at highway speeds, locations are returned at ~ 1 / km. |
elasticityMultiplier |
Float |
1 |
Controls the scale of automatic speed-based distanceFilter elasticity. Increasing elasticityMultiplier will result in few location samples as speed increases. |
stopAfterElapsedMinutes |
Integer |
0 |
The plugin can optionally automatically stop tracking after some number of minutes elapses after the #start method was called. |
stopOnStationary |
Boolean |
false |
The plugin can optionally automatically stop tracking when the stopTimeout timer elapses. |
desiredOdometerAccuracy |
Integer |
100 |
Location accuracy threshold in meters for odometer calculations. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
stationaryRadius |
Integer |
25 |
When stopped, the minimum distance the device must move beyond the stationary location for aggressive background-tracking to engage. |
useSignificantChangesOnly |
Boolean |
false |
Defaults to false. Set true in order to disable constant background-tracking and use only the iOS Significant Changes API. |
locationAuthorizationRequest |
String |
Always |
The desired iOS location-authorization request, either Always, WhenInUse or Any. |
locationAuthorizationAlert |
Object |
{} |
When you configure the plugin locationAuthorizationRequest Always or WhenInUse and the user changes that value in the app's location-services settings or disables location-services, the plugin will display an Alert directing the user to the Settings screen. |
disableLocationAuthorizationAlert |
Boolean |
false |
Disables automatic authorization alert when plugin detects the user has disabled location authorization. You will be responsible for handling disabled location authorization by listening to the providerchange event. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
locationUpdateInterval |
Integer |
1000 |
With distanceFilter: 0, Sets the desired interval for location updates, in milliseconds. distanceFilter > 0 |
fastestLocationUpdateInterval |
Integer |
10000 |
Explicitly set the fastest interval for location updates, in milliseconds. |
deferTime |
Integer |
0 |
Sets the maximum wait time in milliseconds for location updates to be delivered to your callback, when they will all be delivered in a batch. |
allowIdenticalLocations |
Boolean |
false |
The Android plugin will ignore a received location when it is identical to the last location. Set true to override this behaviour and record every location, regardless if it is identical to the last location. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
activityRecognitionInterval |
Integer |
10000 |
The desired time between activity detections. Larger values will result in fewer activity detections while improving battery life. A value of 0 will result in activity detections at the fastest possible rate. |
stopTimeout |
Integer |
5 |
The number of minutes to wait before turning off location-services after the ActivityRecognition System (ARS) detects the device is STILL |
minimumActivityRecognitionConfidence |
Integer |
75 |
Each activity-recognition-result returned by the API is tagged with a "confidence" level expressed as a %. You can set your desired confidence to trigger a state-change. |
stopDetectionDelay |
Integer |
0 |
Number of minute to delay the stop-detection system from being activated. |
disableStopDetection |
Boolean |
false |
Disable accelerometer-based Stop-detection System. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
activityType |
Integer |
ACTIVITY_TYPE_OTHER |
Presumably, this affects ios GPS algorithm. See Apple docs for more information |
disableMotionActivityUpdates |
Boolean |
false |
Disable iOS motion-activity updates (eg: "walking", "in_vehicle"). This feature requires a device having the M7 co-processor (ie: iPhone 5s and up). |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
url |
String |
null |
Your server url where you wish to HTTP POST locations to |
httpTimeout |
Integer |
60000 |
HTTP request timeout in milliseconds. |
params |
Object |
null |
Optional HTTP params sent along in HTTP request to above #url |
extras |
Object |
null |
Optional meta-data to attach to each recorded location |
headers |
Object |
null |
Optional HTTP headers sent along in HTTP request to above #url |
method |
String |
POST |
The HTTP method. Defaults to POST. Some servers require PUT. |
httpRootProperty |
String |
location |
The root property of the JSON data where location-data will be appended. |
locationTemplate |
String |
undefined |
Optional custom location data schema (eg: { "lat:<%= latitude %>, "lng":<%= longitude %> } |
geofenceTemplate |
String |
undefined |
Optional custom geofence data schema (eg: { "lat:<%= latitude %>, "lng":<%= longitude %>, "geofence":"<%= geofence.identifier %>:<%= geofence.action %>" } |
autoSync |
Boolean |
true |
If you've enabeld HTTP feature by configuring an #url, the plugin will attempt to upload each location to your server as it is recorded. |
autoSyncThreshold |
Integer |
0 |
The minimum number of persisted records to trigger an #autoSync action. |
batchSync |
Boolean |
false |
If you've enabled HTTP feature by configuring an #url, batchSync: true will POST all the locations currently stored in native SQLite datbase to your server in a single HTTP POST request. |
maxBatchSize |
Integer |
-1 |
If you've enabled HTTP feature by configuring an #url and batchSync: true, this parameter will limit the number of records attached to each batch. |
maxDaysToPersist |
Integer |
1 |
Maximum number of days to store a geolocation in plugin's SQLite database. |
maxRecordsToPersist |
Integer |
-1 |
Maximum number of records to persist in plugin's SQLite database. Defaults to -1 (no limit). To disable persisting locations, set this to 0 |
locationsOrderDirection |
String |
ASC |
Controls the order that locations are selected from the database (and synced to your server). Defaults to ascending (ASC), where oldest locations are synced first. Descending (DESC) syncs latest locations first. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
stopOnTerminate |
Boolean |
true |
Set false to continue tracking after user teminates the app. |
startOnBoot |
Boolean |
false |
Set to true to enable background-tracking after the device reboots. |
heartbeatInterval |
Integer |
60 |
Rate in seconds to fire heartbeat events. |
schedule |
Array |
undefined |
Defines a schedule to automatically start/stop tracking at configured times |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
preventSuspend |
Boolean |
false |
Enable this to prevent iOS from suspending your app in the background while in the stationary state. Must be used in conjunction with a #heartbeatInterval. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
foregroundService |
Boolean |
false |
Set true to make the plugin mostly immune to OS termination due to memory pressure from other apps. |
enableHeadless |
Boolean |
false |
Set to true to enable "Headless" mode when the user terminates the application. In this mode, you can respond to all the plugin's events in the native Android environment. For more information, see the wiki for Android Headless Mode |
notificationPriority |
Integer |
NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_DEFAULT |
Controls the priority of the foregroundService notification and notification-bar icon. |
notificationTitle |
String |
"Your App Name" | When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. Defaults to the application name |
notificationText |
String |
"Location service activated" | When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. |
notificationColor |
String |
null |
When running the service with foregroundService: true, controls the color of the persistent notification in the Notification Bar. |
notificationSmallIcon |
String |
Your App Icon | When running the service with foregroundService: true, controls your customize notification small icon. Defaults to your application icon. |
notificationLargeIcon |
String |
undefined |
When running the service with foregroundService: true, controls your customize notification large icon. Defaults to undefined. |
forceReloadOnMotionChange |
Boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever the #motionchange event fires. |
forceReloadOnLocationChange |
Boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever the #location event fires. |
forceReloadOnGeofence |
Boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever the #geofence event fires. |
forceReloadOnHeartbeat |
Boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever the #heartbeat event fires. |
forceReloadOnSchedule |
Boolean |
false |
Launch your app whenever a schedule event fires. |
forceReloadOnBoot |
Boolean |
false |
If the user reboots the device with the plugin configured for startOnBoot: true, your will app will launch when the device is rebooted. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
geofenceProximityRadius |
Integer |
1000 |
Radius in meters to query for geofences within proximity. |
geofenceInitialTriggerEntry |
Boolean |
true |
Set false to disable triggering a geofence immediately if device is already inside it. |
| Option | Type | Default | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
debug |
Boolean |
false |
When enabled, the plugin will emit sounds & notifications for life-cycle events of background-geolocation |
logLevel |
Integer |
LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE |
Sets the verbosity of the plugin's logs from LOG_LEVEL_OFF to LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE |
logMaxDays |
Integer |
3 |
Maximum days to persist a log-entry in database. |
| Event Name | Description |
|---|---|
location |
Fired whenever a new location is recorded. |
motionchange |
Fired when the device changes state between stationary and moving |
activitychange |
Fired when the activity-recognition system detects a change in detected-activity (still, on_foot, in_vehicle, on_bicycle, running) |
providerchange |
Fired when a change in the state of the device's Location Services has been detected. eg: "GPS ON", "Wifi only". |
geofence |
Fired when a geofence crossing event occurs. |
geofenceschange |
Fired when the list of monitored geofences within #geofenceProximityRadius changed |
http |
Fired after a successful HTTP response. response object is provided with status and responseText. |
heartbeat |
Fired each #heartbeatInterval while the plugin is in the stationary state with. Your callback will be provided with a params {} containing the last known location {Object} |
schedule |
Fired when a schedule event occurs. Your callbackFn will be provided with the current state Object. |
powersavechange |
Fired when the state of the operating-system's "Power Saving" system changes. Your callbackFn will be provided with a Boolean showing whether "Power Saving" is enabled or disabled |
connectivitychange |
Fired when the state of the device's network connectivity changes (enabled -> disabled and vice-versa) |
enabledchange |
Fired when the plugin's enabled state changes. For example, executing #start and #stop will fire the enabledchange event. |
Event-listeners can be attached using the method #on, supplying the Event Name in the following table. #on accepts both a successFn and failureFn.
BackgroundGeolocation.on("location", successFn, failureFn);Event-listeners are removed with the method #un. You must supply a reference to the exact successFn reference used with the #on method:
function onLocation(location) {
console.log('- location: ', location);
}
function onLocationError(error) {
console.log('- location error: ', error);
}
// Add a location listener
BackgroundGeolocation.on('location', onLocation, onLocationError);
.
.
.
// Remove a location listener supplying only the successFn (onLocation)
BackgroundGeolocation.un('location', onLocation);BackgroundGeolocation Javascript API supports Promises for nearly every method (the exceptions are #watchPosition and adding event-listeners via #on method.
// Traditional API still works:
bgGeo.getCurrentPosition((location) => {
console.log('- current position: ', location);
}, (error) => {
console.log('- location error: ', error);
}, {samples: 1, persist: false});
// Promise API
bgGeo.getCurrentPosition({samples:1, persist: false}).then(location => {
console.log('- current position: ', location);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('- location error: ', error);
});By marking one of your application methods as async you can use the await mechanism instead of callbacks:
async onClickGetPosition() {
let location = await bgGeo.getCurrentPosition({samples:1, persist: false});
conosle.log('- current position: ', location);
let count = await bgGeo.getCount();
console.log('- There are ', count, ' records in the database');
}| Method Name | Arguments | Notes |
|---|---|---|
ready |
{defaultConfig}, successFn, failureFn |
Initializes the plugin with previously persisted configuration. The supplied defaultConfig will be applied only for the first boot of you app — thereafter, the plugin will automatically load its configuration from persisent storage |
configure |
{config}, successFn, failureFn |
Initializes the plugin and configures its config options. The success callback will be executed after the plugin has successfully configured and provided with the current state Object. |
setConfig |
{config}, successFn, failureFn |
Re-configure the plugin with new config options. |
reset |
{defaultConfig}, successFn, failureFn |
Resets the plugin configuration to documented default-values. If a defaultConfig is provided, it will be applied after the configuration reset. |
on |
event,successFn,failureFn |
Adds an event-listener |
un |
event,callbackFn, |
Removes an event-listener |
start |
callbackFn |
Enable location tracking. Supplied callbackFn will be executed when tracking is successfully engaged. This is the plugin's power ON button. |
stop |
callbackFn |
Disable location tracking. Supplied callbackFn will be executed when tracking is successfully halted. This is the plugin's power OFF button. |
getState |
callbackFn |
Fetch the current-state of the plugin, including enabled, isMoving, as well as all other config params |
getCurrentPosition |
successFn, failureFn, {options} |
Retrieves the current position using maximum power & accuracy by fetching a number of samples and returning the most accurate to your callbackFn. |
watchPosition |
successFn, failureFn, {options} |
Start a stream of continuous location-updates. |
stopWatchPosition |
successFn, failureFn |
Halt #watchPosition updates. |
changePace |
Boolean, successFn |
Toggles the plugin's state between stationary and moving. |
getOdometer |
callbackFn |
The plugin constantly tracks distance travelled. The supplied callback will be executed and provided with the distance (meters) as the 1st parameter. |
setOdometer |
Integer, callbackFn |
Set the odometer to any arbitrary value. NOTE setOdometer will perform a getCurrentPosition in order to record to exact location where odometer was set; as a result, the callback signatures are identical to those of getCurrentPosition. |
resetOdometer |
callbackFn |
Reset the odometer to 0. Alias for setOdometer(0) |
startSchedule |
callbackFn |
If a schedule was configured, this method will initiate that schedule. |
stopSchedule |
callbackFn |
This method will stop the Scheduler service. Your callbackFn will be executed after the Scheduler has stopped |
removeListeners |
none |
Remove all events-listeners registered with #on method |
startBackgroundTask |
callbackFn |
Sends a signal to the native OS that you wish to perform a long-running task. The OS will not suspend your app until you signal completion with the #finish method. |
finish |
taskId |
Sends a signal to the native OS the supplied taskId is complete and the OS may proceed to suspend your application if applicable. |
isPowerSaveMode |
callbackFn |
Fetches the state of the operating-systems "Power Saving" mode, whether enabled or disabled |
| Method Name | Arguments | Notes |
|---|---|---|
getLocations |
callbackFn |
Fetch all the locations currently stored in native plugin's SQLite database. Your callbackFn will receive an Array of locations in the 1st parameter |
getCount |
callbackFn |
Fetches count of SQLite locations table SELECT count(*) from locations |
destroyLocations |
callbackFn |
Delete all records in plugin's SQLite database |
sync |
successFn, failureFn |
If the plugin is configured for HTTP with an #url and #autoSync: false, this method will initiate POSTing the locations currently stored in the native SQLite database to your configured #url |
| Method Name | Arguments | Notes |
|---|---|---|
startGeofences |
callbackFn |
Engages the geofences-only trackingMode. In this mode, no active location-tracking will occur -- only geofences will be monitored |
addGeofence |
{config}, successFn, failureFn |
Adds a geofence to be monitored by the native plugin. |
addGeofences |
[geofences], sucessFn, failureFn |
Adds a list geofences to be monitored by the native plugin. |
removeGeofence |
identifier, successFn, failureFn |
Removes a geofence identified by the provided identifier |
removeGeofences |
successFn, failureFn |
Removes all geofences |
getGeofences |
callbackFn |
Fetch the list of monitored geofences. |
| Method Name | Arguments | Notes |
|---|---|---|
setLogLevel |
Integer, callbackFn |
Set the Log filter: LOG_LEVEL_OFF, LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, LOG_LEVEL_WARNING, LOG_LEVEL_INFO, LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG, LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE |
getLog |
callbackFn |
Fetch the entire contents of the current log database as a String. |
destroyLog |
callbackFn, failureFn |
Destroy the contents of the Log database. |
emailLog |
email, callbackFn |
Fetch the entire contents of Log database and email it to a recipient using the device's native email client. |
getSensors |
callbackFn, failureFn |
Returns the presense of device sensors accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer, in addition to iOS/Android-specific sensors |
logger.error |
message |
Record a ❗ log message into the plugin's log database. |
logger.warn |
message |
Record a |
logger.debug |
message |
Record a 🪲 log message into the plugin's log database. |
logger.info |
message |
Record a ℹ️ log message into the plugin's log database. |
logger.notice |
message |
Record a 🔵 log message into the plugin's log database. |
logger.header |
message |
Record a header log message into the plugin's log database. |
logger.on |
message |
Record a 🎾 log message into the plugin's log database. |
logger.off |
message |
Record a 🔴 log message into the plugin's log database. |
logger.ok |
message |
Record a ✅ log message into the plugin's |
playSound |
Integer |
Here's a fun one. The plugin can play a number of OS system sounds for each platform. For IOS and Android. I offer this API as-is, it's up to you to figure out how this works. |
Specify the desired-accuracy of the geolocation system with 1 of 4 values, 0, 10, 100, 1000 where 0 means HIGHEST POWER, HIGHEST ACCURACY and 1000 means LOWEST POWER, LOWEST ACCURACY
You may also use the following constants upon BackgroundGeolocation:
| Name | Value | Location Providers | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
DESIRED_ACCURACY_NAVIGATION |
-2 |
(iOS only) GPS + Wifi + Cellular | Highest power; highest accuracy |
DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH |
-1 |
GPS + Wifi + Cellular | Highest power; highest accuracy |
DESIRED_ACCURACY_MEDIUM |
10 |
Wifi + Cellular | Medium power; Medium accuracy; |
DESIRED_ACCURACY_LOW |
100 |
Wifi (low power) + Cellular | Lower power; No GPS |
DESIRED_ACCURACY_VERY_LOW |
1000 |
Cellular only | Lowest power; lowest accuracy |
DESIRED_ACCURACY_THREE_KILOMETER |
3000 |
(iOS only) Lowest power; lowest accuracy |
BackgroundGeoloction.configure({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH
});DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH uses GPS. speed, heading and altitude are available only from GPS.
📘 For platform-specific information about location accuracy, see the corresponding API docs:
The minimum distance (measured in meters) a device must move horizontally before an update event is generated.
However, by default, distanceFilter is elastically auto-calculated by the plugin: When speed increases, distanceFilter increases; when speed decreases, so too does distanceFilter.
ℹ️ To disable this behaviour, configure disableElasticity: true
ℹ️ To control the scale of the automatic distanceFilter calculation, see elasticityMultiplier
distanceFilter is auto calculated by rounding speed to the nearest 5 m/s and adding distanceFilter meters for each 5 m/s increment.
For example, at biking speed of 7.7 m/s with a configured distanceFilter: 30:
rounded_speed = round(7.7, 5)
=> 10
multiplier = rounded_speed / 5
=> 10 / 5 = 2
adjusted_distance_filter = multiplier * distanceFilter
=> 2 * 30 = 60 meters
At highway speed of 27 m/s with a configured distanceFilter: 50:
rounded_speed = round(27, 5)
=> 30
multiplier = rounded_speed / 5
=> 30 / 5 = 6
adjusted_distance_filter = multiplier * distanceFilter * elasticityMultipiler
=> 6 * 50 = 300 meters
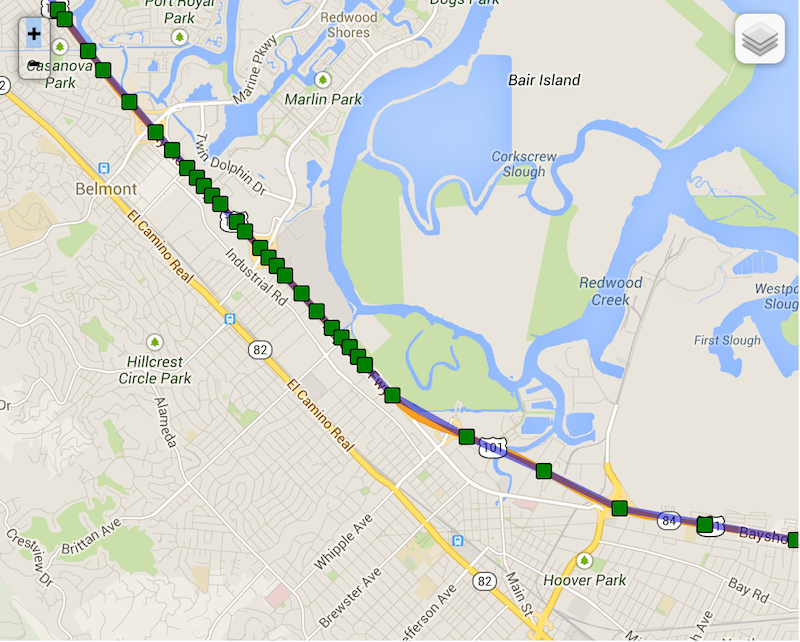
Note the following real example of background-geolocation on highway 101 towards San Francisco as the driver slows down as he runs into slower traffic (geolocations become compressed as distanceFilter decreases)
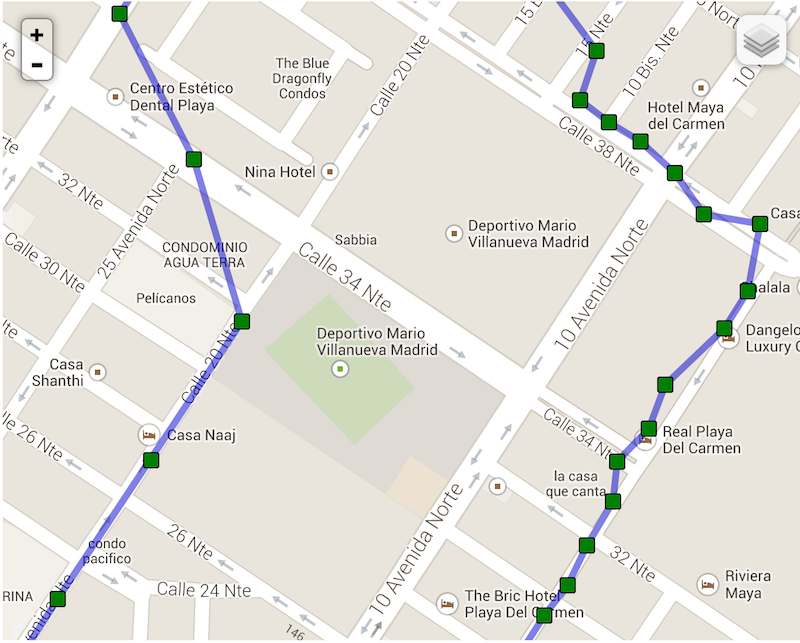
Compare now background-geolocation in the scope of a city. In this image, the left-hand track is from a cab-ride, while the right-hand track is walking speed.
Defaults to false. Set true to disable automatic, speed-based #distanceFilter elasticity.
Controls the scale of automatic speed-based #distanceFilter elasticity. Increasing elasticityMultiplier will result in fewer location samples as speed increases. A value of 0 has the same effect as disableElasticity: true
The plugin can optionally automatically stop tracking after some number of minutes elapses after the #start method was called.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
stopAfterElapsedMinutes: 30
}, function(state) {
BackgroundGeolocation.start(); // <-- plugin will automatically #stop in 30 minutes
});The plugin can optionally automatically stop tracking when the stopTimeout timer elapses. For example, when the plugin first detects a motionchange into the "moving" state, the next time a motionchange event occurs into the "stationary" state, the plugin will have automatically called #stop upon itself.
stopOnStationary will only occur due to stopTimeout timer elapse. It will not occur by manually executing changePace(false).
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
stopOnStationary: true
}, function(state) {
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
});Specify an accuracy threshold in meters for odometer calculations. Defaults to 100. If a location arrives having accuracy > desiredOdometerAccuracy, that location will not be used to update the odometer. If you only want to calculate odometer from GPS locations, you could set desiredOdometerAccuracy: 10. This will prevent odometer updates when a device is moving around indoors, in a shopping mall, for example.
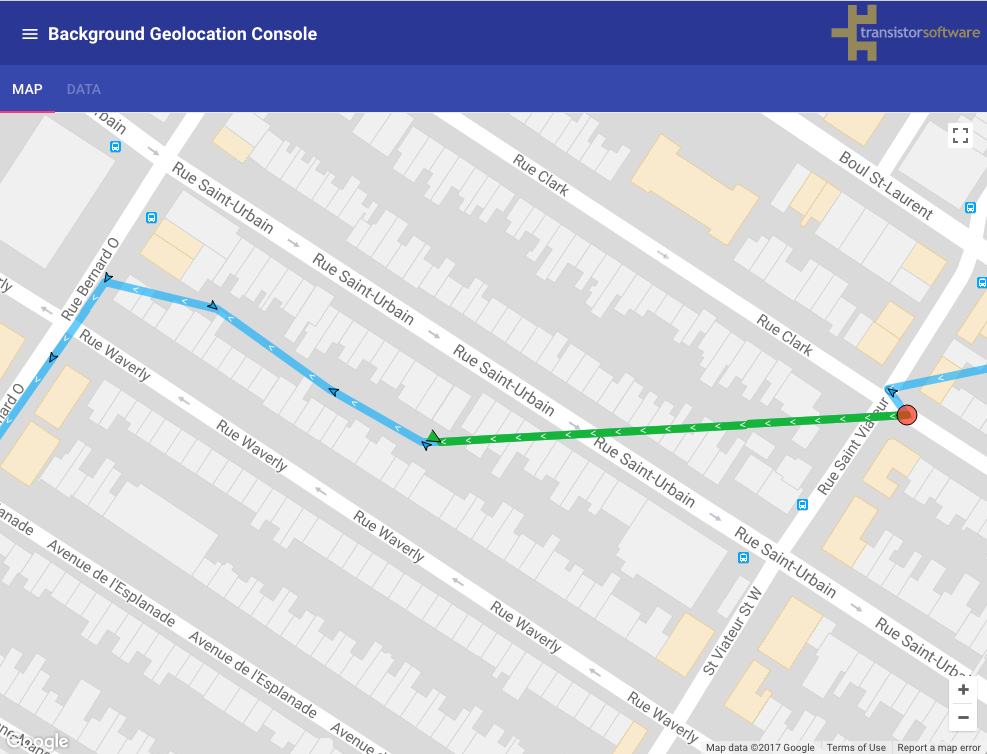
When stopped, the minimum distance the device must move beyond the stationary location for aggressive background-tracking to engage.
Configuring stationaryRadius: 0 has NO EFFECT (in fact the plugin enforces a minimum stationaryRadius of 25).
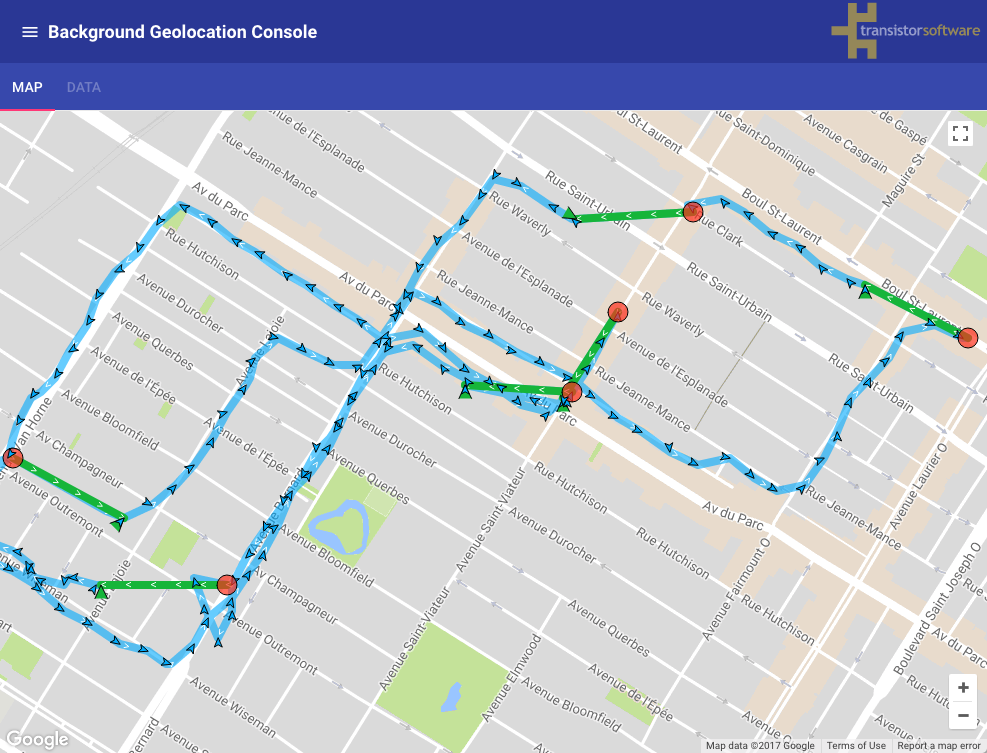
The following image shows the typical distance iOS requires to detect exit of the stationaryRadius, where the green polylines represent a transition from stationary state to moving and the red circles locations where the plugin entered the stationary state.:
📘 For more information, see Philosophy of Operation
Defaults to false. Set true in order to disable constant background-tracking and use only the iOS Significant Changes API.
UIBackgroundMode: "location", this can be a solution. NOTE The Significant Changes API will report a location only every 500 to 1000 meters. Many of the plugin's configuration parameters will be ignored, such as #distanceFilter, #stationaryRadius, #activityType, etc.
undefined. You should only specifiy this option if you know exactly what you're doing.
The default behaviour of the plugin is to turn off location-services automatically when the device is detected to be stationary. When set to false, location-services will never be turned off (and disableStopDetection will automatically be set to true) -- it's your responsibility to turn them off when you no longer need to track the device. This feature should not generally be used. preventSuspend will no longer work either.
The desired iOS location-authorization request, either Always, WhenInUse or Any. locationAuthorizationRequest tells the plugin the mode it expects to be in — if the user changes this mode in their settings, the plugin will detect this (@see locationAuthorizationAlert). Defaults to Always. WhenInUse will display a blue bar at top-of-screen informing user that location-services are on.
If you configure Any, the plugin allow the user to choose either Always or WhenInUse. The plugin will not show the location-authorization dialog when the user changes the selection in Privacy->Location Services
WhenInUse will disable many of the plugin's features, since iOS forbids any API which operates in the background to operate (such as geofences, which the plugin relies upon to automatically engage background tracking).
When you configure the plugin location-authorization Always or WhenInUse and the user changes the value in the app's location-services settings or disabled location-services, the plugin will display an Alert directing the user to the Settings screen. This config allows you to configure all the Strings for that Alert popup and accepts an {Object} containing the following keys:
@config {String} titleWhenOff [Location services are off] The title of the alert if user changes, for example, the location-request to WhenInUse when you requested Always.
@config {String} titleWhenNotEnabled [Background location is not enabled] The title of the alert when user disables location-services or changes the authorization request to Never
@config {String} instructions [To use background location, you must enable {locationAuthorizationRequest} in the Location Services settings] The body text of the alert.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
locationAuthorizationAlert: {
titleWhenNotEnabled: "Yo, location-services not enabled",
titleWhenOff: "Yo, location-services OFF",
instructions: "You must enable 'Always' in location-services, buddy",
cancelButton: "Cancel",
settingsButton: "Settings"
}
})Disables automatic authorization alert when plugin detects the user has disabled location authorization. You will be responsible for handling disabled location authorization by listening to the providerchange event.
By default, the plugin automatically shows a native alert (configured via locationAuthorizationAlert) to the user when location-services are disabled, directing them to the settings screen. If you do not desire this automated behaviour, set disableLocationAuthorizationAlert: true.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('providerchange', (provider) => {
if (!provider.enabled) {
alert('Please enable location services');
}
});
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
disableLocationAuthorizationAlert: true
}, (state) => {
console.log('BackgroundGeolocation ready: ', state);
});locationUpdateInterval you must also configure distanceFilter: 0. distanceFilter overrides locationUpdateInterval.
Set the desired interval for active location updates, in milliseconds.
The location client will actively try to obtain location updates for your application at this interval, so it has a direct influence on the amount of power used by your application. Choose your interval wisely.
This interval is inexact. You may not receive updates at all (if no location sources are available), or you may receive them slower than requested. You may also receive them faster than requested (if other applications are requesting location at a faster interval).
Applications with only the coarse location permission may have their interval silently throttled.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
distanceFilter: 0, // Must be 0 or locationUpdateInterval is ignored!
locationUpdateInterval: 5000 // Get a location every 5 seconds
});Explicitly set the fastest interval for location updates, in milliseconds.
This controls the fastest rate at which your application will receive location updates, which might be faster than #locationUpdateInterval in some situations (for example, if other applications are triggering location updates).
This allows your application to passively acquire locations at a rate faster than it actively acquires locations, saving power.
Unlike #locationUpdateInterval, this parameter is exact. Your application will never receive updates faster than this value.
If you don't call this method, a fastest interval will be set to 30000 (30s).
An interval of 0 is allowed, but not recommended, since location updates may be extremely fast on future implementations.
If #fastestLocationUpdateInterval is set slower than #locationUpdateInterval, then your effective fastest interval is #locationUpdateInterval.
Defaults to 0 (no defer). Sets the maximum wait time in milliseconds for location updates. If you pass a value at least 2x larger than the interval specified with #locationUpdateInterval, then location delivery may be delayed and multiple locations can be delivered at once. Locations are determined at the #locationUpdateInterval rate, but can be delivered in batch after the interval you set in this method. This can consume less battery and give more accurate locations, depending on the device's hardware capabilities. You should set this value to be as large as possible for your needs if you don't need immediate location delivery.
By default, the Android plugin will ignore a received location when it is identical to the last location. Set true to override this behaviour and record everylocation, regardless if it is identical to the last location.
In the logs, you will see a location being ignored:
TSLocationManager: ℹ️ IGNORED: same as last location
An identical location is often generated when changing state from stationary -> moving, where a single location is first requested (the motionchange location) before turning on regular location updates. Changing geolocation config params can also generate a duplicate location (eg: changing distanceFilter).
These are the comma-delimited list of activity-names returned by the ActivityRecognition API which will trigger a state-change from stationary to moving. By default, the plugin will trigger on any of the moving-states:
| Activity Name |
|---|
in_vehicle |
on_bicycle |
on_foot |
running |
walking |
If you wish, you can configure the plugin to only engage the moving state for vehicles by providing only "in_vehicle".
// Only trigger tracking for vehicles
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
triggerActivities: 'in_vehicle'
});
// Only trigger tracking for on_foot, walking and running
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
triggerActivities: 'on_foot, walking, running'
});Defaults to 10000 (10 seconds). The desired time between activity detections. Larger values will result in fewer activity detections while improving battery life. A value of 0 will result in activity detections at the fastest possible rate.
Each activity-recognition-result returned by the API is tagged with a "confidence" level expressed as a %. You can set your desired confidence to trigger a motionchange event. Defaults to 75.
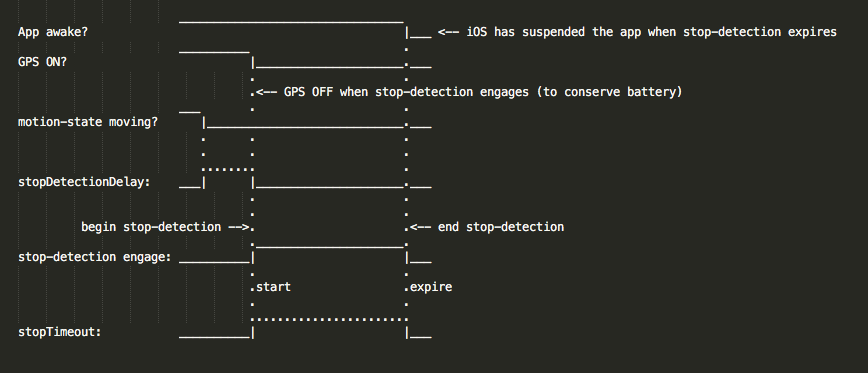
When in the moving state, specifies the number of minutes to wait before turning off location-services and enter stationary state after the ActivityRecognition System detects the device is STILL (Android: defaults to 0, no timeout, iOS: defaults to 5min). If you don't set a value, the plugin is eager to turn off the GPS ASAP. An example use-case for this configuration is to delay GPS OFF while in a car waiting at a traffic light.
📘 See Philosophy of Operation
iOS
Disables the accelerometer-based Stop-detection System. When disabled, the plugin will use the default iOS behaviour of automatically turning off location-services when the device has stopped for exactly 15 minutes. When disabled, you will no longer have control over #stopTimeout.
Android
Location-services will never turn OFF if you set this to true! It will be purely up to you or the user to execute changePace(false) or #stop to turn off location-services.
@config {Integer} activityType [ACTIVITY_TYPE_AUTOMOTIVE_NAVIGATION, ACTIVITY_TYPE_OTHER_NAVIGATION, ACTIVITY_TYPE_FITNESS, ACTIVITY_TYPE_OTHER]
Presumably, this affects iOS stop-detect algorithm. Apple is vague on what exactly this configuration does.
Available values are defined as constants upon the BackgroundGeolocation plugin object:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
ACTIVITY_TYPE_OTHER |
1 |
ACTIVITY_TYPE_AUTOMOTIVE_NAVIGATION |
2 |
ACTIVITY_TYPE_FITNESS |
3 |
ACTIVITY_TYPE_OTHER_NAVIGATION |
4 |
eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
activityType: BackgroundGeolocation.ACTIVITY_TYPE_OTHER
});📘 Apple docs.
Defaults to 0. Allows the stop-detection system to be delayed from activating. When the stop-detection system is engaged, location-services will be turned off and only the accelerometer is monitored. Stop-detection will only engage if this timer expires. The timer is cancelled if any movement is detected before expiration. If a value of 0 is specified, the stop-detection system will engage as soon as the device is detected to be stationary.
Defaults to false. Set true to disable iOS CMMotionActivityManager updates (eg: walking, in_vehicle). This feature requires a device having the M7 co-processor (ie: iPhone 5s and up).
ℹ️ This feature will ask the user for "Health updates" permission using the MOTION_USAGE_DESCRIPTION. If you do not wish to ask the user for the "Health updates", set this option to true; However, you will no longer receive accurate activity data in the recorded locations.
MOTION_USAGE_DESCRIPTION, for example:
"Accelerometer use increases battery efficiency by intelligently toggling location-tracking"
Defaults to 1000 meters. @see releated event geofenceschange. When using Geofences, the plugin activates only thoses in proximity (the maximim geofences allowed to be simultaneously monitored is limited by the platform, where iOS allows only 20 and Android. However, the plugin allows you to create as many geofences as you wish (thousands even). It stores these in its database and uses spatial queries to determine which 20 or 100 geofences to activate.
📺 View animation of this behaviour
Defaults to true. Set false to disable triggering a geofence immediately if device is already inside it.
Your server url where you wish to HTTP POST location data to.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
url: 'http://my-server.com/locations'
});📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
stopOnTerminate: false, since your Cordova app (where your Javascript lives) will terminate — only the plugin's native Android background service will continue to operate, recording locations and uploading to your server. The plugin's native HTTP service is better at this task than Javascript Ajax requests, since the plugin will automatically retry on server failure.
HTTP request timeout in milliseconds. The http failureFn will execute when an HTTP timeout occurs. Defaults to 60000 ms (1 minute).
BackgroundGeolocation.on('http', function(request) {
console.log('HTTP SUCCESS: ', response);
}, function(request) {
console.log('HTTP FAILURE', response);
});
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
url: 'http://my-server.com/locations',
httpTimeout: 3000
});The HTTP method to use when creating an HTTP request to your configured #url. Defaults to POST. Valid values are POST, PUT and OPTIONS.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
url: 'http://my-server.com/locations',
method: 'PUT'
});Optional HTTP params sent along in each HTTP request.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
url: 'http://my-server.com/locations',
params: {
user_id: 1234,
device_id: 'abc123'
}
});POST /locations
{
"location": {
"coords": {
"latitude": 45.51927004945047,
"longitude": -73.61650072045029
.
.
.
}
},
"user_id": 1234,
"device_id": 'abc123'
}Optional HTTP params sent along in HTTP request to above #url.
The root property of the JSON data where location-data will be placed.
📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
{
"rootProperty":{
"coords": {
"latitude":23.232323,
"longitude":37.373737
}
}
}You may also specify the character httpRootProperty:"." to place your data in the root of the JSON:
{
"coords": {
"latitude":23.232323,
"longitude":37.373737
}
}Optional custom template for rendering location JSON request data in HTTP requests. Evaulate variables in your locationTemplate using Ruby erb-style tags:
<%= variable_name %>📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
locationTemplate: '{"lat":<%= latitude %>,"lng":<%= longitude %>,"event":"<%= event %>",isMoving:<%= isMoving %>}'
});
// Or use a compact [Array] template!
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
locationTemplate: '[<%=latitude%>, <%=longitude%>, "<%=event%>", <%=is_moving%>]'
})#extras, these key-value pairs will be merged directly onto your location data. Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
httpRootProperty: 'data',
locationTemplate: '{"lat":<%= latitude %>,"lng":<%= longitude %>}',
extras: {
"foo":"bar"
}
})Will result in JSON:
{
"data": {
"lat":23.23232323,
"lng":37.37373737,
"foo":"bar"
}
}Template Tags
| Tag | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
latitude |
Float |
|
longitude |
Float |
|
speed |
Float |
Meters |
heading |
Float |
Degress |
accuracy |
Float |
Meters |
altitude |
Float |
Meters |
altitude_accuracy |
Float |
Meters |
timestamp |
String |
ISO-8601 |
uuid |
String |
Unique ID |
event |
String |
`motionchange |
odometer |
Float |
Meters |
activity.type |
String |
`still |
activity.confidence |
Integer |
0-100% |
battery.level |
Float |
0-100% |
battery.is_charging |
Boolean |
Is device plugged in? |
Optional custom template for rendering geofence JSON request data in HTTP requests. The geofenceTemplate is similar to #locationTemplate with the addition of two extra geofence.* tags.
Evaulate variables in your geofenceTemplate using Ruby erb-style tags:
<%= variable_name %>📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
geofenceTemplate: '{ "lat":<%= latitude %>, "lng":<%= longitude %>, "geofence":"<%= geofence.identifier %>:<%= geofence.action %>" }'
});
// Or use a compact [Array] template!
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
geofenceTemplate: '[<%= latitude %>, <%= longitude %>, "<%= geofence.identifier %>", "<%= geofence.action %>"]'
})Template Tags
The tag-list is identical to #locationTemplate with the addition of geofence.identifier and geofence.action.
| Tag | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
geofence.identifier |
String |
Which geofence? |
geofence.action |
String |
`ENTER |
latitude |
Float |
|
longitude |
Float |
|
speed |
Float |
Meters |
heading |
Float |
Degress |
accuracy |
Float |
Meters |
altitude |
Float |
Meters |
altitude_accuracy |
Float |
Meters |
timestamp |
String |
ISO-8601 |
uuid |
String |
Unique ID |
event |
String |
`motionchange |
odometer |
Float |
Meters |
activity.type |
String |
`still |
activity.confidence |
Integer |
0-100% |
battery.level |
Float |
0-100% |
battery.is_charging |
Boolean |
Is device plugged in? |
Default is false. If you've enabled HTTP feature by configuring an #url, batchSync: true will POST all the locations currently stored in native SQLite datbase to your server in a single HTTP POST request. With batchSync: false, an HTTP POST request will be initiated for each location in database.
If you've enabled HTTP feature by configuring an #url with batchSync: true, this parameter will limit the number of records attached to each batch request. If the current number of records exceeds the maxBatchSize, multiple HTTP requests will be generated until the location queue is empty.
Default is true. If you've enabeld HTTP feature by configuring an #url, the plugin will attempt to HTTP POST each location to your server as it is recorded. If you set autoSync: false, it's up to you to manually execute the #sync method to initate the HTTP POST (NOTE The plugin will continue to persist every recorded location in the SQLite database until you execute #sync).
The minimum number of persisted records to trigger an autoSync action. If you configure a value greater-than 0, the plugin will wait until that many locations are recorded before executing HTTP requests to your server through your configured #url.
Optional arbitrary key/value {} to attach to each recorded location
Eg: Every recorded location will have the following extras appended:
📘 See HTTP Guide for more information.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
url: 'http://my-server.com/locations',
extras: {
route_id: 1234
},
params: {
device_id: 'abc123'
}
});- POST /locations
{
"device_id": "abc123" // <-- params appended to root of JSON
"location": {
"coords": {
"latitude": 45.51927004945047,
"longitude": -73.61650072045029,
.
.
.
},
"extras": { // <-- extras appended to *each* location
"route_id": 1234
}
}
}Maximum number of days to store a geolocation in plugin's SQLite database when your server fails to respond with HTTP 200 OK. The plugin will continue attempting to sync with your server until maxDaysToPersist when it will give up and remove the location from the database.
Maximum number of records to persist in plugin's SQLite database. Default -1
means no limit.
Controls the order that locations are selected from the database (and synced to your server). Defaults to ascending (ASC), where oldest locations are synced first. Descending (DESC) syncs latest locations first.|
Defaults to true. When the user terminates the app, the plugin will stop tracking. Set this to false to continue tracking after application terminate.
If you do configure stopOnTerminate: false, your Javascript application will terminate at that time. However, both Android and iOS differ in their behaviour after this point:
iOS
Before an iOS app terminates, the plugin will ensure that a stationary geofence is created around the last known position. When the user moves beyond the stationary geofence (typically ~200 meters), iOS will completely reboot your application in the background, including your Javascript application and the plugin will resume tracking. iOS maintains geofence monitoring at the OS level, in spite of application terminate / device reboot.
In the following image, imagine the user terminated the application at the "red circle" on the right then continued moving: Once the device moves by about 200 meters, exiting the "stationary geofence", iOS reboots the app and tracking resumes.
ℹ️ Demo Video of stopOnTerminate: false
Android
Unlike iOS, the Android plugin's tracking will not pause at all when user terminates the app. However, only the plugin's native background service continues to operate, "headless" (in this case, you should configure an #url in order for the background-service to continue uploading locations to your server).
ℹ️ See Android Headless Mode
Defaults to false. Set true to engage background-tracking after the device reboots.
iOS
iOS cannot immediately engage tracking after a device reboot. Just like stopOnTerminate:false, iOS will not re-boot your app until the device moves beyond the stationary geofence around the last known location. In addition, iOS subscribes to "background-fetch" events, which typically fire about every 15 minutes — these too are capable of rebooting your app after a device reboot.
Android
Android will reboot the plugin's background-service immediately after device reboot. However, just like stopOnTerminate:false, the plugin will be running "headless" without your Application code. If you wish for your Application code to boot as well, you may configure forceReloadOnBoot: true
Controls the rate (in seconds) the heartbeat event will fire. The plugin will not provide any updated locations to your callbackFn, since it will provide only the last-known location. If you wish for an updated location in your callbackFn, it's up to you to request one with #getCurrentPosition.
heartbeat event will fire only when configured with preventSuspend: true
60 seconds. It is impossible to have a heartbeatInterval faster than this on Android.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('heartbeat', function(params) {
var lastKnownLocation = params.location;
console.log('- heartbeat: ', lastKnownLocation);
// Or you could request a new location
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(location) {
console.log('- current position: ', location);
});
});Provides an automated schedule for the plugin to start/stop tracking at pre-defined times. The format is cron-like:
"{DAY(s)} {START_TIME}-{END_TIME}"The START_TIME, END_TIME are in 24h format. The DAY param corresponds to the Locale.US, such that Sunday=1; Saturday=7). You may configure a single day (eg: 1), a comma-separated list-of-days (eg: 2,4,6) or a range (eg: 2-6), eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
.
.
.
schedule: [
'1 17:30-21:00', // Sunday: 5:30pm-9:00pm
'2-6 9:00-17:00', // Mon-Fri: 9:00am to 5:00pm
'2,4,6 20:00-00:00',// Mon, Web, Fri: 8pm to midnight (next day)
'7 10:00-19:00' // Sat: 10am-7pm
]
}, function(state) {
// Start the Scheduler
BackgroundGeolocation.startSchedule(function() {
console.info('- Scheduler started');
});
});
// Listen to "schedule" events:
BackgroundGeolocation.on('schedule', function(state) {
console.log('- Schedule event, enabled:', state.enabled);
if (!state.schedulerEnabled) {
BackgroundGeolocation.startSchedule();
}
});
// Later when you want to stop the Scheduler (eg: user logout)
BackgroundGeolocation.stopSchedule(function() {
console.info('- Scheduler stopped');
// You must explicitly stop tracking if currently enabled
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
});
// Or modify the schedule with usual #setConfig method
BackgroundGeolocation.setConfig({
schedule: [
'1-7 9:00-10:00',
'1-7 11:00-12:00',
'1-7 13:00-14:00',
'1-7 15:00-16:00',
'1-7 17:00-18:00',
'2,4,6 19:00-22:00'
]
});The schedule can also be configured with a literal start date of the form:
"yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm-HH:mm"
eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
schedule: [
"2018-01-01 09:00-17:00"
]
})Or two literal dates to specify both a start and stop date (note the format here is a bit ugly):
"yyyy-mm-dd-HH:mm yyyy-mm-dd-HH:mm"
schedule: [
"2018-01-01-09:00 2019-01-01-17:00" // <-- track for 1 year
]iOS
iOS cannot evaluate the Schedule at the exact time you configure — it can only evaluate the schedule periodically, whenever your app comes alive. When the app is running in a scheduled off period, iOS will continue to monitor the low-power, significant location changes API (SLC) in order to ensure periodic schedule evaluation. SLC is required in order guarantee periodic schedule-evaluation when you're configured stopOnTerminate: false, since the iOS Background Fetch is halted if user manually terminates the app. SLC will awaken your app whenever a "significant location change" occurs, typically every 1000 meters. If the schedule is currently in an off period, this location will not be persisted nor will it be sent to the location event — only the schedule will be evaluated.
When a schedule is provided on iOS, it will be evaluated in the following cases:
- Application
pause/resumeevents. - Whenever a location is recorded (including SLC)
- Background fetch event
Android
The Android Scheduler uses [AlarmManager](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/AlarmManager.html#setExactAndAllowWhileIdle(int, long, android.app.PendingIntent)) and typically operates on-the-minute.
Defaults to false. Set true to prevent iOS from suspending after location-services have been switched off while your application is in the background. Must be used in conjunction with a heartbeatInterval.
preventSuspend: true should only be used in very specific use-cases and should typically not be used as it will have a very noticable impact on battery performance. You should carefully manage preventSuspend, engaging it for controlled periods-of-time. You should not expect to run your app in this mode 24 hours / day, 7 days-a-week.
Defaults to false. When the Android OS is under memory pressure from other applications (eg: a phone call), the OS can and will free up memory by terminating other processes and scheduling them for re-launch when memory becomes available. If you find your tracking being terminated unexpectedly, this is why.
If you set this option to true, the plugin will run its Android service in the foreground, supplying the ongoing notification to be shown to the user while in this state. Running as a foreground-service makes the tracking-service much more inmmune to OS killing it due to memory/battery pressure. By default services are background, meaning that if the system needs to kill them to reclaim more memory (such as to display a large page in a web browser).
ℹ️ See related config options notificationTitle, notificationText & notificationColor
📘 For more information, see the Android Service docs.
Set to true to enable "Headless" mode when the user terminates the application where you've configured stopOnTerminate: false. In this mode, you can respond to all the plugin's events in the native Android environment. For more information, see the wiki for Android Headless Mode.
ℹ️ "Headless" mode is an alternartive to using the forceReloadOnXXX configuration options below.
When the user terminates your Android app with BackgroundGeolocation configured with stopOnTerminate: false, the foreground MainActivity (where your Javascript app lives) will terminate — only the plugin's pure native background-service is running, "headless", in this case. The background service will continue tracking the location. However, the background-service can optionally re-launch your foreground application.
To "force reload" your application, set any of the following options to true:
Launch your app whenever the #motionchange event fires.
Launch your app whenever the #location event fires.
Launch your app whenever the #geofence event fires.
Launch your app whenever the #heartbeat event fires.
Launch your app whenever a schedule event fires.
If the user reboots the device with the plugin configured for startOnBoot: true, your will app will launch when the device is rebooted.
When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This will control the priority of that notification as well as the position of the notificaiton-bar icon.
ℹ️ To completely hide the icon in the notification-bar, use NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_MIN (:warning: It is no longer possible to hide the notification-bar icon in Android O)
The following notificationPriority values defined as constants on the BackgroundGeolocation object:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_DEFAULT |
Notification weighted to top of list; notification-bar icon weighted left |
NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_HIGH |
Notification strongly weighted to top of list; notification-bar icon strongly weighted to left |
NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_LOW |
Notification weighted to bottom of list; notification-bar icon weighted right |
NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_MAX |
Same as NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_HIGH |
NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_MIN |
Notification strongly weighted to bottom of list; notification-bar icon hidden |
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
foregroundService: true,
notificationPriority: BackgroundGeolocation.NOTIFICATION_PRIORITY_MIN
});When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This will configure the title of that notification. Defaults to the application name.
When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This will configure the text of that notification. Defaults to "Location service activated".
When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This will configure the color of the notification icon (API >= 21).Supported formats are:
#RRGGBB#AARRGGBB
When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This allows you customize that icon. Defaults to your application icon. NOTE You must specify the type (drawable|mipmap) of resource you wish to use in the following format:
{type}/icon_name,
.png)
eg:
// 1. drawable
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
notificationSmallIcon: "drawable/my_custom_notification_small_icon"
});
// 2. mipmap
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
notificationSmallIcon: "mipmap/my_custom_notification_small_icon"
});When running the service with foregroundService: true, Android requires a persistent notification in the Notification Bar. This allows you customize that icon. Defaults to undefined. NOTE You must specify the type (drawable|mipmap) of resource you wish to use in the following format:
.png)
{type}/icon_name,
eg:
// 1. drawable
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
notificationLargeIcon: "drawable/my_custom_notification_large_icon"
});
// 2. mipmap
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
notificationLargeIcon: "mipmap/my_custom_notification_large_icon"
});Defaults to false. When set to true, the plugin will emit debugging sounds and notifications for life-cycle events of background-geolocation!
iOS: In you wish to hear debug sounds in the background, you must manually enable the [x] Audio and Airplay background mode in Background Capabilities of XCode.
📘 See Debugging Sounds
BackgroundGeolocation contains powerful logging features. By default, the plugin boots with a value of LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE, storing 3 days worth of logs (configurable with logMaxDays) in its SQLite database.
The following log-levels are defined as constants on the BackgroundGeolocation object:
| logLevel | Label |
|---|---|
0 |
LOG_LEVEL_OFF |
1 |
LOG_LEVEL_ERROR |
2 |
LOG_LEVEL_WARNING |
3 |
LOG_LEVEL_INFO |
4 |
LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG |
5 |
LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE |
Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_WARNING
});ℹ️ To retrieve the plugin's logs, see getLog & emailLog.
logLevel appropriately (eg: LOG_LEVEL_ERROR)
Maximum number of days to persist a log-entry in database. Defaults to 3 days.
Your successFn will be called with the following signature whenever a new location is recorded:
@param {Object} location The Location data (@see Wiki for Location Data Schema)
ℹ️ When performing a motionchange or getCurrentPosition, the plugin requests multiple location samples in order to record the most accurate location possible. These samples are not persisted to the database but they will be provided to your location listener, for your convenience, since it can take some seconds for the best possible location to arrive. For example, you might use these samples to progressively update the user's position on a map. You can detect these samples in your callbackFn via location.sample === true. If you're manually POSTing location to your server, you should ignore these locations.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('location', function(location) {
var coords = location.coords,
timestamp = location.timestamp
latitude = coords.latitude,
longitude = coords.longitude,
speed = coords.speed;
console.log("- Location: ", timestamp, latitude, longitude, speed);
}, function(errorCode) {
console.warn("- Location error: ", errorCode);
});| Code | Error |
|---|---|
| 0 | Location unknown |
| 1 | Location permission denied |
| 2 | Network error |
| 408 | Location timeout |
Your callbackFn will be executed each time the device has changed-state between MOVING or STATIONARY. The callbackFn will be provided with the following parameters:
BackgroundGeolocation.on('motionchange', function(isMoving, location) {
if (isMoving) {
console.log('Device has just started MOVING', location);
} else {
console.log('Device has just STOPPED', location);
}
});Your callbackFn will be executed each time the activity-recognition system receives an event (still, on_foot, in_vehicle, on_bicycle, running).
It will be provided an event {Object} containing the following parameters:
BackgroundGeolocation.on('activitychange', function(event) {
console.log('- Activity changed: ', event.activity, event.confidence);
});Your callbackFn fill be executed when a change in the state of the device's Location Services has been detected. eg: "GPS ON", "Wifi only". Your callbackFn will be provided with an {Object} provider containing the following properties
| Name | Value | Platform |
|---|---|---|
AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_NOT_DETERMINED |
0 |
iOS only |
AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_RESTRICTED |
1 |
iOS only |
AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_DENIED |
2 |
iOS & Android |
AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_ALWAYS |
3 |
iOS & Android |
AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_WHEN_IN_USE |
4 |
iOS only |
ℹ️ When Android location permission is granted, status == AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_ALWAYS, otherwise, AUTHORIZATION_DENIED.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('providerchange', function(provider) {
console.log('- Provider Change: ', provider);
console.log(' enabled: ', provider.enabled);
console.log(' gps: ', provider.gps);
console.log(' network: ', provider.network);
console.log(' status: ', provider.status);
switch(provider.status) {
case BackgroundGeolocation.AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_DENIED:
// Android & iOS
console.log('- Location authorization denied');
break;
case BackgroundGeolocation.AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_ALWAYS:
// Android & iOS
console.log('- Location always granted');
break;
case BackgroundGeolocation.AUTHORIZATION_STATUS_WHEN_IN_USE:
// iOS only
console.log('- Location WhenInUse granted');
break;
}
});Adds a geofence event-listener. Your supplied callbackFn will be called when any monitored geofence crossing occurs.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('geofence', function(geofence) {
var location = geofence.location;
var identifier = geofence.identifier;
var action = geofence.action;
console.log('A geofence has been crossed: ', identifier);
console.log('ENTER or EXIT?: ', action);
console.log('geofence: ', JSON.stringify(geofence));
});Fired when the list of monitored-geofences changed. The Background Geolocation contains powerful geofencing features that allow you to monitor any number of circular geofences you wish (thousands even), in spite of limits imposed by the native platform APIs (20 for iOS; 100 for Android).
The plugin achieves this by storing your geofences in its database, using a geospatial query to determine those geofences in proximity (@see config geofenceProximityRadius), activating only those geofences closest to the device's current location (according to limit imposed by the corresponding platform).
When the device is determined to be moving, the plugin periodically queries for geofences in proximity (eg. every minute) using the latest recorded location. This geospatial query is very fast, even with tens-of-thousands geofences in the database.
It's when this list of monitored geofences changes, the plugin will fire the geofenceschange event.
📘 For more information, see Geofencing Guide
BackgroundGeolocation.on('geofenceschange', function(event) {
var on = event.on; //<-- new geofences activiated.
var off = event.off; //<-- geofences that were de-activated.
// Create map circles
for (var n=0,len=on.length;n<len;n++) {
var geofence = on[n];
createGeofenceMarker(geofence)
}
// Remove map circles
for (var n=0,len=off.length;n<len;n++) {
var identifier = off[n];
removeGeofenceMarker(identifier);
}
});This event object provides only the changed geofences, those which just activated or de-activated.
When all geofences have been removed, the event object will provide an empty-array [] for both #on and #off keys, ie:
{
on: [{}, {}, ...], // <-- Entire geofence objects {}
off: ['identifier_foo', 'identifier_bar'] <-- just the identifiers
}BackgroundGeolocation.on('geofenceschange', function(event) {
console.log("geofenceschange fired! ", event);
});
// calling remove geofences will cause the `geofenceschange` event to fire
BackgroundGeolocation.removeGeofences();
=> geofenceschange fired! {on: [], off: []}The callbackFn will be executed for each HTTP request where the response-code is one of 200, 201 or 204. failureFn will be executed for all other HTTP response codes. The successFn and failureFn will be provided a single response {Object} parameter with the following properties:
Example:
BackgroundGeolocation.on('http', function(response) {
var status = response.status;
var success = response.success;
var responseText = response.responseText;
var res = JSON.parse(responseText); // <-- if your server returns JSON
console.log("- HTTP success", status, res);
}, function(response) {
var success = response.success;
var status = response.status;
var responseText = response.responseText;
console.log("- HTTP failure: ", status, responseText);
});The callbackFn will be executed for each #heartbeatInterval while the device is in stationary state (iOS requires preventSuspend: true as well). The callbackFn will be provided a single params {Object} parameter with the following properties:
@param {String} motionType [still|on_foot|running|on_bicycle|in_vehicle|shaking|unknown] The current motion-type.
@param {Object} location When the plugin detects movement (iOS only), it will always request a new high-accuracy location in order to determine if the device has moved beyond stationaryRadius and if the location has speed > 0. This fresh location will be provided to your callbackFn. Android will simply return the "last known location"
Example:
BackgroundGeolocation.on('heartbeat', function(params) {
console.log('- hearbeat');
// You could request a new location if you wish.
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(location) {
console.log('- current location: ', location);
});
});The callbackFn will be executed each time a schedule event fires. Your callbackFn will be provided with the current state object (@see #getState). state.enabled will reflect the state according to your configured schedule.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('schedule', function(state) {
if (state.enabled) {
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation scheduled start tracking');
} else {
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation scheduled stop tracking');
}
});Fired when the state of the operating-system's "Power Saving" mode changes. Your callbackFn will be provided with a Boolean showing whether "Power Saving" is enabled or disabled. Power Saving mode can throttle certain services in the background, such as HTTP requests or GPS.
ℹ️ You can manually request the current-state of "Power Saving" mode with the method #isPowerSaveMode.
iOS Power Saving mode can be engaged manually by the user in Settings -> Battery or from an automatic OS dialog.
Android Power Saving mode can be engaged manually by the user in Settings -> Battery -> Battery Saver or automatically with a user-specified "threshold" (eg: 15%).
BackgroundGeolocation.on('powersavechange', function(isPowerSaveMode) {
console.log("- powersavechange, power-saving mode enabled? ", isPowerSaveMode);
});Fired when the state of the device's network-connectivity changes (enabled -> disabled and vice-versa). By default, the plugin will automatically fire a connectivitychange event with the current state network-connectivity whenever the #start method is executed.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('connectivitychange', function(event) {
console.log("- connectivitychange, network is connected? ", event.connected);
});Fired when the plugin's enabled state changes. For example, executing #start and #stop will cause the enabledchange event to fire. This event is primarily desigend for use with the configuration option [stopAfterElapsedMinutes], which automatically executes the plugin's #stop method.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('enabledchange', function(event) {
console.log("- enabledchange, plugin is enabled? ", event.enabled);
});BackgroundGeolocation Javascript API supports Promises for nearly every method (the exceptions are #watchPosition and adding event-listeners via #on method.
// Traditional API still works:
bgGeo.getCurrentPosition((location) => {
console.log('- current position: ', location);
}, (error) => {
console.log('- location error: ', error);
}, {samples: 1, persist: false});
// Promise API
bgGeo.getCurrentPosition({samples:1, persist: false}).then(location => {
console.log('- current position: ', location);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('- location error: ', error);
});By marking one of your application methods as async you can use the await mechanism instead of callbacks:
async onClickGetPosition() {
let location = await bgGeo.getCurrentPosition({samples:1, persist: false});
conosle.log('- current position: ', location);
let count = await bgGeo.getCount();
console.log('- There are ', count, ' records in the database');
}The #ready method is your first point-of-contact with the plugin. The supplied defaultConfig will be applied only at first launch of your app — for every launch thereafter, the plugin will automatically load its last-known configuration from persisent storage. The plugin always remembers the configuration you apply to it.
Observe the following example. Imagine you've deleted the app from the device and re-installed it:
bgGeo.ready({distanceFilter: 10}, (state) => {
console.log('- Plugin is ready. distanceFilter: ', state.distanceFilter);
});In the console, you'll see
> - Plugin is ready. distanceFilter: 10
Somewhere else in your code, you change the distanceFilter:
bgGeo.setConfig({distanceFilter: 250});Now terminate the app and reboot. In the console, you'll see:
> - Plugin is ready. distanceFilter: 250
#ready method only applies the supplied defaultConfig for the first launch of the app — Forever after, the plugin is going to remember every configuration change you apply at runtime (eg: #setConfig) and reload that same config every time your app boots.
The #reset Method
If you wish, you can use the #reset method to reset all configuration options to documented default-values (with optional overrides):
// Reset to documented default-values
bgGeo.reset();
// Reset to documented default-values with overrides
bgGeo.reset({distanceFilter: 10});Optionally, you can specify reset: true to #ready. This will esentially force the supplied {config} to be applied with each launch of your application, making it behave like the traditional #configure method.
bgGeo.ready({
reset: true, // <-- set true to ALWAYS apply supplied config; not just at first launch.
distanceFilter: 50
}, (state) => {
conosle.log('Ready with reset: true: ', state.distanceFilter);
});bgGeo.ready({distanceFilter: 50}).then(state => {
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ', state);
}).catch(error => {
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation ready failure: ', error);
});#ready. The #configure method is essentially the same as performing #reset + #ready.
The #configure must be called once (and only once) each time your application boots, providing the initial configuration options. The successFn will be executed after the plugin has successfully configured.
If you later need to re-configure the plugin's config options, use the setConfig method.
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 50,
stationaryRadius: 25,
locationUpdateInterval: 1000,
foregroundService: true
}, function(state) {
console.log("Background Geolocation started. Current state: ", state.enabled);
if (!state.enabled) {// <-- plugin persists its enabled state. it may have already started.
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
}
}, function(error) {
console.warn("Background Geolocation failed to configure");
})ℹ️ BackgroundGeolocation persists its enabled state between application terminate or device reboot and #configure will automatically #start tracking if it finds enabled == true. However, there's no harm in calling #start while the plugin is already enabled, before your successFn is executed.
#on until your successFn executes. For example:
// OK to add event-listeners before #configure callback fires.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('location', onLocation);
BackgroundGeolocation.on('motionchange', onMotionChange);
BackgroundGeolocation.configure(options, function(state) {
// YES
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(succes, fail);
});
// NO! Wait for #configure callback to execute.
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(success, fail);Re-configure plugin's configuration parameters.
BackgroundGeolocation.setConfig({
desiredAccuracy: 10,
distanceFilter: 100
}, function(){
console.log("- setConfig success");
}, function(){
console.warn("- Failed to setConfig");
});Resets the plugin configuration to documented default-values. If a {config} is provided, it will be applied after the configuration reset.
BackgroundGeolocation.reset({distanceFilter: 50}, function(state) {
// All config options are now reset to documented default-values
// + distanceFilter: 50
});Event-listeners can be attached using the method #on, supplying the event you wish to listen to. #on accepts both a successFn and failureFn. See Events for a list of available events.
BackgroundGeolocation.on("location", successFn, failureFn);Event-listeners are removed with the method #un. You must supply a reference to the exact successFn reference used with the #on method. See Events for a list of available events.
@param {Function} callbackFn The exact successFn reference used to originally subscribe to the event with the #on method.
function onLocation(location) { // <-- successFn
console.log('- location: ', location);
}
function onLocationError(error) {
console.log('- location error: ', error);
}
// Add a location listener
BackgroundGeolocation.on('location', onLocation, onLocationError);
.
.
.
// Remove a location listener supplying only the successFn (onLocation)
BackgroundGeolocation.un('location', onLocation);Enable location tracking. Supplied successFn will be executed when tracking is successfully engaged. This is the plugin's power ON button. The plugin will initially start into its stationary state, fetching an initial location before turning off location services.
Android will be monitoring its Activity Recognition System while iOS will create a stationary geofence around the current location. NOTE If you've configured a #schedule, this method will override that schedule and engage tracking immediately.
BackgroundGeolocation.start(function(state) {
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation started, state: ', state);
});📘 For more information, see Philosophy of Operation
Disable location tracking. Supplied successFn will be executed when tracking is successfully halted. This is the plugin's power OFF button.
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();schedule, #stop will not halt the Scheduler. You must explicitly stop the Scheduler as well:
// Later when you want to stop the Scheduler (eg: user logout)
BackgroundGeolocation.stopSchedule(function() {
console.info('- Scheduler stopped');
// You must explicitly stop tracking if currently enabled
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
});Fetch the current-state of the plugin, including all configuration parameters.
BackgroundGeolocation.getState(function(state) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(state));
});
{
"stopOnTerminate": true,
"disableMotionActivityUpdates": false,
"params": {
"device": {
"manufacturer": "Apple",
"available": true,
"platform": "iOS",
"cordova": "3.9.1",
"uuid": "61CA53C7-BC4B-44D3-991B-E9021AE7F8EE",
"model": "iPhone8,1",
"version": "9.0.2"
}
},
"url": "http://192.168.11.120:8080/locations",
"desiredAccuracy": 0,
"stopDetectionDelay": 0,
"activityRecognitionInterval": 10000,
"distanceFilter": 50,
"activityType": 2,
"useSignificantChangesOnly": false,
"autoSync": false,
"isMoving": false,
"maxDaysToPersist": 1,
"stopTimeout": 2,
"enabled": false,
"debug": true,
"batchSync": false,
"headers": {},
"disableElasticity": false,
"stationaryRadius": 20
}Retrieves the current position. This method instructs the native code to fetch exactly one location using maximum power & accuracy. The native code will persist the fetched location to its SQLite database just as any other location in addition to POSTing to your configured #url (if you've enabled the HTTP features).
If an error occurs while fetching the location, the failureFn will be executed with an Integer Error Code as the first argument.
@config {Integer} timeout [30] An optional location-timeout. If the timeout expires before a location is retrieved, the failureFn will be executed.
@config {Integer millis} maximumAge [0] Accept the last-recorded-location if no older than supplied value in milliseconds.
@config {Boolean} persist [true] Defaults to true. Set false to disable persisting the retrieved location in the plugin's SQLite database.
@config {Integer} samples [3] Sets the maximum number of location-samples to fetch. The plugin will return the location having the best accuracy to your successFn. Defaults to 3. Only the final location will be persisted.
@config {Integer} desiredAccuracy [stationaryRadius] Sets the desired accuracy of location you're attempting to fetch. When a location having accuracy <= desiredAccuracy is retrieved, the plugin will stop sampling and immediately return that location. Defaults to your configured stationaryRadius.
@config {Object} extras Optional extra-data to attach to the location. These extras {Object} will be merged to the recorded location and persisted / POSTed to your server (if you've configured the HTTP Layer).
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(location) {
// This location is already persisted to plugin’s SQLite db.
// If you’ve configured #autoSync: true, the HTTP POST has already started.
console.log(“- Current position received: “, location);
}, function(errorCode) {
alert('An location error occurred: ' + errorCode);
}, {
timeout: 30, // 30 second timeout to fetch location
maximumAge: 5000, // Accept the last-known-location if not older than 5000 ms.
desiredAccuracy: 10, // Try to fetch a location with an accuracy of `10` meters.
samples: 3, // How many location samples to attempt.
extras: { // [Optional] Attach your own custom `metaData` to this location. This metaData will be persisted to SQLite and POSTed to your server
foo: "bar"
}
});ℹ️ While the successFn will receive only one location, the plugin does request multiple location samples in order to record the most accurate location possible. These samples are not persisted to the database but they will be provided to your location event-listener, for your convenience, since it can take some seconds for the best possible location to arrive. For example, you might use these samples to progressively update the user's position on a map. You can detect these samples in your location callbackFn via location.sample === true. If you're manually POSTing location to your server, you should ignore these locations.
@param {Integer} errorCode If a location failed to be retrieved, one of the following error-codes will be returned
| Code | Error |
|---|---|
| 0 | Location unknown |
| 1 | Location permission denied |
| 2 | Network error |
| 408 | Location timeout |
Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(succesFn, function(errorCode) {
switch (errorCode) {
case 0:
alert('Failed to retrieve location');
break;
case 1:
alert('You must enable location services in Settings');
break;
case 2:
alert('Network error');
break;
case 408:
alert('Location timeout');
break;
}
})Start a stream of continuous location-updates. The native code will persist the fetched location to its SQLite database just as any other location in addition to POSTing to your configured #url (if you've enabled the HTTP features).
#watchPosition is not reccommended for long term monitoring in the background — It's primarily designed for use in the foreground only. You might use it for fast-updates of the user's current position on the map, for example.
iOS
#watchPositionwill continue to run in the background, preventing iOS from suspending your application. Take care to listen tosuspendevent and call#stopWatchPositionif you don't want your app to keep running (TODO make this configurable).
// Start watching position when app comes to foreground
onAppResume() {
BackgroundGeolocation.watchPosition(function(location) {
console.log(“- Watch position: “, location);
}, function(errorCode) {
alert('An location error occurred: ' + errorCode);
}, {
interval: 1000, // <-- retrieve a location every 5s.
persist: false, // <-- default is true
});
}
// Stop watching position when app moves to background
onAppSuspend() {
BackgroundGeolocation.stopWatchPosition();
}ℹ️ Also see #stopWatchPosition
Halt #watchPosition updates.
BackgroundGeolocation.stopWatchPosition(); // <-- callbacks are optionalManually Toggles the plugin motion state between stationary and moving. When enabled is set to true, the plugin will engage location-services and begin aggressively tracking the device's location immediately, bypassing stationary monitoring. If you were making a "Jogging" application, this would be your [Start Workout] button to immediately begin location-tracking. Send false to turn off location-services and return the plugin to the stationary state.
BackgroundGeolocation.changePace(true); // <-- Location-services ON
BackgroundGeolocation.changePace(false); // <-- Location-services OFFThe plugin constantly tracks distance travelled, computing the distance between the current location and last and maintaining the sum. To fetch the current odometer reading:
BackgroundGeolocation.getOdometer(function(distance) {
console.log("Distance travelled: ", distance);
});ℹ️ Also see desiredOdometerAccuracy to set discard poor accuracy locations being used in odometer calculations.
Set the odometer to any arbitrary value. NOTE setOdometer will perform a getCurrentPosition in order to record to exact location where odometer was set; as a result, the callback signatures are identical to those of getCurrentPosition.
BackgroundGeolocation.setOdometer(1234.56, function(location) {
// Callback is called with the location where odometer was set at.
console.log('- setOdometer success: ', location);
}, function(errorCode) {
// If the plugin failed to fetch a location, it will still have set your odometer to your desired value.
console.log('- Error: ', errorCode);
});Reset the odometer to 0. Alias for setOdometer(0)
If a #schedule was configured, this method will initiate that schedule. The plugin will automatically be started or stopped according to the configured #schedule.
BackgroundGeolocation.startSchedule(function() {
console.log('- Scheduler started');
});This method will stop the Scheduler service.
BackgroundGeolocation.stopSchedule(function() {
console.log('- Scheduler stopped');
});#stopSchedule will not execute #stop if the plugin is currently tracking. You must explicitly execute #stop.
// Later when you want to stop the Scheduler (eg: user logout)
BackgroundGeolocation.stopSchedule(function() {
// You must explicitly stop tracking if currently enabled
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
});Sends a signal to iOS that you wish to perform a long-running task. The OS will not suspend your app until you signal completion with the #finish method. The callbackFn will be provided with a single parameter taskId which you will send to the #finish method.
@param {Integer} taskId The taskId to send to the #finish method.
Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.setOdometer(0, function(location) {
console.log('- setOdometer at location: ', location);
BackgroundGeolocation.startBackgroundTask(function(taskId) { // <-- taskId provided to callback
// Perform some long-running task (eg: HTTP request)
performLongRunningTask(function() {
// When long running task is complete, signal completion of taskId.
BackgroundGeolocation.finish(taskId);
});
});
});#finish your taskId to prevent the OS from force-killing your application.
Sends a signal to the native OS that your long-running task, addressed by taskId is complete and the OS may proceed to suspend your application if applicable.
Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.setOdometer(0, function(location) {
console.log('- setOdometer at location: ', location);
BackgroundGeolocation.startBackgroundTask(function(taskId) { // <-- taskId provided to callback
// Perform some long-running task (eg: HTTP request)
performLongRunningTask(function() {
// When long running task is complete, signal completion of taskId.
BackgroundGeolocation.finish(taskId);
});
});
});Fetches the state of the operating-systems "Power Saving" mode, whether enabled or disabled. Power Saving mode can throttle certain services in the background, such as HTTP requests or GPS.
ℹ️ You can listen to changes in the state of "Power Saving" mode with the event #powersavechange.
iOS Power Saving mode can be engaged manually by the user in Settings -> Battery or from an automatic OS dialog.
Android Power Saving mode can be engaged manually by the user in Settings -> Battery -> Battery Saver or automatically with a user-specified "threshold" (eg: 15%).
Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.isPowerSaveMode(function(isPowerSaveMode) {
console.log('- is Power Saving mode enabled?', isPowerSaveMode);
});Remove all event-listeners registered with #on method. You're free to add more listeners again after executing #removeListeners.
BackgroundGeolocation.on('location', function(location) {
console.log('- Location', location);
})
.
.
.
BackgroundGeolocation.removeListeners();
BackgroundGeolocation.on('location', function(location) {
console.log('- Location listener added again: ', location);
});Fetch all the locations currently stored in native plugin's SQLite database. Your callbackFn will receive an Array of locations in the 1st parameter. Eg:
BackgroundGeolocation.getLocations(function(locations) {
console.log("locations: ", locations);
});Fetches count of SQLite locations table SELECT count(*) from locations. The successFn will be executed with count as the only parameter.
BackgroundGeolocation.getCount(function(count) {
console.log('- count: ', count);
});Manually insert a location into the native plugin's SQLite database. Your successFn will be executed if the operation was successful. The inserted location's schema must match this plugin's published Location Data Schema. The plugin will have no problem inserting a location retrieved from the plugin itself.
@config {Object} config The location params/object matching the Location Data Schema.
BackgroundGeolocation.insertLocation({
"uuid": "f8424926-ff3e-46f3-bd48-2ec788c9e761", // <-- required
"timestamp": "2016-02-10T22:25:54.905Z" // <-- required
"coords": { // <-- required
"latitude": 45.5192746,
"longitude": -73.616909,
"accuracy": 22.531999588012695,
"speed": 0,
"heading": 0,
"altitude": 0
}
}, function() {
console.log('- Inserted location success');
}, function(error) {
console.warn('- Failed to insert location: ', error);
});
// insertLocation can easily consume any location which it returned. Note that #getCurrentPosition ALWAYS persists so this example
// will manually persist a 2nd version of the same location. The purpose here is to show that the plugin can consume any location object which it generated.
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(location) {
location.extras = {foo: 'bar'}; // <-- add some arbitrary extras-data
// Insert it.
BackgroundGeolocation.insertLocation(location, function() {
console.log('- Inserted location success');
});
});DEPRECATED. Use #destroyLocations.
Remove all records in plugin's SQLite database.
BackgroundGeolocation.destroyLocations(function() {
console.log('- cleared database');
});If the plugin is configured for HTTP with an #url and autoSync: false, this method will initiate POSTing the locations currently stored in the native SQLite database to your configured #url. When your HTTP server returns a response of 200 OK, that record(s) in the database will be DELETED.
If you configured batchSync: true, all the locations will be sent to your server in a single HTTP POST request, otherwise the plugin will create execute an HTTP post for each location in the database (REST-style). Your callbackFn will be executed and provided with an Array of all the locations from the SQLite database. If you configured the plugin for HTTP (by configuring an #url, your callbackFn will be executed after the HTTP request(s) have completed. If the plugin failed to sync to your server (possibly because of no network connection), the failureFn will be called with an errorMessage. If you are not using the HTTP features, sync will delete all records from its SQLite datbase. Eg:
Your callback will be provided with the following params
BackgroundGeolocation.sync(function(locations) {
// Here are all the locations from the database. The database is now EMPTY.
console.log('synced locations: ', locations);
}, function(errorMessage) {
console.warn('Sync FAILURE: ', errorMessage);
});📘 For more information, see HTTP Guide
Engages the geofences-only trackingMode. In this mode, no active location-tracking will occur -- only geofences will be monitored. To stop monitoring "geofences" trackingMode, simply use the usual #stop method. The state object now contains the new key trackingMode [location|geofence].
BackgroundGeolocation.configure(config, function(state) {
// Add some geofences.
BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofences([
notifyOnExit: true,
radius: 200,
identifier: 'ZONE_OF_INTEREST',
latitude: 37.234232,
longitude: 42.234234
]);
if (!state.enabled) {
BackgroundGeolocation.startGeofences(function(state) {
console.log('- Geofence-only monitoring started', state.trackingMode);
});
}
});
// Listen to geofences
BackgroundGeolocation.on('geofence', function(params) {
if (params.identifier == 'ZONE_OF_INTEREST') {
// If you wish, you can choose to engage location-tracking mode when a
// particular geofence event occurs.
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
}
});Adds a geofence to be monitored by the native plugin. If a geofence already exists with the configured identifier, the previous one will be deleted before the new one is inserted.
@config {Float} radius The radius (meters) of the geofence. In practice, you should make this >= 100 meters.
@config {Integer milliseconds} loiteringDelay When notifyOnDwell is true, the delay before DWELL event is fired after entering a geofence (@see Creating and Monitoring Geofences)
BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofence({
identifier: "Home",
radius: 150,
latitude: 45.51921926,
longitude: -73.61678581,
notifyOnEntry: true,
notifyOnExit: false,
notifyOnDwell: true,
loiteringDelay: 30000, // 30 seconds
extras: { // Optional arbitrary meta-data
zone_id: 1234
}
}, function() {
console.log("Successfully added geofence");
}, function(error) {
console.warn("Failed to add geofence", error);
});ℹ️ When adding a list-of-geofences, it's about 10 faster* to use #addGeofences instead.
📘 See Geofencing Guide for more information.
Adds a list of geofences to be monitored by the native plugin. If a geofence already exists with the configured identifier, the previous one will be deleted before the new one is inserted. The geofences param is an Array of geofence Objects {} with the following params:
@config {Array} geofences An list of geofences configured with the same parmeters as #addGeofence
Example:
BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofences([{
identifier: "Home",
radius: 150,
latitude: 45.51921926,
longitude: -73.61678581,
notifyOnEntry: true,
notifyOnExit: false,
notifyOnDwell: true,
loiteringDelay: 30000, // 30 seconds
extras: { // Optional arbitrary meta-data
zone_id: 1234
}
}], function() {
console.log("Successfully added geofence");
}, function(error) {
console.warn("Failed to add geofence", error);
});Removes a geofence having the given {String} identifier.
BackgroundGeolocation.removeGeofence("Home", function() {
console.log("Successfully removed geofence");
}, function(error) {
console.warn("Failed to remove geofence", error);
});Removes all geofences.
BackgroundGeolocation.removeGeofences(function() {
console.log("Successfully removed alll geofences");
}, function(error) {
console.warn("Failed to remove geofence", error);
});Fetch the list of monitored geofences. Your successFn will be provided with an Array of geofences. If there are no geofences being monitored, you'll receive an empty Array [].
Example:
BackgroundGeolocation.getGeofences(function(geofences) {
for (var n=0,len=geofences.length;n<len;n++) {
console.log("Geofence: ", geofence.identifier, geofence.radius, geofence.latitude, geofence.longitude);
}
}, function(error) {
console.warn("Failed to fetch geofences from server");
});| logLevel | Label |
|---|---|
0 |
LOG_LEVEL_OFF |
1 |
LOG_LEVEL_ERROR |
2 |
LOG_LEVEL_WARNING |
3 |
LOG_LEVEL_INFO |
4 |
LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG |
5 |
LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE |
BackgroundGeolocation.setLogLevel(BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE,function() {
console.log("Changed logLevel success");
});Fetches the entire contents of the current circular-log and return it as a String.
@param {String} log The complete log in a single string. You can split this string on \n to convert to an Array of lines.
BackgroundGeolocation.getLog(function(log) {
console.log(log); // <-- send log to console. copy/paste result into your own text file.
});Fetch the entire contents of the current circular log and email it to a recipient using the device's native email client.
None
BackgroundGeolocation.emailLog("[email protected]");Destory the entire contents of Log database.
BackgroundGeolocation.destroyLog(function() {
console.log('- Destroyed log');
}, function() {
console.log('- Destroy log failure');
});None
None
Send your own log-messages into the plugin's logging database. The following methods are available on the BackgroundGeolocation.logger object:
| method | logLevel | icon |
|---|---|---|
error |
ERROR |
❗ |
warn |
WARNING |
|
debug |
DEBUG |
🪲 |
info |
INFO |
ℹ️ |
notice |
INFO |
🔵 |
header |
INFO |
message wrapped in box |
on |
INFO |
🎾 |
off |
INFO |
🔴 |
ok |
INFO |
✅ |
Log messages will be recorded in the following format, including the name of name of your javascript caller method where the log message was executed:
2017-08-18 10:12:25.324 ⚠️-[TSLocationManager log:message:caller:] [javascriptCallerMethod] Message
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.error("Something bad happened");
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.warn("Something weird happened");
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.debug("Debug message");
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.info("Something informative");
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.notice("Something interesting");
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.header("Something bold");
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.on("Something on or positive");
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.off("Something off or negative");
BackgroundGeolocation.logger.ok("Something affirmative happened");Returns the presense of device sensors accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer, in addition to iOS/Android-specific sensors. These core sensors are used by the motion activity-recognition system — when any of these sensors are missing from a device (particularly on cheap Android devices), the performance of the motion activity-recognition system will be severly degraded and highly inaccurate.
Your callbackFn will be provided an event {Object} containing the following parameters:
iOS
Android
BackgroundGeolocation.getSensors(function(sensors) {
console.log('- has accelerometer? ', sensors.accelerometer);
console.log('- has gyroscope? ', sensors.gyroscope);
console.log('- has magnetometer? ', sensors.magnetometer);
if (sensors.platform === 'ios') {
console.log('- has motion hardware (M7 chip)?', sensors.motion_hardware);
} else if (sensors.platform === 'android') {
console.log('- has significant motion sensor? ', sensors.significant_motion);
}
});Here's a fun one. The plugin can play a number of OS system sounds for each platform. For IOS and Android. I offer this API as-is, it's up to you to figure out how this works.
// A soundId iOS recognizes
BackgroundGeolocation.playSound(1303);
// An Android soundId
BackgroundGeolocation.playSound(90);