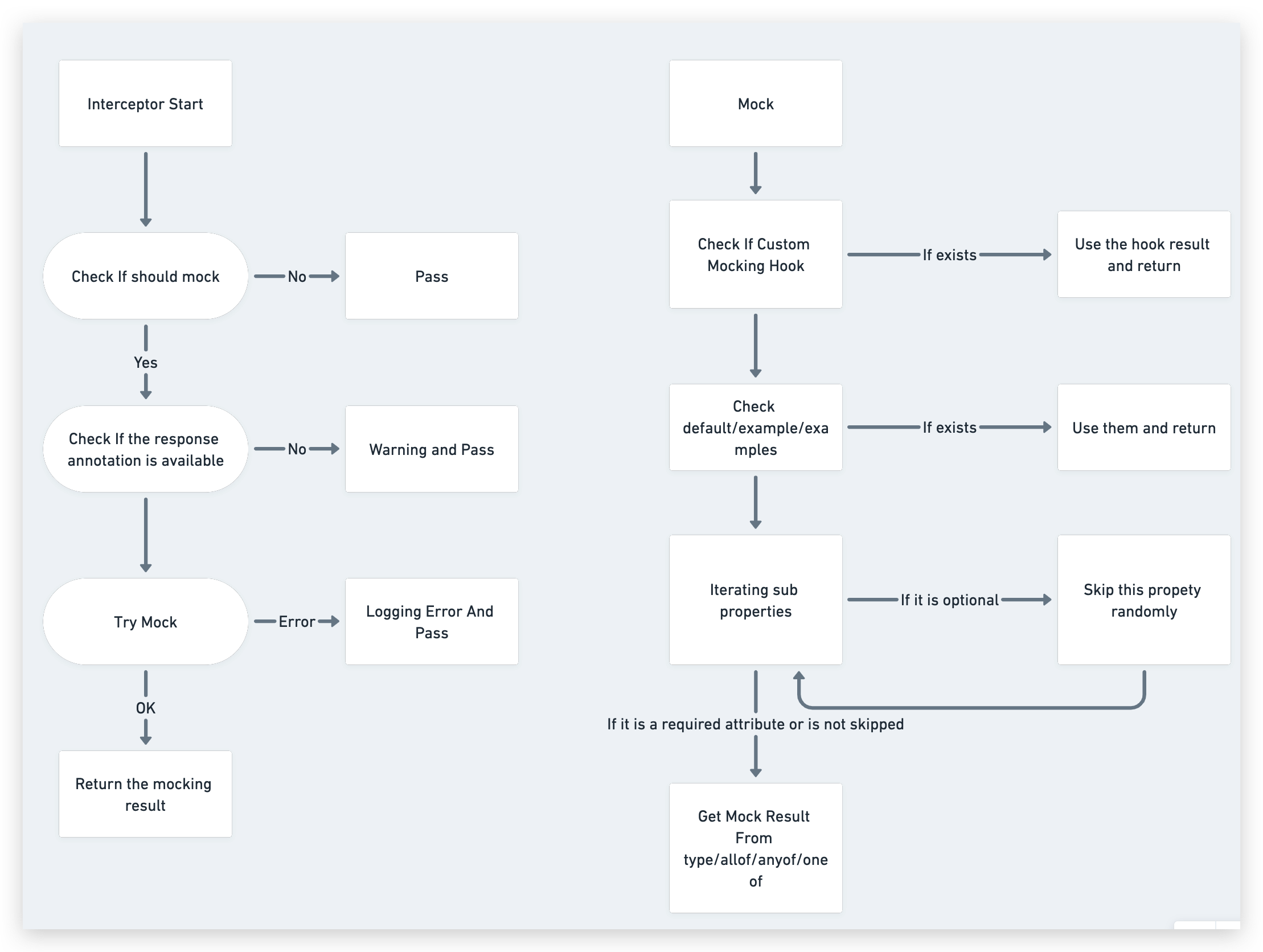
Mocking Interceptor for @nest/swagger base on decorators.
## use npm
npm install reflect-metadata nest-swagger-mocker
## or, use yarn
yarn add reflect-metadata nest-swagger-mocker// main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core'
import { DocumentBuilder, SwaggerModule } from '@nestjs/swagger'
import { MockInterceptorFactory } from 'nest-swagger-mocker'
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule)
const options = new DocumentBuilder()
const swaggerDocument = SwaggerModule.createDocument(app, options)
app.useGlobalInterceptors(
MockInterceptorFactory.create({
document: swaggerDocument,
}),
)## by default, when the request has a header x-mock:true, the mock feature will be activated
curl --location --request GET 'https://foo.bar.com/your-api-path' \
--header 'x-mock: true'- 👼 Out of the box and ready to use,automatically construct mock responses based on swagger annotation information
- 😃 You can use some built-in decorators to customize the construction rules for mock responses
- 🫡 Internally using fakerjs, you can freely manipulate faker instances to implement features such as i18n
- 👏 Customize the timing of returning mock responses
- 🏋️♂️ Supported swagger annotation:
- type: string, number, boolean, object, array, enum, {class}
- default, example, examples
- allof (all schema will be merge)
- oneof (one of schema will be used)
- anyof (Randomly select one or more schema to merge)
Create an MockInterceptor for NestJs app.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| options? | { ... } | The options to use. | |
| options.shouldMockChecker? | (context: ExecutionContext) => boolean | context => context.switchToHttp().getRequest().headers['x-mock'] === 'true' } | A function to determine if a mock response is used to return results. Providing the NestInterceptor standard ExecutionContext as a param. By default, read the x-mock in the request header. |
| options.logger? | LoggerService | console | The NestJS logger to be used. |
| options.fakerOptions? | { ... } | This lib use fakerjs as core, we can set up some options for fakerjs. | |
| options.fakerOptions.defaultProbability? | number | 0.9 | Default probability for faker.maybe. (fake.maybe will be used when the property is not required to have value) Should be 0~1, the larger the number is, the greater the possibility that the optional attribute has a value |
| options.fakerOptions.setup? | (faker: Faker) => void | () => null | By this function you can do something with the faker instance. For example, faker.setLocale() |
Returns: MockInterceptor
Defines the rules for generating a mock string.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| options? | FakeStringOptions | { type: 'default' } | |
| options.type? | 'default' | 'uuid' |'template' |'words' | 'random' | 'default' | 1. if 'random' is specified, the string will containing UTF-16 chars between 33 and 125 (! to }).2. if 'template' is specified the string will be generated by the given template. 3. if 'words' or 'default' is specified, the string will be with a set of random words. 4. if 'uuid' is specified, the string will be a v4 uuid |
| options.minLength? | number | min length of the random string | |
| options.maxLength? | number | 5 | max length of the random string |
| options.minWordsCount? | number | min word number of the random string | |
| options.maxWordsCount? | number | 5 | max word number of the random string |
Defines the rules for generating a mock number.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| options? | FakeNumberOptions | ||
| options.min? | number | 0 | lower bound for generated number |
| options.max? | number | options.min + 99999 | upper bound for generated number |
| options.precision? | number | 0.01 | precision of the generated number, only works when 'isFloat' is true and should be less than 1 |
| options.isFloat? | boolean | false | whether the number can be a float |
Defines the rules for generating a mock boolean.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| options? | IFakeBooleanOptions | ||
| options.probability | number | 0.5 | the probability of be true |
Defines the rule of how many array items will be
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| minCount | number | 3 | |
| maxCount | number | minCount |
Set the type(non-primitive-type) of the item of the array. You will need this when you want to generate a mock response for an object array because typescript(<=4.8) will not decorate the type of the array item and the mock rule is base on metadata.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | { new (...args: any[]): any; prototype: Object } | The type of array item |
Register a hook function to operate the response value after the mock generator generates the mock response value.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| hook | (response: TResponse) => unknown | the function to operate the response |
If you need to customize the mock rule instead of using the mock function provided by this library, you can use this function to specify how the mock value is generated.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| mockingFunction | (faker: Faker) => TResponse | the function to specify how the mock value is generated |
This library works based on metadata, but if a property is not decorated with any decorator, typescript will not emit metadata for it, so we need to use this decorator to mark a property when we want to mock it when there is not any decorator else. Otherwise, the property will be ignored and mocked to {}.
N/A
In some case the mock rule decorators can not work and I got some warning begin with 'Cannot find metadata for...'
Without manual marking, TypeScript's metadata reflection system has several limitations which make it impossible to, for instance, determine what type an object array which marked by class (The only thing the reflection system knows is the array is constructed by normal function). However, the mock rule feature of this library works based on metadata, and in these cases, this library cannot get enough information from the swagger's annotations or metadata, and some auxiliary decorators can help to supplement the information, these decorators are:
- FakeArrayItemClassType
- FakeExtraClassTypes
- FakeProperty
This lib works based on swagger itself, when all property is optional, swagger will remove the require array instead of keeping it an empty array from the schema, so the lib can not judge when to make property optional. You can use @FakeOptional instead.
If you are not using nest cli swagger plugin
If you are using nest cli swagger plugin
If you are using an independent mocking server:
- The mocking config may be outside your app git repository which may lead to logical fragmentation
- Nest Guards/Interceptor/Pipe/Middleware/Filter/Router will not work for the mocking server, so some verification, conversion, and inspection will not work
- May need to solve cross-domain problems
- Need to maintain the mapping between swagger annotations and mock rules manually
This project is tested by e2e-tesing with @nestjs/core and @nestjs/swagger 6.1.2.