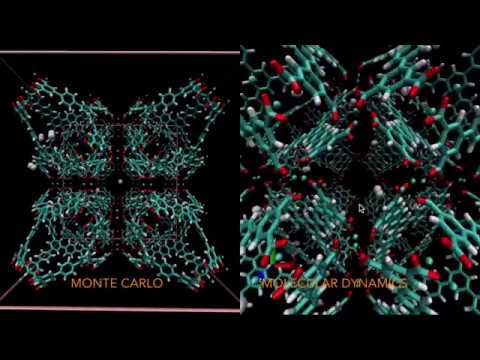
This is a Monte Carlo and Molecular Dynamics Simulation software used primarily for gas sorption in crystalline materials. It is a project that began as a re-write and expansion of Massively Parallel Monte Carlo (MPMC), another code developed and maintained by our laboratory, led by Brian Space at the University of South Florida, Dept. of Chemistry, Smart Metal-organic Materials Advanced Research and Technology Transfer (SMMARTT).
Using a terminal,
0. (On Windows only) Get the Linux Subsystem (easier instructions for beginners) (or equivalent software, e.g. CygWin):
-
Download:
git clone https://github.com/khavernathy/mcmdor download .zip file -
Compile:
cd mcmd
cd src
bash compile.sh [ options ]
cd ..
export PATH=$PATH:/path/to/mcmd/ -
Run:
mcmd mcmd.inp
cd mcmd
git pull
cd src
bash compile.sh [ options ]
Take a look at mcmd/src/compile.sh for different options in compilation (OS-specific, CUDA implementation, OpenMP, optimization on different HPC systems, etc.)
You can find details on available options, built-in potentials, etc. on the wiki page: https://github.com/khavernathy/mcmd/wiki
Douglas Franz: [email protected] University of South Florida Dept. of Chemistry
-> Monte Carlo simulation in NPT, NVT, NVE, and μVT ensembles.
-> Molecular Dynamics simulation in NVT, NVE, and μVT ensembles.
-> A crystal builder to create fully parameterized supercells from unit cells.
-> A fragment creator based around uniquely named atoms.
-> A LAMMPS input file exporter.
-> Trajectories and restart files in various formats.
-> Automatic radial distribution calculator
-> Hard-coded molecular models for easy input, including multi-molecule support
-> Easy system basis parametrization via a, b, c, α, β, γ crystal parameters, or basis vectors
-> Quick routines for energy/force computation
-> Simulated annealing
-> Any periodic cell is supported for both MC and MD; non-periodic systems also supported.
-> Potentials available are Lennard-Jones (12-6), Tang-Toennies (6-8-10), Ewald electrostatics, and Thole-Applequist polarization.
-> Built-in force fields from UFF, OPLS, and other sources
-> Sample inputs are included. The program takes just one argument: the input file (which itself usually points to a file containing starting atoms).
The program outputs several quantities of interest:
->Uptake of sorbates in wt%, reduced wt%, cm^3/g, mmol/g and mg/g
->Excess adsorption ratio in mg/g
->Selectivities for multi-sorbate simulation
->Qst (heat of sorption) for sorbate
->Sorbate occupation about some site/atom (g(r))
->Diffusion coefficient and specific heat
->Trajectory and restart files to easily pickup a halted job and visualize simulation
->3D histogram data for visualization of sorbate occupation in a material (density visualization).
->Induced dipole strengths for polarization simulations
MCMD works out-of-the-box on
-> Linux (tested on Ubuntu 16.04)
-> Mac (tested on OS X El Capitan v10.11.6)
-> Windows (tested using Cygwin and Windows 7 with gcc 5.4.0 installed)
-> Raspberry Pi (3, using Raspian OS).
We recommend Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD) for data visualization, but the output is compatible with most other software, e.g. Avogadro, Molden, Ovito, etc.
Below is a list of scientific publications/presentations that have been facilitated by this software.
-
Mukherjee, S. et al. Trace CO2 Capture by an Ultramicroporous Physisorbent with Low Water Affinity. Science Advances, 2019. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.aax9171
-
Franz, D. M., Forrest, K. A., Pham, T., & Space, B. (2016). Accurate H2 Sorption Modeling in the rht-MOF NOTT-112 Using Explicit Polarization. Crystal Growth & Design, 16(10), 6024-6032. DOI:10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01058
-
Mukherjee et al. Halogen‐C2H2 Binding in Ultramicroporous MOFs for Benchmark C2H2/CO2 Separation Selectivity. Chem. Eur. J. 2020. DOI:10.1002/chem.202000008
-
Pham, T., Forrest, K. A., Franz, D. M., Guo, Z., Chen, B., & Space, B. (2017). Predictive models of gas sorption in a metal–organic framework with open-metal sites and small pore sizes. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 19(28), 18587-18602. DOI:10.1039/C7CP02767B
-
Pham, T., Forrest, K. A., Franz, D. M., & Space, B. (2017). Experimental and theoretical investigations of the gas adsorption sites in rht-metal-organic frameworks. CrystEngComm, 19, 4646-4665. DOI:10.1039/C7CE01032J
-
Franz, D. M.; Dyott, Z.; Forrest, K. A.; Hogan, A.; Pham, T.; Space, B. Simulations of hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and small hydrocarbon sorption in a nitrogen-rich rht-metal–organic framework. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017. DOI:10.1039/C7CP06885A
-
Franz, D. M.; Djulbegovic, M.; Pham, T.; Space, B. Theoretical study of the effect of halogen substitution in molecular porous materials for CO2 and C2H2 sorption. AIMS Materials Science. 2017. DOI:10.3934/matersci.2018.2.226
-
Forrest, K. A.; Franz, D. M.; Pham, T. ; Space, B. Investigating C2H2 sorption in a-[M3(O2CH)6] (M = Mg, Mn) Through Theoretical Studies. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018. DOI:10.1021/acs.cgd.8b00770
-
Yu et al. Enhanced Gas Uptake in a Microporous Metal–Organic Framework via a Sorbate Induced-Fit Mechanism. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 2019. DOI:10.1021/jacs.9b07807
-
Pal et al. A Microporous Co-MOF for Highly Selective CO2 Sorption in High Loadings Involving Aryl C–H...O=C=O Interactions: Combined Simulation and Breakthrough Studies" ACS Inorganic Chem., 2019. DOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01402