RODA-in is a tool specially designed for producers and archivists to create Submission Information Packages (SIP) ready to be submitted to an Open Archival Information System (OAIS). The tool creates SIPs from files and folders available on the local file system.
In version 2 we revolutionized the way SIPs are created to satisfy the need for mass processing of data. In this version you can create thousands of valid SIPs with just a few clicks, complete with data and metadata.
The tool includes features such as:
- Create, load and edit classification schemas
- Automatic association of files/folders to SIP
- Automatic association of metadata to SIP
- Definition of metadata templates
- Support for various metadata formats (EAD, DC, etc.)
- Creation of SIP of unlimited size
- Creation of SIP in various formats: BagIt and E-ARK (versions 1.x & 2.x)
This application was part of the RODA project and now has been released as a project by its own due to the increasing interest in its particular functionality. It was further developed in the E-ARK project and now it is being developed in the CEF eArchiving Building Block.
RODA-in supports several Submission Information Package formats. At the moment we have included support for:
- BagIt, a hierarchical file packaging format for storage and transfer of arbitrary digital content. A "bag" has just enough structure to enclose descriptive "tags" and a "payload" but does not require knowledge of the payload's internal semantics. This BagIt format should be suitable for disk-based or network-based storage and transfer. BagIt is widely used in the practice of digital preservation. The specification of BagIt can be found here.
- E-ARK SIP format, both versions 1.x & 2.x, a Submission Information Package format developed by the EU funded E-ARK Project and maintained by the Digital Information LifeCycle Interoperability Standards Board (DILCIS Board). The specification can be found here.
RODA-in has been successfully tested on Windows, MacOS and Linux Desktop versions. The RODA-in installer comes with a free and open-source version of Java included and will use the internal Java by default.
The latest version of RODA-in is available here.
The basic workflow of the application is as follows:
- Choose a working folder in your file system (panel on the left). This will serve as the root of your project.
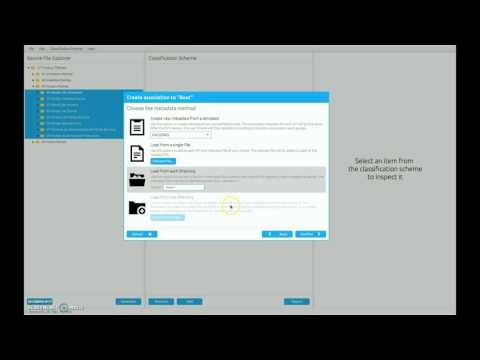
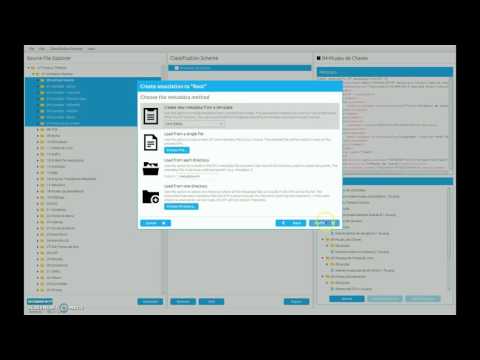
- Choose or create a classification scheme (panel on the center). There's two options:
- Load a classification scheme. You can obtain a classification scheme from RODA repository, for example.
- Create a new classification scheme.
- Drag files/folders from the left panel to the center panel into the appropriate node in the classification scheme.
- Choose the creatorOption of data and metadata association. This will have impact on the number and structure of the SIPs created.
- (Optional) Inspect the created SIPs, edit metadata and content.
- Export the SIPs to a folder
To select more than one file/folder you can press SHIFT or CTRL.
The following actions are supported to edit the classification scheme:
- Add node
- Edit the title and the description level of the node
- Move node (using drag and drop)
- Change parent
- Move to the root of the tree
- Remove node
In this section you may find a few video tutorials on how to use the RODA-in tool to create Submission Information Packages (SIP).
Since it's tedious to edit the template files by hand, we added a way to create forms based on the fields of the templates. These files are located in the "roda-in" folder (My Documents when using Windows and the user's home directory if using Unix), under the "templates" folder. Using the powerful Handlebars engine, anyone can create template files with the necessary information to create the form. In addition to a simple tag, (e.g. {{person}}), we can now add options which will modify the way each field is created. These options are key-value elements, e.g. title="SIP creation using RODA-in", where the key is the name of the option and the value is the value that will be given to that option. Only the first tag should have options, i.e., if there's two tags with the same name, the options of the second are ignored. The options are not required, the form is still created with a simple tag, which creates a simple text field.
The available options that alter the fields created for each tag are:
- value - the predefined value of the field
- order - the order of the field
- type - the type of the field. The possible values are:
- text - text field
- text-area - Text area. Larger than a field text.
- date - text field with a date picker
- list - list with the possible values (combo box)
- list - List with the possible values that a field can have. Usable when
type="list". The format is a JSON array. Example:[option A, option B, "option C"] - label - The label that appears to the left of the field.
- mandatory - If set to true the label is styled in bold to draw attention.
- hidden - If set to true the field is hidden
- auto-generate - Fills the value with one of the available generators. Overrides the value option:
- now - the current date in the format year/month/day
- id - generates an identifier
- title - generates a title
- level - adds the current description level
- parentid - adds the parent's id, if it exists
- language - adds the system language, based on the locale. Example: "português" or "English"
The following is an example of how the tags can be used:
- Make sure you have installed Java 8 and Maven.
- Clone the repository by issuing the command
git clone https://github.com/keeps/roda-in.git - Change directory to "roda-in"
- Install by running the following command:
mvn -Dmaven.test.skip=true clean package
That's it! Binaries will be on the target folder. To run the application just double click on the file or run the following command on the console/terminal:
java -jar roda-in-app-x.y.z.jar
RODA-in uses TestFX to execute tests using the user interface. TestFX needs full control of the mouse and keyboard when running the tests, so you won't be able to use them. In order to make the tests run in the headless mode (so that they can run in the background) follow these steps:
- Download the Monocle graphic environment jar
- Copy the jar to
<JDK_HOME>/jre/lib/ext - Run the command
mvn clean package -Dtestfx.robot=glass -Dglass.platform=Monocle -Dmonocle.platform=Headless -Dprism.order=sw
Metadata templates exist under the folder "roda-in" in your home directory ("Documents" for Windows users). Open the files with your favourite text editor and make sure they remain valid XML files acording to the provided schemas.
The application might need more memory than what is available by default (normally 64MB). To increase the available memory use the -Xmx option. For example, the following command will increase the heap size to 3 GB.
$ java -Xmx3g -jar roda-in-app-x.y.z.jar
The application needs enough memory to put the file structure definition in memory (not the data).
For more information or commercial support, contact KEEP SOLUTIONS.
- Bagit specification
- E-ARK SIP specification (all versions)
- E-ARK SIP specification (latest version)
- E-ARK Common specification (all versions)
- E-ARK Common specification (latest version)
- RODA source code
- RODA Community Web site
- E-ARK Project Web site
- CEF eArchiving Building Block
- RODA-in master thesis (2016)
Maven is required to build RODA-in.
- Fork it!
- Create your feature branch:
git checkout -b my-new-feature - Commit your changes:
git commit -am 'Add some feature' - Push to the branch:
git push origin my-new-feature - Submit a pull request :D
To increase the changes of you code being accepted and merged into RODA source here's a checklist of things to go over before submitting a contribution. For example:
- Has unit tests (that covers at least 80% of the code)
- Has documentation (at least 80% of public API)
To help make RODA-in better you can translate it to your language.
RODA-in uses Transifex, a localization platform, and you can find the project here. If you don't know how to use Transifex, check out these instructions, it's really easy and simple.
- Zoltán Szatucsek, Hungarian National Archives
RODA-in licence is LGPLv3
GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
Version 3, 29 June 2007
Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc. <http://fsf.org/>
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
This version of the GNU Lesser General Public License incorporates
the terms and conditions of version 3 of the GNU General Public
License, supplemented by the additional permissions listed below.
0. Additional Definitions.
As used herein, "this License" refers to version 3 of the GNU Lesser
General Public License, and the "GNU GPL" refers to version 3 of the GNU
General Public License.
"The Library" refers to a covered work governed by this License,
other than an Application or a Combined Work as defined below.
An "Application" is any work that makes use of an interface provided
by the Library, but which is not otherwise based on the Library.
Defining a subclass of a class defined by the Library is deemed a mode
of using an interface provided by the Library.
A "Combined Work" is a work produced by combining or linking an
Application with the Library. The particular version of the Library
with which the Combined Work was made is also called the "Linked
Version".
The "Minimal Corresponding Source" for a Combined Work means the
Corresponding Source for the Combined Work, excluding any source code
for portions of the Combined Work that, considered in isolation, are
based on the Application, and not on the Linked Version.
The "Corresponding Application Code" for a Combined Work means the
object code and/or source code for the Application, including any data
and utility programs needed for reproducing the Combined Work from the
Application, but excluding the System Libraries of the Combined Work.
1. Exception to Section 3 of the GNU GPL.
You may convey a covered work under sections 3 and 4 of this License
without being bound by section 3 of the GNU GPL.
2. Conveying Modified Versions.
If you modify a copy of the Library, and, in your modifications, a
facility refers to a function or data to be supplied by an Application
that uses the facility (other than as an argument passed when the
facility is invoked), then you may convey a copy of the modified
version:
a) under this License, provided that you make a good faith effort to
ensure that, in the event an Application does not supply the
function or data, the facility still operates, and performs
whatever part of its purpose remains meaningful, or
b) under the GNU GPL, with none of the additional permissions of
this License applicable to that copy.
3. Object Code Incorporating Material from Library Header Files.
The object code form of an Application may incorporate material from
a header file that is part of the Library. You may convey such object
code under terms of your choice, provided that, if the incorporated
material is not limited to numerical parameters, data structure
layouts and accessors, or small macros, inline functions and templates
(ten or fewer lines in length), you do both of the following:
a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the object code that the
Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are
covered by this License.
b) Accompany the object code with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license
document.
4. Combined Works.
You may convey a Combined Work under terms of your choice that,
taken together, effectively do not restrict modification of the
portions of the Library contained in the Combined Work and reverse
engineering for debugging such modifications, if you also do each of
the following:
a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the Combined Work that
the Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are
covered by this License.
b) Accompany the Combined Work with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license
document.
c) For a Combined Work that displays copyright notices during
execution, include the copyright notice for the Library among
these notices, as well as a reference directing the user to the
copies of the GNU GPL and this license document.
d) Do one of the following:
0) Convey the Minimal Corresponding Source under the terms of this
License, and the Corresponding Application Code in a form
suitable for, and under terms that permit, the user to
recombine or relink the Application with a modified version of
the Linked Version to produce a modified Combined Work, in the
manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL for conveying
Corresponding Source.
1) Use a suitable shared library mechanism for linking with the
Library. A suitable mechanism is one that (a) uses at run time
a copy of the Library already present on the user's computer
system, and (b) will operate properly with a modified version
of the Library that is interface-compatible with the Linked
Version.
e) Provide Installation Information, but only if you would otherwise
be required to provide such information under section 6 of the
GNU GPL, and only to the extent that such information is
necessary to install and execute a modified version of the
Combined Work produced by recombining or relinking the
Application with a modified version of the Linked Version. (If
you use option 4d0, the Installation Information must accompany
the Minimal Corresponding Source and Corresponding Application
Code. If you use option 4d1, you must provide the Installation
Information in the manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL
for conveying Corresponding Source.)
5. Combined Libraries.
You may place library facilities that are a work based on the
Library side by side in a single library together with other library
facilities that are not Applications and are not covered by this
License, and convey such a combined library under terms of your
choice, if you do both of the following:
a) Accompany the combined library with a copy of the same work based
on the Library, uncombined with any other library facilities,
conveyed under the terms of this License.
b) Give prominent notice with the combined library that part of it
is a work based on the Library, and explaining where to find the
accompanying uncombined form of the same work.
6. Revised Versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License.
The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions
of the GNU Lesser General Public License from time to time. Such new
versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may
differ in detail to address new problems or concerns.
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
Library as you received it specifies that a certain numbered version
of the GNU Lesser General Public License "or any later version"
applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and
conditions either of that published version or of any later version
published by the Free Software Foundation. If the Library as you
received it does not specify a version number of the GNU Lesser
General Public License, you may choose any version of the GNU Lesser
General Public License ever published by the Free Software Foundation.
If the Library as you received it specifies that a proxy can decide
whether future versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License shall
apply, that proxy's public statement of acceptance of any version is
permanent authorization for you to choose that version for the
Library.