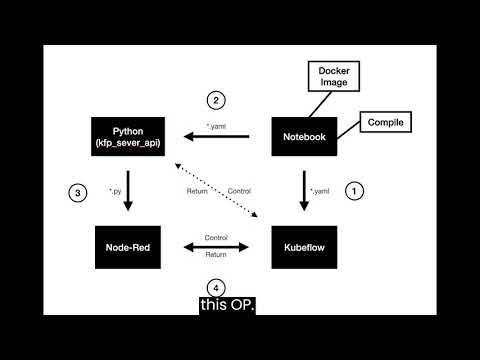
Kube-node-red is aiming to integrate Kubeflow/Kubebeters with node-red, leveraging node-red's low-code modules, and using Kubeflow resources (e.g. Kubeflow pipeline, Kserve) to enhance its AI/ML ability.
https://github.com/NightLightTw/kubeflow-Node-RED/tree/main
https://github.com/kubeflow/pipelines/tree/1.8.21/backend/api/python_http_client
Kubeflow-Node-red implementation Random Forest training flo
As this project focused on the node-red integration with Kubeflow, one running Kubeflow instance should be ready on a publicly available network. (If you need to provision your Kubeflow instance, you could refer to our mulitkf project to allocate one instance for developing.)
You can proceed to the examples folder and run the ./build.sh to build the image locally or just run the ./run.sh which would download the base image from our public repository.
We organized some examples under examples folder, and make sensitive information pass via environment variables. Please refer to the following example to launch an individual example:
# If you use Windows system, it is recommended to use WSL
$ git clone https://github.com/NightLightTw/kubeflow-Node-RED.git
# enter folder
cd kubeflow-Node-RED
cd examples && \
KUBEFLOW_HOST=<your-kubeflow-instance-endpoint> \
KUBEFLOW_USERNAME=<your-username-account> \
KUBEFLOW_PASSWORD=<your-password> \
./run.sh <example-index>
Info: Here please use 1.connect-kubeflow
-
then you can go to UI, and check it out: http://127.0.0.1:1880/
-
press the “install dependency” button to install dependency items such as specific Python libraries and wait for their completion
-
switch different pipelines and press the time stamp button to trigger the flow process
Info: If the environment variable does not work, please fill in the account password directly in the Python file
# Open another terminal and check the docker status
docker ps
#enter container
docker exec -it <containerID> bash
#enter document folder
cd /data/1.connect-kubeflow/py/api_examples
#execute function
python3 <file-name>
You can test the file in api_example
Info: Some of these files require a custom name, description, or assigned id in
Q1: MissingSchema Invalid URL '' A1: This problem means that the login information is not accessed correctly, which may be caused by the environment variable not being read. You can directly override the login information of the specified file
Change your login information
host = "https://[email protected]"
username = "test01"
password = "123456"
Please refer to Kubeflow implementation: add Random Forest algorithm
Modify using your yaml file path
Info: Line 66: uploadfile='pipelines/only_randomforest.yaml'
Info: Line 122~129 use json parser for filtering different outputs from get_run()
from __future__ import print_function
import time
import kfp_server_api
import os
import requests
import string
import random
import json
from kfp_server_api.rest import ApiException
from pprint import pprint
from kfp_login import get_istio_auth_session
from kfp_namespace import retrieve_namespaces
host = os.getenv("KUBEFLOW_HOST")
username = os.getenv("KUBEFLOW_USERNAME")
password = os.getenv("KUBEFLOW_PASSWORD")
auth_session = get_istio_auth_session(
url=host,
username=username,
password=password
)
# The client must configure the authentication and authorization parameters
# by the API server security policy.
# Examples for each auth method are provided below, use the example that
# satisfies your auth use case.
# Configure API key authorization: Bearer
configuration = kfp_server_api.Configuration(
host = os.path.join(host, "pipeline"),
)
configuration.debug = True
namespaces = retrieve_namespaces(host, auth_session)
#print("available namespace: {}".format(namespaces))
def random_suffix() -> string:
return ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits, k=10))
# Enter a context with an instance of the API client
with kfp_server_api.ApiClient(configuration, cookie=auth_session["session_cookie"]) as api_client:
# Create an instance of the Experiment API class
experiment_api_instance = kfp_server_api.ExperimentServiceApi(api_client)
name="experiment-" + random_suffix()
description="This is an experiment for only_randomforest."
resource_reference_key_id = namespaces[0]
resource_references=[kfp_server_api.models.ApiResourceReference(
key=kfp_server_api.models.ApiResourceKey(
type=kfp_server_api.models.ApiResourceType.NAMESPACE,
id=resource_reference_key_id
),
relationship=kfp_server_api.models.ApiRelationship.OWNER
)]
body = kfp_server_api.ApiExperiment(name=name, description=description, resource_references=resource_references) # ApiExperiment | The experiment to be created.
try:
# Creates a new experiment.
experiment_api_response = experiment_api_instance.create_experiment(body)
experiment_id = experiment_api_response.id # str | The ID of the run to be retrieved.
except ApiException as e:
print("Exception when calling ExperimentServiceApi->create_experiment: %s\n" % e)
# Create an instance of the pipeline API class
api_instance = kfp_server_api.PipelineUploadServiceApi(api_client)
uploadfile='pipelines/only_randomforest.yaml'
name='pipeline-' + random_suffix()
description="This is a only_randomForest pipline."
try:
pipeline_api_response = api_instance.upload_pipeline(upload file, name=name, description=description)
pipeline_id = pipeline_api_response.id # str | The ID of the run to be retrieved.
except ApiException as e:
print("Exception when calling PipelineUploadServiceApi->upload_pipeline: %s\n" % e)
# Create an instance of the run API class
run_api_instance = kfp_server_api.RunServiceApi(api_client)
display_name = 'run_only_randomForest' + random_suffix()
description = "This is a only_randomForest run."
pipeline_spec = kfp_server_api.ApiPipelineSpec(pipeline_id=pipeline_id)
resource_reference_key_id = namespaces[0]
resource_references=[kfp_server_api.models.ApiResourceReference(
key=kfp_server_api.models.ApiResourceKey(id=experiment_id, type=kfp_server_api.models.ApiResourceType.EXPERIMENT),
relationship=kfp_server_api.models.ApiRelationship.OWNER )]
body = kfp_server_api.ApiRun(name=display_name, description=description, pipeline_spec=pipeline_spec, resource_references=resource_references) # ApiRun |
try:
# Creates a new run.
run_api_response = run_api_instance.create_run(body)
run_id = run_api_response.run.id # str | The ID of the run to be retrieved.
except ApiException as e:
print("Exception when calling RunServiceApi->create_run: %s\n" % e)
Completed_flag = False
polling_interval = 10 # Time in seconds between polls
while not Completed_flag:
try:
time.sleep(1)
# Finds a specific run by ID.
api_instance = run_api_instance.get_run(run_id)
output = api_instance.pipeline_runtime.workflow_manifest
output = json.loads(output)
try:
nodes = output['status']['nodes']
conditions = output['status']['conditions'] # Comfirm completion.
except for KeyError:
nodes = {}
conditions = []
output_value = None
Completed_flag = conditions[1]['status'] if len(conditions) > 1 else False
except ApiException as e:
print("Exception when calling RunServiceApi->get_run: %s\n" % e)
break
if not Completed_flag:
print("Pipeline is still running. Waiting...")
time.sleep(polling_interval-1)
for node_id, node in nodes.items():
if 'inputs' in node and 'parameters' in node['inputs']:
for parameter in node['inputs']['parameters']:
if parameter['name'] == 'random-forest-classifier-Accuracy': #change parameter
output_value = parameter['value']
if output_value is not None:
print(f"Random Forest Classifier Accuracy: {output_value}")
else:
print("Parameter not found.")
print(nodes)
#ensure dependency items
pip install kfp
python <python-file>
A node mainly consists of two files
- Javascript file(.js) define what the node does
- HTML file(.html) Define the properties of the node and the windows and help messages in the Node-RED editor
When finally package into npm module, will need package.json
A standard file for describing the content of node.js modules
A standard package.json can be generated using npm init. This command will ask a series of questions to find a reasonable default value. When asked for the name of the module name: enter the example name node-red-contrib-<self_defined>
When it is established, you need to manually add the node-red attribute
*p.s. Where the example files need to be changed *
{
"name": "node-red-contrib-pythonshell-custom",
...
"node-red": {
"nodes": {
"decisionTree": "decisiontree.js",
"randomForest": "randomforest.js",
"logisticRegression": "logisticregression.js"
"<self_defined>":"<self_defined.js>"
}
},
...
}
<script type="text/javascript">
# Replace the node name displayed/registered in the palette
RED.nodes.registerType('decisionTree',{
category: 'input',
defaults: {
name: {required: false},
# Replace the .py path to be used
pyfile: {value: "/data/1.connect-kubeflow/py/decisionTree.py"},
virtualenv: {required: false},
continuous: {required: false},
stdInData: {required: false},
python3: {required: false}
},
- open decisionTree.js
function PythonshellInNode(config) {
if (!config.pyfile){
throw 'pyfile not present';
}
this.pythonExec = config.python3 ? "python3" : "python";
# Replace the path or change the following path to config .pyfile
this.pyfile = "/data/1.connect-kubeflow/py/decisionTree.py";
this.virtualenv = config.virtualenv;
2.open deccisiontree.js
var util = require("util");
var httpclient;
#change the path/file name of the module file
var PythonshellNode = require('./decisionTree');
# To change the name to be registered, it must be consistent with the change of .html
RED.nodes.registerType("decisionTree", PythonshellInNode);
Import the folder where the above file is located to the node_modules directory of the container
e.g. docker desktop