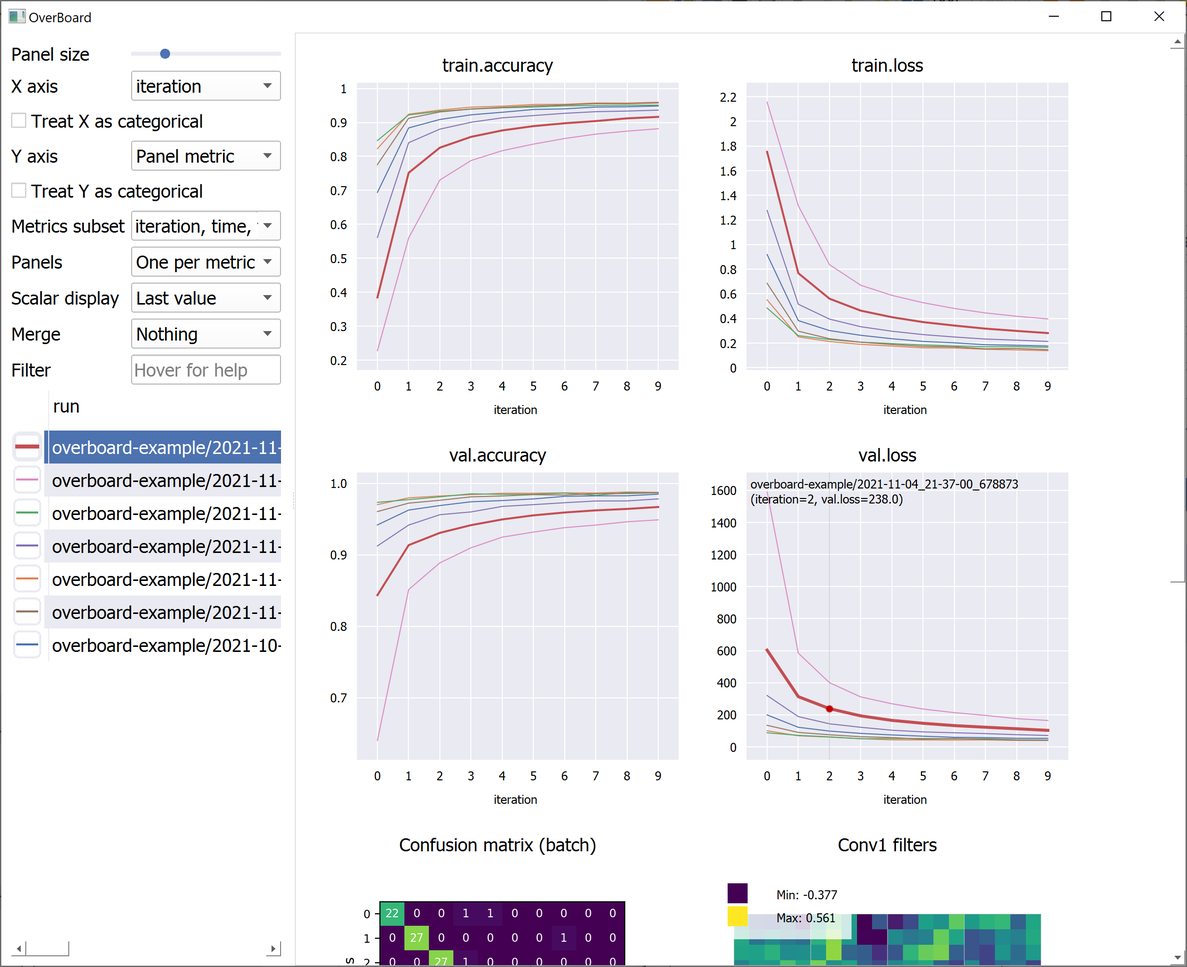
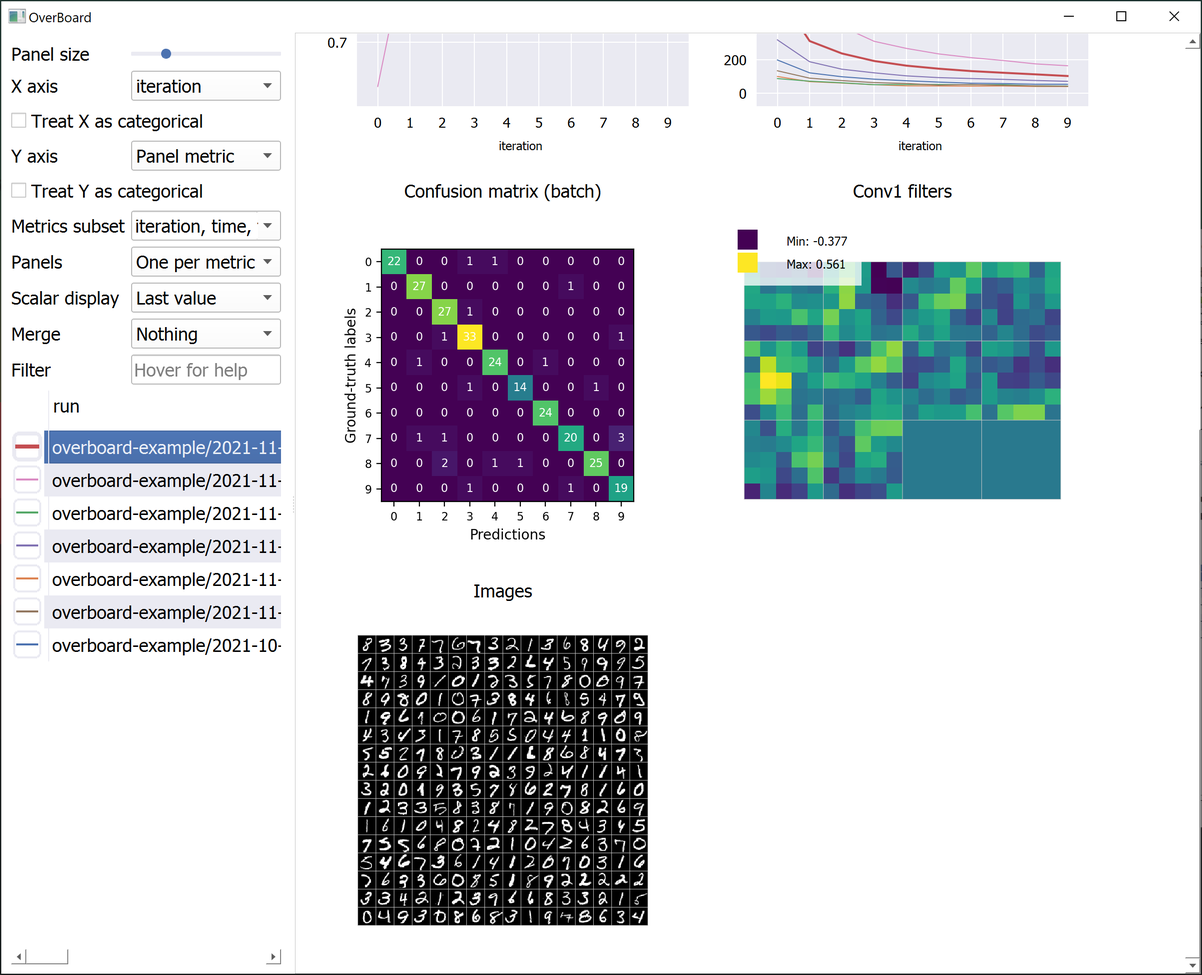
OverBoard is a lightweight yet powerful dashboard to monitor your experiments.
Load remote experiments in real-time through SSH/FTP and others.
Custom visualisations (tensors and any custom plot with familiar MatPlotLib syntax).
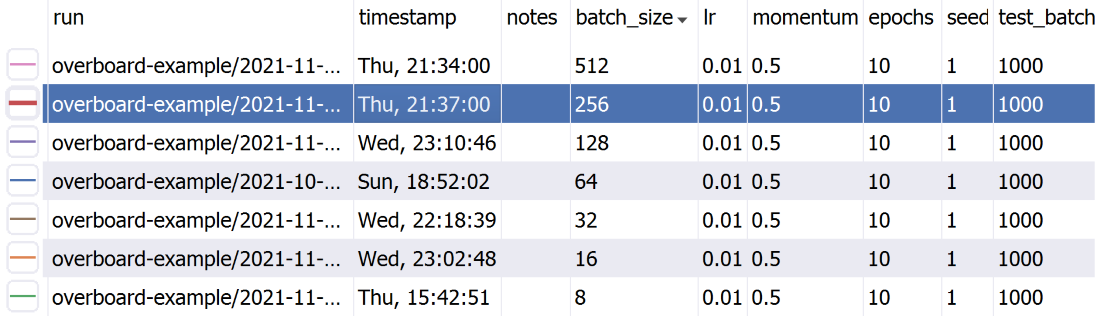
A sortable table of hyper-parameters with Python-syntax filtering.
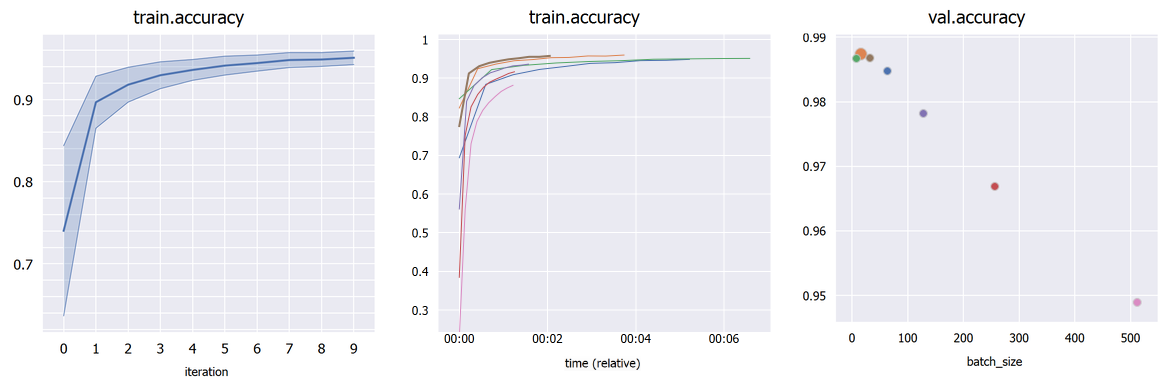
Plot percentile intervals (shaded plots), custom X/Y axes, and hyper-parameters (bubble plots).
You can install the dependencies with:
-
With Conda:
conda install pyqt=5.12 pyqtgraph=0.11 -c conda-forge -
With pip:
pip install pyqt5==5.12 pyqtgraph==0.11
Finally, OverBoard itself can be installed with: pip install fs==2.4 overboard
(Conda seems to be too strict when installing PyFileSystem/fs, so pip should be preferred.)
Optional:
-
pip install fs.sshfsto support remote files through SSH. -
PyOpenGL 3.1 (either through conda or pip) if you intend to use custom 3D plots with PyQtGraph.
-
MatPlotLib if you intend to use it for custom plots.
Your scripts can log data without installing the full GUI and its dependencies (so your remote GPU cluster does not need PyQt at all).
Just use: pip install overboard_logger
And remember to import overboard_logger instead of overboard in your scripts.
-
Main interface:
python3 -m overboard <logs-directory> -
Logging experiments is simple:
from overboard import Logger
with Logger('./logs') as logger:
for iteration in range(100):
logger.append({'loss': 0, 'error': 0})You can also pass in a meta keyword argument, which can be a dict with hyper-parameters names and values (or other meta-data), to help organize your experiments. These will be displayed in a handy table, which supports sorting and filtering. The meta data can also be an argparse.Namespace, which is useful if your hyper-parameters are command-line arguments parsed with argparse.
By default a unique folder (using the current timestamp) is created for the logs. For full documentation on initialization arguments and other methods, type pydoc overboard on the command-line (Python built-in doc viewer).
You can also check the examples directory:
examples/basic.py: A minimal example. Generates some test logs.examples/mnist.py: The mandatory MNIST example. Also shows a custom MatPlotLib plot (a confusion matrix).examples/example_2d.py: Example custom 2D plot, with PyQtGraph (faster than MatPlotLib).examples/example_3d.py: Example custom 3D plot, with PyQtGraph. Requires PyOpenGL.
A note about importing: You can either import the Logger class from overboard or from overboard_logger. If you installed the "logger only" version as described above (no dependencies), then you can only import from overboard_logger.
It's as simple as:
python -m overboard ssh://username:password@hostname/path-to-experiments
...replacing your SSH user name, password, host name/server, and the directory where OverBoard should look for experiments. The default port is 22, which you can override with :23 or another port number after the host name.
There are a number of other settings, which you can append after the path. For example, append ?keepalive=60&config_path=~/.ssh/config to set the keepalive packets interval to 60 seconds, and specify an OpenSSH configuration file path.
Other remote file systems are available by using appropriate prefixes (e.g. ftp://).
-
Click a plot title to hide it (moving it to the bottom) or to show it again.
-
Click a plot line to select that experiment in the table, and vice-versa.
-
Use the mouse wheel to zoom and drag to pan in a plot or custom visualization.
-
Click the "A" button in the bottom-left of a plot to reset the zoom/pan.
-
Choose an hyper-parameter as the "X axis" in the sidebar to compare different hyper-parameters graphically (bubble plot). Click a bubble to highlight that experiment. If the hyper-parameter is numerical but has wildly different orders of magnitude, check "Treat X as categorical". By default, each bubble's Y coordinate (e.g. accuracy) is taken from the last iteration; in "Scalar display" you can choose the maximum or minimum across iterations.
-
If you have multiple runs with different random seeds (stored as hyper-parameter "seed" for example), select "Merge: seed" in the sidebar to merge them into shaded plots (you can then select whether to show the mean, median, range or standard deviations).
-
You can split all experiments into different plots by selected "Panels: One per run" in the sidebar, and selecting a metric to plot in "Y axis". Similarly, they can be split by a hyper-parameter value (e.g. a different algorithm in each panel, but each has multiple plots/runs).
João Henriques, Visual Geometry Group (VGG), University of Oxford