Compile-time Language Integrated Query for Scala
Quill provides a Quoted Domain Specific Language (QDSL) to express queries in Scala and execute them in a target language. The library's core is designed to support multiple target languages and the current version features support for Structured Query Language (SQL).
- Boilerplate-free mapping: The database schema is mapped using simple case classes.
- Quoted DSL: Queries are defined inside a
quoteblock. Quill parses each quoted block of code (quotation) at compile time and translates them to an internal Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) - Compile-time SQL generation: The
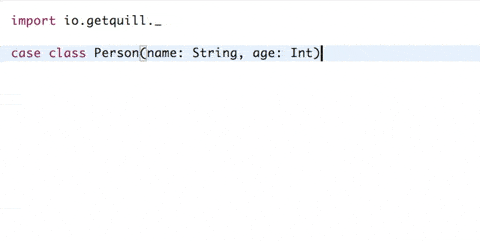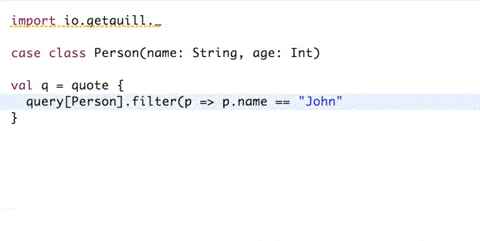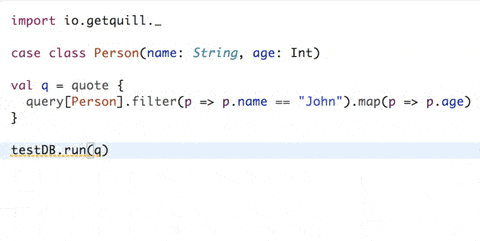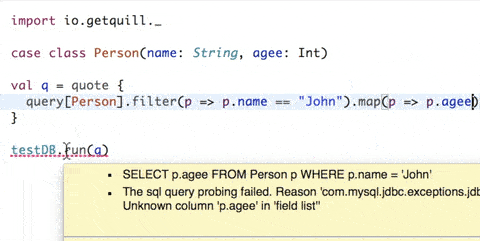
db.runcall reads the quotation's AST and translates it to the target language at compile time, emitting the SQL string as a compilation message. As the query string is known at compile time, the runtime overhead is very low and similar to using the database driver directly. - Compile-time query validation: If configured, the query is verified against the database at compile time and the compilation fails if it is not valid.
- Quotation
- Mirror sources
- Compile-time quotations
- Parametrized quotations
- Schema
- Queries
- Actions
- Dynamic queries
- Extending quill
- Sources
- Acknowledgments
- License
The QDSL allows the user to write plain Scala code, leveraging scala's syntax and type system. Quotations are created using the quote method and can contain any excerpt of code that uses supported operations. To create quotations, first import quote and some other auxiliary methods:
import io.getquill._A quotation can be a simple value:
val pi = quote(3.14159)And be used within another quotation:
case class Circle(radius: Float)
val areas = quote {
query[Circle].map(c => pi * c.radius * c.radius)
}Quotations can also contain high-order functions:
val area = quote {
(c: Circle) => pi * c.radius * c.radius
}val areas = quote {
query[Circle].map(c => area(c))
}Quill's normalization engine applies reduction steps before translating the quotation to the target language. The correspondent normalized quotation for both versions of the areas query is:
val areas = quote {
query[Circle].map(c => 3.14159 * c.radius * c.radius)
}Scala doesn't have support for high-order functions with type parameters. Quill supports anonymous classes with an apply method for this purpose:
val existsAny = quote {
new {
def apply[T](xs: Query[T])(p: T => Boolean) =
xs.filter(p(_)).nonEmpty
}
}
val q = quote {
query[Circle].filter { c1 =>
existsAny(query[Circle])(c2 => c2.radius > c1.radius)
}
}Sources represent the database and provide an execution interface for queries. Quill provides mirror sources for test purposes. Please refer to sources for information on how to create normal sources.
Instead of running the query, mirror sources return a structure with the information that would be used to run the query. There are two mirror source versions:
io.getquill.source.mirror.mirrorSource: Mirrors the quotation ASTio.getquill.source.sql.mirror.mirrorSource: Mirrors the SQL query
This documentation uses the SQL mirror in its examples under the db name:
val db = io.getquill.source.sql.mirror.mirrorSourceQuotations are both compile-time and runtime values. Quill uses a type refinement to store the quotation's AST as an annotation available at compile-time and the q.ast method exposes the AST as runtime value.
It is important to avoid giving explicit types to quotations when possible. For instance, this quotation can't be read at compile-time as the type refinement is lost:
val q: Quoted[Query[Circle]] = quote {
query[Circle].filter(c => c.radius > 10)
}
db.run(q) // Dynamic queryQuill falls back to runtime normalization and query generation if the quotation's AST can be read at compile-time. Please refer to dynamic queries for more information
Quotations are designed to be self-contained, without references to runtime values outside their scope. If a quotation needs to receive a runtime value, it needs to be done by defining the quotation as a function:
val q = quote {
(i: Int) =>
query[Circle].filter(r => r.radius > i)
}The runtime value can be specified when running it:
db.run(q).using(10) // SELECT r.radius FROM Circle r WHERE r.radius > ?The method run is a bridge between the compile-time quotations and the runtime execution.
The database schema is represented by case classes. By default, quill uses the class and field names as the database identifiers:
case class Circle(radius: Float)
val q = quote {
query[Circle].filter(c => c.radius > 1)
}
db.run(q) // SELECT c.radius FROM Circle c WHERE c.radius > 1Alternatively, the identifiers can be customized:
val circles = quote {
query[Circle]("circle_table", _.radius -> "radius_column")
}
val q = quote {
circles.filter(c => c.radius > 1)
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT c.radius_column FROM circle_table c WHERE c.radius_column > 1If multiple tables require custom identifiers, it is good practice to define a schema object with all table queries to be reused across multiple queries:
case class Circle(radius: Int)
case class Rectangle(length: Int, width: Int)
object schema {
val circles = quote {
query[Circle]("circle_table",
_.radius -> "radius_column")
}
val rectangles = quote {
query[Rectangle]("rectangle_table",
_.length -> "length_column",
_.width -> "width_column")
}
}The overall abstraction of quill queries is use database tables as if they were in-memory collections. Scala for-comprehensions provide syntatic sugar to deal with this kind of monadic operations:
case class Person(id: Int, name: String, age: Int)
case class Contact(personId: Int, phone: String)
val q = quote {
for {
p <- query[Person] if(p.id == 999)
c <- query[Contact] if(c.personId == p.id)
} yield {
(p.name, c.phone)
}
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT p.name, c.phone FROM Person p, Contact c WHERE (p.id = 999) AND (c.personId = p.id)Quill normalizes the quotation and translates the monadic joins to applicative joins in SQL, generating a database-friendly query that avoids nested queries.
Any of the following features can be used together with the others and/or within a for-comprehension:
filter
val q = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 18)
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT p.id, p.name, p.age FROM Person p WHERE p.age > 18map
val q = quote {
query[Person].map(p => p.name)
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT p.name FROM Person pflatMap
val q = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 18).flatMap(p => query[Contact].filter(c => c.personId == p.id))
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT c.personId, c.phone FROM Person p, Contact c WHERE (p.age > 18) AND (c.personId = p.id)sortBy
val q = quote {
query[Person].sortBy(p => p.age)
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT p.id, p.name, p.age FROM Person p ORDER BY p.agedrop/take
val q = quote {
query[Person].drop(2).take(1)
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT x.id, x.name, x.age FROM Person x LIMIT 1 OFFSET 2groupBy
val q = quote {
query[Person].groupBy(p => p.age).map {
case (age, people) =>
(age, people.size)
}
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT p.age, COUNT(*) FROM Person p GROUP BY p.ageunion
val q = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 18).union(query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 60))
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT x.id, x.name, x.age FROM (SELECT id, name, age FROM Person p WHERE p.age > 18
// UNION SELECT id, name, age FROM Person p1 WHERE p1.age > 60) xunionAll/++
val q = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 18).unionAll(query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 60))
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT x.id, x.name, x.age FROM (SELECT id, name, age FROM Person p WHERE p.age > 18
// UNION ALL SELECT id, name, age FROM Person p1 WHERE p1.age > 60) x
val q2 = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 18) ++ query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 60)
}
db.run(q2)
// SELECT x.id, x.name, x.age FROM (SELECT id, name, age FROM Person p WHERE p.age > 18
// UNION ALL SELECT id, name, age FROM Person p1 WHERE p1.age > 60) xaggregation
val r = quote {
query[Person].map(p => p.age)
}
db.run(r.min) // SELECT MIN(p.age) FROM Person p
db.run(r.max) // SELECT MAX(p.age) FROM Person p
db.run(r.avg) // SELECT AVG(p.age) FROM Person p
db.run(r.sum) // SELECT SUM(p.age) FROM Person p
db.run(r.size) // SELECT COUNT(p.age) FROM Person pisEmpty/nonEmpty
val q = quote {
query[Person].filter{ p1 =>
query[Person].filter(p2 => p2.id != p1.id && p2.age == p1.age).isEmpty
}
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT p1.id, p1.name, p1.age FROM Person p1 WHERE
// NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM Person p2 WHERE (p2.id <> p1.id) AND (p2.age = p1.age))
val q2 = quote {
query[Person].filter{ p1 =>
query[Person].filter(p2 => p2.id != p1.id && p2.age == p1.age).nonEmpty
}
}
db.run(q2)
// SELECT p1.id, p1.name, p1.age FROM Person p1 WHERE
// EXISTS (SELECT * FROM Person p2 WHERE (p2.id <> p1.id) AND (p2.age = p1.age))outer joins
val q = quote {
query[Person].leftJoin(query[Contact]).on((p, c) => c.personId == p)
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT p.id, p.name, p.age, c.personId, c.phone
// FROM Person p LEFT JOIN Contact c ON c.personId = p
val q2 = quote {
query[Person].rightJoin(query[Contact]).on((p, c) => c.personId == p)
}
db.run(q2)
// SELECT p.id, p.name, p.age, c.personId, c.phone
// FROM Person p RIGHT JOIN Contact c ON c.personId = p
val q3 = quote {
query[Person].fullJoin(query[Contact]).on((p, c) => c.personId == p)
}
db.run(q3)
// SELECT p.id, p.name, p.age, c.personId, c.phone
// FROM Person p FULL JOIN Contact c ON c.personId = pDatabase actions are defined using quotations as well. These actions don't have a collection-like API but rather a custom DSL to express inserts, deletes and updates.
insert
val a = quote {
(personId: Int, phone: String) =>
query[Contact].insert(_.personId -> personId, _.phone -> phone)
}
db.run(a).using(List((999, "+1510488988")))
// INSERT INTO Contact (personId,phone) VALUES (?, ?)Note: Actions receive a List of tuples as they are batched by default.
update
val a = quote {
(id: Int, age: Int) =>
query[Person].filter(p => p.id == id).update(_.age -> age)
}
db.run(a).using(List((999, 18)))
// UPDATE Person SET age = ? WHERE id = ?delete
val a = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.name == "").delete
}
db.run(a)
// DELETE FROM Person WHERE name = ''Quill's default operation mode is compile-time, but there are queries that have their structure defined only at runtime. Quill automatically falls back to runtime normalization and query generation if the query's structure is not static. Example:
sealed trait QueryType
case object Minor extends QueryType
case object Senior extends QueryType
def people(t: QueryType): Quoted[Query[Person]] =
t match {
case Minor => quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.age < 18)
}
case Senior => quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.age > 65)
}
}
db.run(people(Minor))
// SELECT p.id, p.name, p.age FROM Person p WHERE p.age < 18
db.run(people(Senior))
// SELECT p.id, p.name, p.age FROM Person p WHERE p.age > 65Infix is a very flexible mechanism to use non-supported features without having to use plain SQL queries. It allows insertion of arbitrary SQL strings within quotations.
For instance, quill doesn't support the FOR UPDATE SQL feature. It can still be used through infix:
val forUpdate = quote {
new {
def apply[T](q: Query[T]) = infix"$q FOR UPDATE".as[Query[T]]
}
}
val a = quote {
query[Person].filter(p => p.age < 18)
}
db.run(forUpdate(a))
// SELECT p.id, p.name, p.age FROM (SELECT * FROM Person p WHERE p.age < 18 FOR UPDATE) pThe forUpdate quotation can be reused for multiple queries.
The same approach can be used for RETURNING ID:
val returningId = quote {
new {
def apply[T](a: Action[T]) = infix"$a RETURNING ID".as[Action[T]]
}
}
val a = quote {
query[Person].insert(_.name -> "John", _.age -> 21)
}
db.run(returningId(a))
// INSERT INTO Person (name,age) VALUES ('John', 21) RETURNING IDA custom database function can also be used through infix:
val myFunction = quote {
(i: Int) => infix"MY_FUNCTION($i)".as[Int]
}
val q = quote {
query[Person].map(p => myFunction(p.age))
}
db.run(q)
// SELECT MY_FUNCTION(p.age) FROM Person pQuill uses Encoders to encode runtime values defined with the using method and Decoders to parse the query return value. The library has some encoders and decoders built-in and it is possible to provide new ones.
If the correspondent database type is already supported, use mappedEncoding:
case class CustomValue(i: Int)
implicit val decodeCustomValue = mappedEncoding[CustomValue, Int](_.i)
implicit val encodeCustomValue = mappedEncoding[Int, CustomValue](CustomValue(_))If the database type is not supported, it is possible to provide "raw" encoders and decoders:
import io.getquill.source.mirror.Row
implicit val customValueEncoder =
new db.Encoder[CustomValue] {
def apply(index: Int, value: CustomValue, row: Row) =
??? // database-specific implementation
}
implicit val customValueDecoder =
new db.Decoder[CustomValue] {
def apply(index: Int, row: Row) =
??? // database-specific implementation
}Sources represent the database and provide an execution interface for queries. Example:
import io.getquill.naming.SnakeCase
import io.getquill.source.jdbc.JdbcSource
import io.getquill.source.sql.idiom.MySQLDialect
object db extends JdbcSource[MySQLDialect, SnakeCase]The SQL dialect to be used by the source is defined by the first type parameter. Some source types are specific to a database and thus not require it.
Quill has two built-in dialects:
io.getquill.source.sql.idiom.MySQLDialectio.getquill.source.sql.idiom.PostgresDialect
The second type parameter defines the naming strategy to be used when translating identifiers (table and column names) to SQL.
| strategy | example |
|---|---|
io.getquill.naming.Literal |
some_ident -> some_ident |
io.getquill.naming.Escape |
some_ident -> "some_ident" |
io.getquill.naming.UpperCase |
some_ident -> SOME_IDENT |
io.getquill.naming.LowerCase |
SOME_IDENT -> some_ident |
io.getquill.naming.SnakeCase |
someIdent -> some_ident |
io.getquill.naming.CamelCase |
some_ident -> someIdent |
Multiple transformations can be defined using mixin. For instance, the naming strategy
SnakeCase with UpperCase
produces this transformation:
someIdent -> SOME_IDENT
The transformations are applied from left to right.
Sources must be defined as object and the object name is used as the key to obtain configurations using the typesafe config library.
MySQL
sbt dependencies
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
"mysql" % "mysql-connector-java" % "5.1.36",
"io.getquill" %% "quill-jdbc" % "0.1.0"
)
source definition
import io.getquill.naming.SnakeCase
import io.getquill.source.jdbc.JdbcSource
import io.getquill.source.sql.idiom.MySQLDialect
object db extends JdbcSource[MySQLDialect, SnakeCase]application.properties
db.dataSourceClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource
db.dataSource.url=jdbc:mysql://host/database
db.dataSource.user=root
db.dataSource.password=root
db.dataSource.cachePrepStmts=true
db.dataSource.prepStmtCacheSize=250
db.dataSource.prepStmtCacheSqlLimit=2048
Postgres
sbt dependencies
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
"org.postgresql" % "postgresql" % "9.4-1206-jdbc41",
"io.getquill" %% "quill-jdbc" % "0.1.0"
)
source definition
import io.getquill.naming.SnakeCase
import io.getquill.source.jdbc.JdbcSource
import io.getquill.source.sql.idiom.PostgresDialect
object db extends JdbcSource[PostgresDialect, SnakeCase]application.properties
db.dataSourceClassName=org.postgresql.ds.PGSimpleDataSource
db.dataSource.user=root
db.dataSource.password=root
db.dataSource.databaseName=database
db.dataSource.portNumber=5432
db.dataSource.serverName=host
Please refer to HikariCP's documentation for a detailed explanation of the available configurations.
MySQL Async
sbt dependencies
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
"io.getquill" %% "quill-async" % "0.1.0"
)
source definition
import io.getquill.naming.SnakeCase
import io.getquill.source.async.mysql.MysqlAsyncSource
object db extends MysqlAsyncSource[SnakeCase]application.properties
db.host=host
db.port=3306
db.user=root
db.password=root
db.database=database
db.poolMaxQueueSize=4
db.poolMaxObjects=4
db.poolMaxIdle=999999999
db.poolValidationInterval=100
Postgres Async
sbt dependencies
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
"io.getquill" %% "quill-async" % "0.1.0"
)
source definition
import io.getquill.naming.SnakeCase
import io.getquill.source.async.postgres.PostgresAsyncSource
object db extends PostgresAsyncSource[SnakeCase]application.properties
db.host=host
db.port=5432
db.user=root
db.password=root
db.database=database
db.poolMaxQueueSize=4
db.poolMaxObjects=4
db.poolMaxIdle=999999999
db.poolValidationInterval=100
sbt dependencies
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
"io.getquill" %% "quill-finagle-mysql" % "0.1.0"
)
source definition
import io.getquill.naming.SnakeCase
import io.getquill.source.finagle.mysql.FinagleMysqlSource
object db extends FinagleMysqlSource[SnakeCase]application.properties
testDB.dest=localhost:3306
testDB.user=root
testDB.password=root
testDB.database=database
Please refer to SLICK.md for a detailed comparison between Quill and Slick.
The project was created having Philip Wadler's talk "A practical theory of language-integrated query" as its initial inspiration. The development was heavily influenced by the following papers:
- A Practical Theory of Language-Integrated Query
- Everything old is new again: Quoted Domain Specific Languages
- The Flatter, the Better
See the LICENSE file for details.