Kubernetes Service Mesh with Istio and CICD using Jenkins
Environment:
- CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804 (Core) minimal installation
- 1 master node (4vCpu, 4Gb RAM, 20GB Disk, Nat or Wan or Bridge Network)
- 1 Worker Node or More (2vCpu, 2Gb RAM, 20GB Disk, Nat or Wan or Bridge Network)
see install.sh for detail
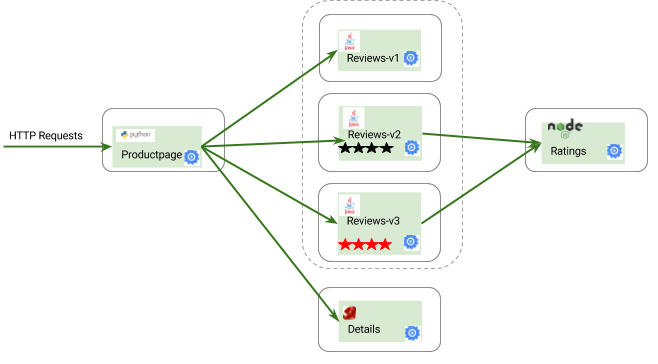
This example deploys a sample application composed of four separate microservices used to demonstrate various Istio features. The application displays information about a book, similar to a single catalog entry of an online book store. Displayed on the page is a description of the book, book details (ISBN, number of pages, and so on), and a few book reviews.
The Bookinfo application is broken into four separate microservices:
- productpage. The productpage microservice calls the details and reviews microservices to populate the page.
- details. The details microservice contains book information.
- reviews. The reviews microservice contains book reviews. It also calls the ratings microservice.
- ratings. The ratings microservice contains book ranking information that accompanies a book review. https://istio.io/docs/examples/bookinfo/
The BookInfo sample application deployed is composed of four microservices:
-
The productpage microservice is the homepage, populated using the details and reviews microservices.
-
The details microservice contains the book information.
-
The reviews microservice contains the book reviews. It uses the ratings microservice for the star rating.
-
The ratings microservice contains the book rating for a book review.
-
The deployment included three versions of the reviews microservice to showcase different behaviour and routing:
-
Version v1 doesn’t call the ratings service.
-
Version v2 calls the ratings service and displays each rating as 1 to 5 black stars.
-
Version v3 calls the ratings service and displays each rating as 1 to 5 red stars.
-
The services communicate over HTTP using DNS for service discovery. An overview of the architecture is shown below.
Istio intro
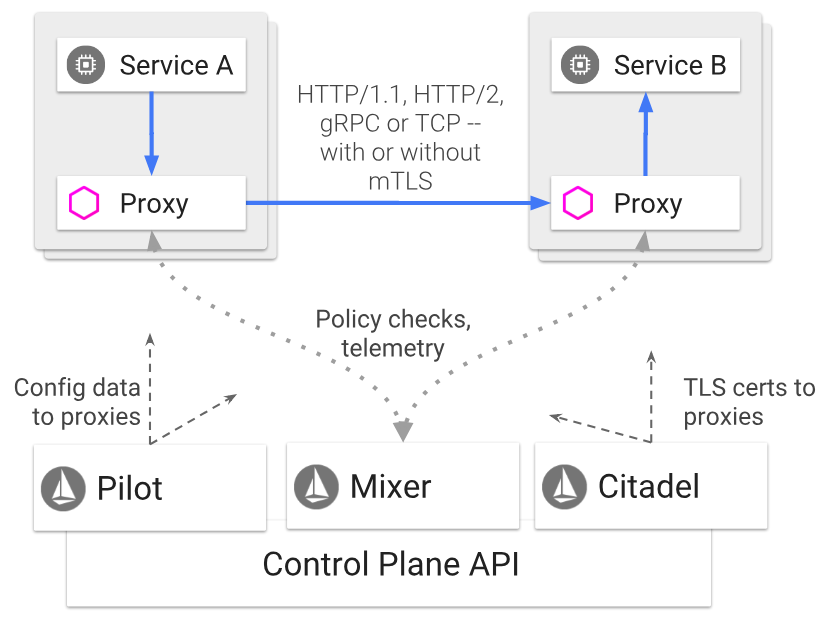
The previous step deployed the Istio Pilot, Mixer, Ingress-Controller, and Egress-Controller, and the Istio CA (Certificate Authority).
- Pilot - Responsible for configuring the Envoy and Mixer at runtime.
- Proxy / Envoy - Sidecar proxies per microservice to handle ingress/egress traffic between services in the cluster and from a service to external services. The proxies form a secure microservice mesh providing a rich set of functions like discovery, rich layer-7 routing, circuit breakers, policy enforcement and telemetry recording/reporting functions.
- Mixer - Create a portability layer on top of infrastructure backends. Enforce policies such as ACLs, rate limits, quotas, authentication, request tracing and telemetry collection at an infrastructure level.
- Citadel / Istio CA - Secures service to service communication over TLS. Providing a key management system to automate key and certificate generation, distribution, rotation, and revocation.
- Ingress/Egress - Configure path based routing for inbound and outbound external traffic.
- Control Plane API - Underlying Orchestrator such as Kubernetes or Hashicorp Nomad.
The overall architecture is shown below.
# LAB-LAB_LAB~LAB
####################################################################################################################
# Get Started with Istio and Kubernetes
# In this scenario, you will learn how to deploy Istio Service Mesh to Kubernetes.
# Istio is an open platform that provides a uniform way to connect, manage, and secure microservices.
# Istio supports managing traffic flows between microservices, enforcing access policies, and aggregating telemetry-
# data, all without requiring changes to the microservice code
# The scenario uses the sample BookInfo application. The application has no dependencies on Istio and demonstrates-
# how any application could build upon Istio without modifications.
####################################################################################################################
####################################################################################################################
# Traffic Shaping Microservices Connections
# In this scenario you will learn how to use Istio to control and manage traffic within your infrastructure.
# You will learn how to use the following Istio objects:
#* Ingress and Gateway
#* Virtual Service
#* Destination Rule
#* Egress and Service Entry
####################################################################################################################
####################################################################################################################
# Deploying Canary Releases
# In this scenario, you will learn how to take apply Traffic Shaping techniques discussed in the previous scenario.
# By apply Traffic Management, you will be able to control who can access versions of your application making it-
# possible to perform canary releases with Istio and Kubernetes.
# "Canary release is a technique to reduce the risk of introducing a new software version in production by slowly-
# rolling out the change to a small subset of users before rolling it out to the entire infrastructure and making-
# it available to everybody." Martin Flower
####################################################################################################################
####################################################################################################################
# Simulating Failures Between Microservices
# Distributed systems are difficult to test. It can be time-consuming to reproduce the errors and situations when
# it's deep within the system. Based on the traffic management capabilities, it's possible for Istio to inject faults -
# and simulate application errors or timeouts.
# In this scenario, you will learn how to cause delays or failures for certain sections of the traffic to allow you to -
# test how the rest of the system handles problems.
# Based on https://istio.io/docs/tasks/traffic-management/fault-injection/
####################################################################################################################
####################################################################################################################
# Handling Timeouts Between Microservices
# In this scenario, you will learn how Istio can help you gracefully handle timeouts.
# Systems can cause timeouts for a number of reasons, sometimes this can cause 30-60 second delays in responses.
# As a result, the workload is queued and has knock-on effects for the rest of the application.
# By implementing a timeout, services will always return within a known time, either as a success or an error.
# Based on https://istio.io/docs/tasks/traffic-management/request-timeouts/
####################################################################################################################
####################################################################################################################
# Handling Failures With Circuit Breakers
# In this scenario, you will learn how to use Circuit Breakers within Envoy Proxy to cause applications
# to fail quick based on certain metrics within the system, such as active HTTP connections.
# Circuit breaking is a critical component of distributed systems.
# It’s nearly always better to fail quickly and apply back pressure downstream as soon as possible." Envoy Proxy
# Based on https://istio.io/docs/tasks/traffic-management/circuit-breaking/
####################################################################################################################
####################################################################################################################
# Identifying Slow Services with Distributed Tracing
# In this scenario you will learn how to use OpenTracing, Jaeger and Istio to identify slow Microservices.
####################################################################################################################
####################################################################################################################
# Graphing System Metrics with Prometheus and Grafana
# In this scenario, you will learn how to use Istio to create graphs showing live real-time system metrics and connections.
# Istio has many built-in dashboards that show how the system is performing. The scenario will discuss what's -
# available and what to look for within each scenario.
####################################################################################################################
####################################################################################################################
# Istio - Visualising Microservices Dependencies with Scope
# In this scenario, you will learn how you can use Weave Scope to identify the-
# dependencies and application connections within your deployment.
####################################################################################################################