MSPredGO: An Ensemble Learning Approach Fusing Multi-Source Features for Protein Function Prediction
Proteins are fundamental components of living organisms and play a vital role in various fields such as drug development and disease research. With the exponential growth of protein sequences, manual annotation can no longer meet the needs of current research. Several deep learning prediction methods have been developed to improve the efficiency of protein labeling. Nevertheless, a single data source to obtain functional properties has limi-tations and cannot meet the demand for accurate classification. To solve this issue, we present an ensemble learning method that fuses features of protein sequences, domains, and protein-protein interactions (PPIs), namely MSPredGO. MSPredGO acquires biological features through protein lan-guage modeling (PLM) and other methods, while designing feature extrac-tors with different attention mechanisms to capture deep protein features respectively. Finally, the three features are integrated by weighting and used to complement the missing biological features of a single data. The Fmax of BP, MF and CC are 56.3%, 69.9% and 62% in human dataset and 50.5%, 69.4% and 57.8% in yeast dataset, which are better than other methods.
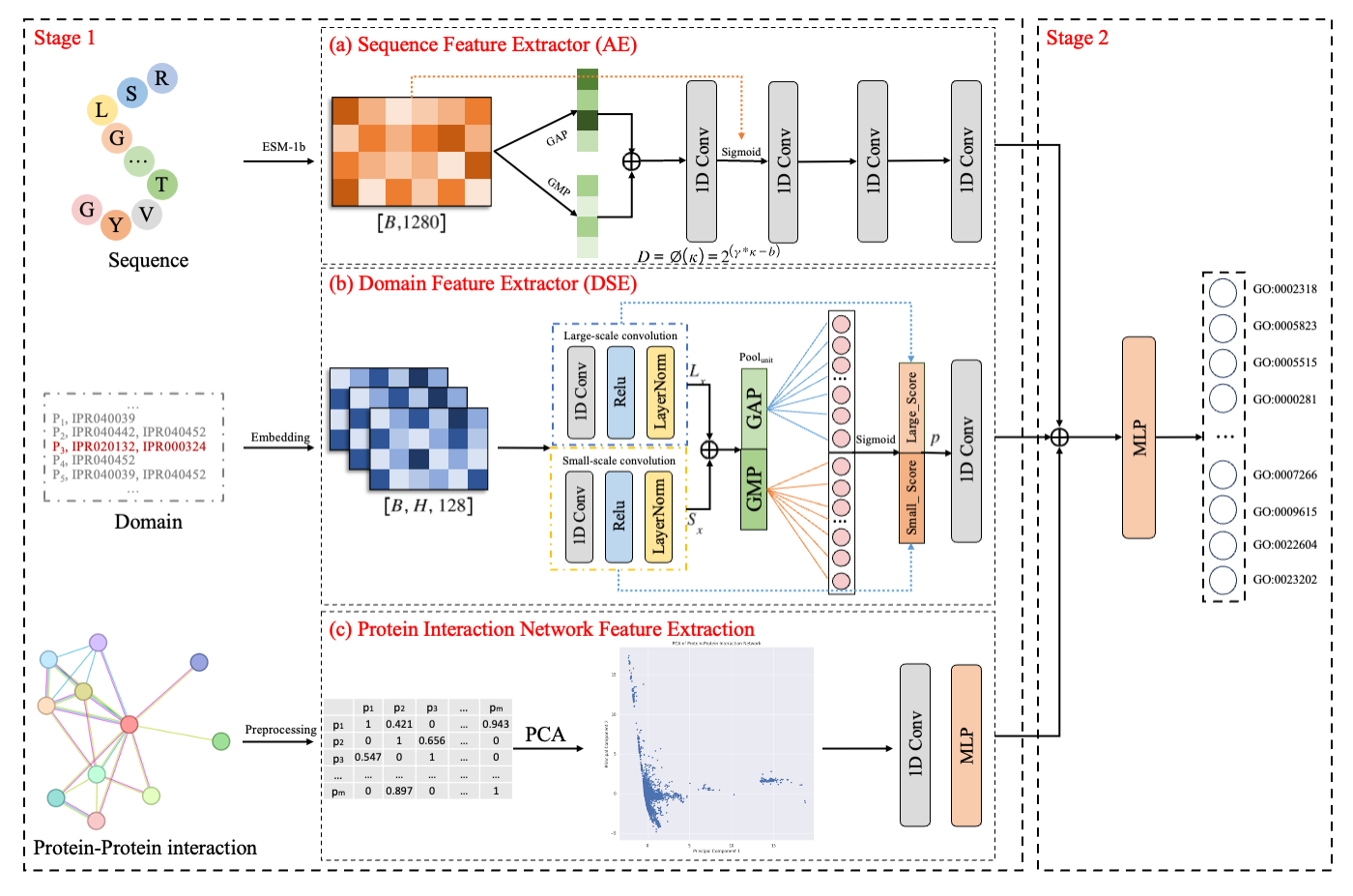
AE obtains overall sequence features by compression units and finer local features of sequences by adaptive convolution, a process that improves the performance of predicting protein functions using only sequences.
An important advantage of the DSE is that the overall attributes of the compressed sequences are taken into account and different local features are obtained through different sizes of receptive fields, thus going beyond homology-based functional prediction.
pytorch==1.12
numpy==1.24.3
tokenizers==0.15
transformers==4.36.2
scikit-learn==1.3.2
python==3.8
pandas==2.0.3
If you want to fully set up the environment, use the following script command:
pip install mspredgo.txt