State Switch is a Monitor/Guard for Managing Your Async Operations.
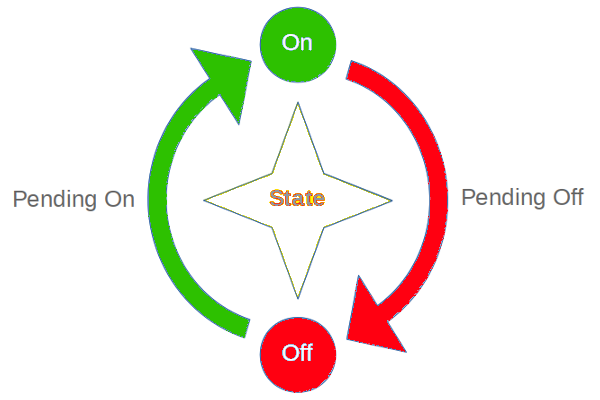
StateSwitch can manage state transition for you, by switching from the following four states:
INACTIVE: state is inactivepending ACTIVE: state is switching from INACTIVE to ACTIVEACTIVE: state is activepending INACTIVE: state is switch from ACTIVE to INACTIVE
You can set/get the state with the API, and you can also monite the state switch events by listening the 'active' and 'inactive' events.
There have another stable() API return a Promise so that you can wait the active of inactive events by:
await state.stable('active')
await state.stable('inactive')
await state.stable() // wait the current stateIf the state is already ACTIVE when you await state.stable('active'), then it will resolved immediatelly.
Talk is cheap, show me the code!
import { StateSwitch } from 'state-switch'
function doSlowConnect() {
console.log('> doSlowConnect() started')
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('> doSlowConnect() done')
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
}
function doSlowDisconnect() {
console.log('> doSlowDisconnect() started')
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('> doSlowDisconnect() done')
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
}
class MyConnection {
private state = new StateSwitch('MyConnection')
constructor() {
/* */
}
public connect() {
/**
* This is the only 1 Right State
*/
if (this.state.inactive() === true) {
this.state.active('pending')
doSlowConnect().then(() => {
this.state.active(true)
console.log(`> I'm now opened`)
})
console.log(`> I'm opening`)
return
}
/**
* These are the other 3 Error States
*/
if (this.state.inactive() === 'pending') {
console.error(`> I'm closing, please wait`)
} else if (this.state.active() === true) {
console.error(`> I'm already open. no need to connect again`)
} else if (this.state.active() === 'pending') {
console.error(`> I'm opening, please wait`)
}
}
public disconnect() {
/**
* This is the only one Right State
*/
if (this.state.active() === true) {
this.state.inactive('pending')
doSlowDisconnect().then(() => {
this.state.inactive(true)
console.log(`> I'm closed.`)
})
console.log(`> I'm closing`)
return
}
/**
* These are the other 3 Error States
*/
if (this.state.active() === 'pending') {
console.error(`> I'm opening, please wait`)
} else if (this.state.inactive() === true) {
console.error(`> I'm already close. no need to disconnect again`)
} else if (this.state.inactive() === 'pending') {
console.error(`> I'm closing, please wait`)
}
}
}
const conn = new MyConnection()
console.log('CALL: conn.connect(): should start to opening')
conn.connect()
console.log('CALL: conn.connect(): should not connect again while opening')
conn.connect()
console.log('CALL: conn.disconnect(): can not disconnect while opening')
conn.disconnect()
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('... 2 seconds later, should be already open ...')
console.log('CALL: conn.connect(): should not connect again if we are open')
conn.connect()
console.log('CALL: conn.disconnect(): should start to closing')
conn.disconnect()
console.log('CALL: conn.disconnect(): should not disconnect again while we are closing')
conn.disconnect()
console.log('CALL: conn.connect(): can not do connect while we are closing')
conn.connect()
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('... 2 seconds later, should be already closed ...')
console.log('CALL: conn.disconnect(): should not disconnect again if we are close')
conn.disconnect()
}, 2000)
}, 2000)What's the meaning of the above code?
StateSwitch helps you manage the following four states easy:
$ npm run demo
> [email protected] demo /home/zixia/git/state-switch
> ts-node example/demo
CALL: conn.connect(): should start to opening
> doSlowConnect() started
> I'm opening
CALL: conn.connect(): should not connect again while opening
> I'm opening, please wait
CALL: conn.disconnect(): can not disconnect while opening
> I'm opening, please wait
> doSlowConnect() done
> I'm now opened
... 2 seconds later, should be already open ...
CALL: conn.connect(): should not connect again if we are open
> I'm already open. no need to connect again
CALL: conn.disconnect(): should start to closing
> doSlowDisconnect() started
> I'm closing
CALL: conn.disconnect(): should not disconnect again while we are closing
> I'm closing, please wait
CALL: conn.connect(): can not do connect while we are closing
> I'm closing, please wait
> doSlowDisconnect() done
> I'm closed.
... 2 seconds later, should be already closed ...
CALL: conn.disconnect(): should not disconnect again if we are close
> I'm already close. no need to disconnect again
That's the idea: we should always be able to know the state of our async operation.
Class StateSwitch
Create a new StateSwitch instance.
private state = new StateSwitch('MyConn')Get the state for ACTIVE: true for ACTIVE(stable), pending for ACTIVE(in-process). false for not ACTIVE.
Set the state for ACTIVE: true for ACTIVE(stable), pending for ACTIVE(in-process).
Get the state for INACTIVE: true for INACTIVE(stable), pending for INACTIVE(in-process). false for not INACTIVE.
Set the state for INACTIVE: true for INACTIVE(stable), pending for INACTIVE(in-process).
Check if the state is pending.
true means there's some async operations we need to wait.
false means no async active fly.
expectedState:'active' | 'inactive', default is the current statenoCross:boolean, default isfalse
Wait the expected state to be stable.
If set noCross to true, then stable() will throw if you are wait a state from it's opposite site, for example: you can expect an Exception be thrown out when you call stable('active', true) when the inactive() === true.
Get the name from the constructor.
Enable log by set log to a Npmlog compatible instance.
Personaly I use Brolog, which is writen by my self, the same API with Npmlog but can also run inside Browser with Angular supported.
const log = Brolog.instance()
StateSwitch.setLog(log)Set a true/false state.
const indicator = new BooleanIndicator()- set
trueorfalse - get
booleanstatus
indicator.value(true)
indicator.value(false)
const value = indicator.value()Return a Promise that will resolved after the boolean state to be the value passed through v.
If the current boolean state is the same as the
v, then it will return aPromisethat will resolved immediately.
await indicator.ready(false)
assert (indicator.value() === false, 'value() should be false after await ready(false)')interface ServiceCtlInterface {
state: StateSwitchInterface
reset : ServiceCtl['reset']
start : ServiceCtl['start']
stop : ServiceCtl['stop']
}Use a Finite State Machine (FSM) to manage the state of your service.
import { ServiceCtlFsm } from 'state-switch'
class MyService extends ServiceCtlFsm {
async onStart (): Promise<void> {
// your start code
}
async onStop (): Promise<void> {
// your stop code
}
}
const service = new MyService()
await service.start() // this will call `onStart()`
await service.stop() // this will call `onStop()`
await service.start()
await service.reset() // this will call `onStop()` then `onStart()`Learn more about the finite state machine design pattern inside our ServiceCtl:
Implementes the same ServiceCtlInterface, but using a StateSwitch to manage the internal state.
The code is originally from Wechaty Puppet, then abstracted to a class.
- Add
BooleanIndicatorclass to replace and deprecate theBusyIndicatorclass for a more powerful and easy to use API.
StateSwitch#pending->StateSwitch#pending()StateSwitch#on()->StateSwitch#active()StateSwitch#off()->StateSwitch#inactive()emit('on')->emit('active')emit('off')->emit('inactive')
TL;DR:
- state.on()
+ state.active()
- state.on(true)
+ state.active(true)
- state.off()
+ state.inactive()
- state.off(true)
+ staet.inactive(true)
- state.pending
+ state.pending()- Oct 27: Add
ServiceCtl/ServiceCtlFsmabstract class andserviceCtlMixin/serviceCtlFsmMixinmixin - Oct 23: Add
BusyIndicatorclass- Add
BusyIndicatorInterfaceandStateSwitchInterface
- Add
- v0.15 (Sep 2021): Publish as ESM package.
- Add RxJS typing unit tests for making sure that the
fromEventtyping inference is right.
Support for using RxJS:
const notPending = (state: true | 'pending') => state === true
const stateOn$ = fromEvent(stateSwitch, 'active').pipe(
filter(notPending)
)- Support emit
onandoffevents with the args of thestateof two values:trueandpending. - Add events unit tests
- DevOps for publishing to NPM@next for odd minor versions.
- Add State Diagram for easy understanding what state-switch do
BREAKING CHANGE: Change the ready() parameter to the opposite side.
- Before:
ready(state, crossWait=false) - AFTER:
ready(state, noCross=false)
- add new method
ready()to let user wait until the expected state is on(true).
BREAKING CHANGES: redesigned all APIs.
- delete all old APIs.
- add 4 new APIs: on() / off() / pending() / name()
Rename to StateSwitch because the name StateMonitor on npmjs.com is taken.
- Make it a solo NPM Module. (#466)
Orignal name is StateMonitor
- Part of the Wechaty project
Huan LI [email protected] (http://linkedin.com/in/zixia)

- Code & Docs 2016-now© zixia
- Code released under the Apache-2.0 license
- Docs released under Creative Commons