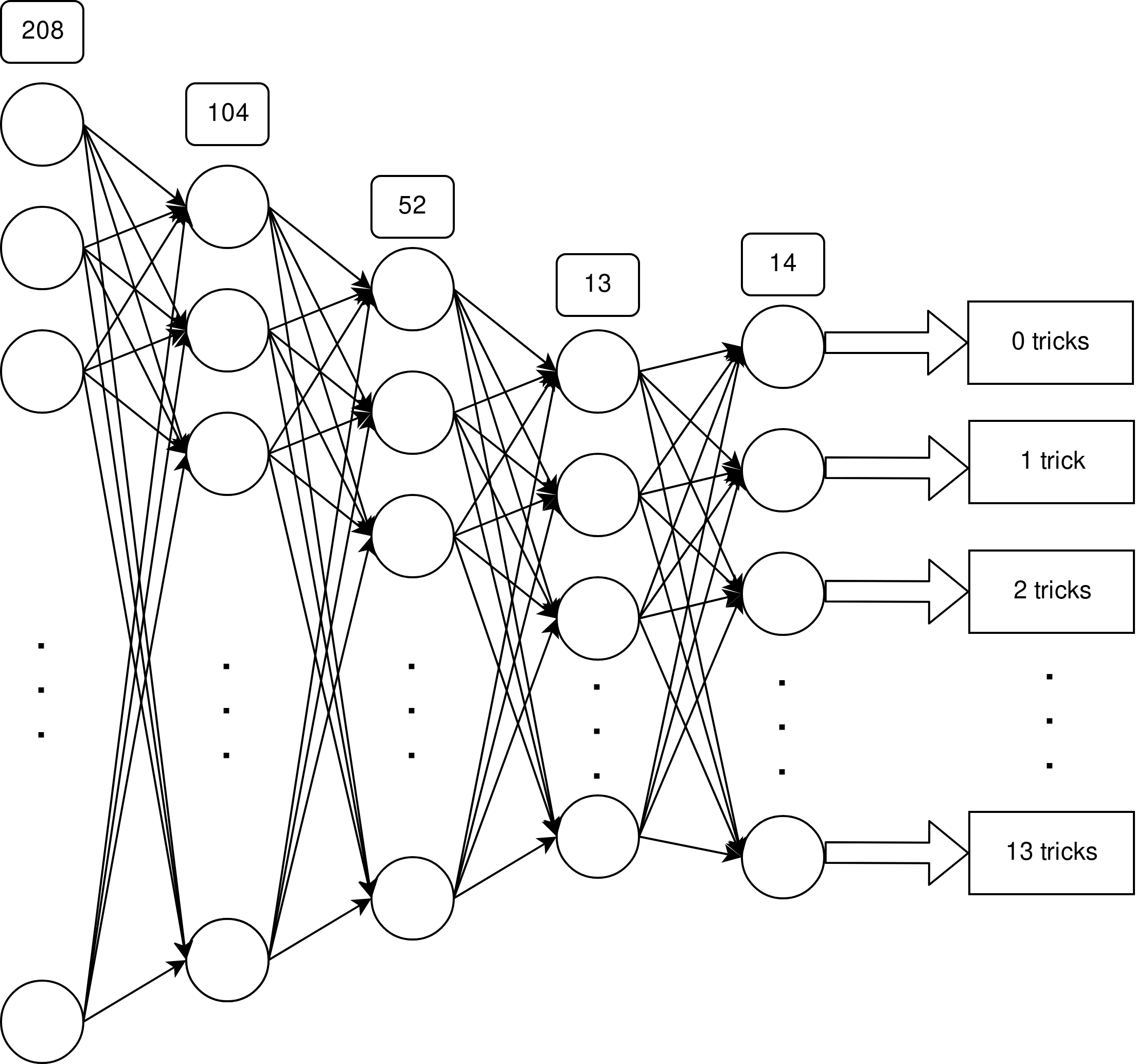
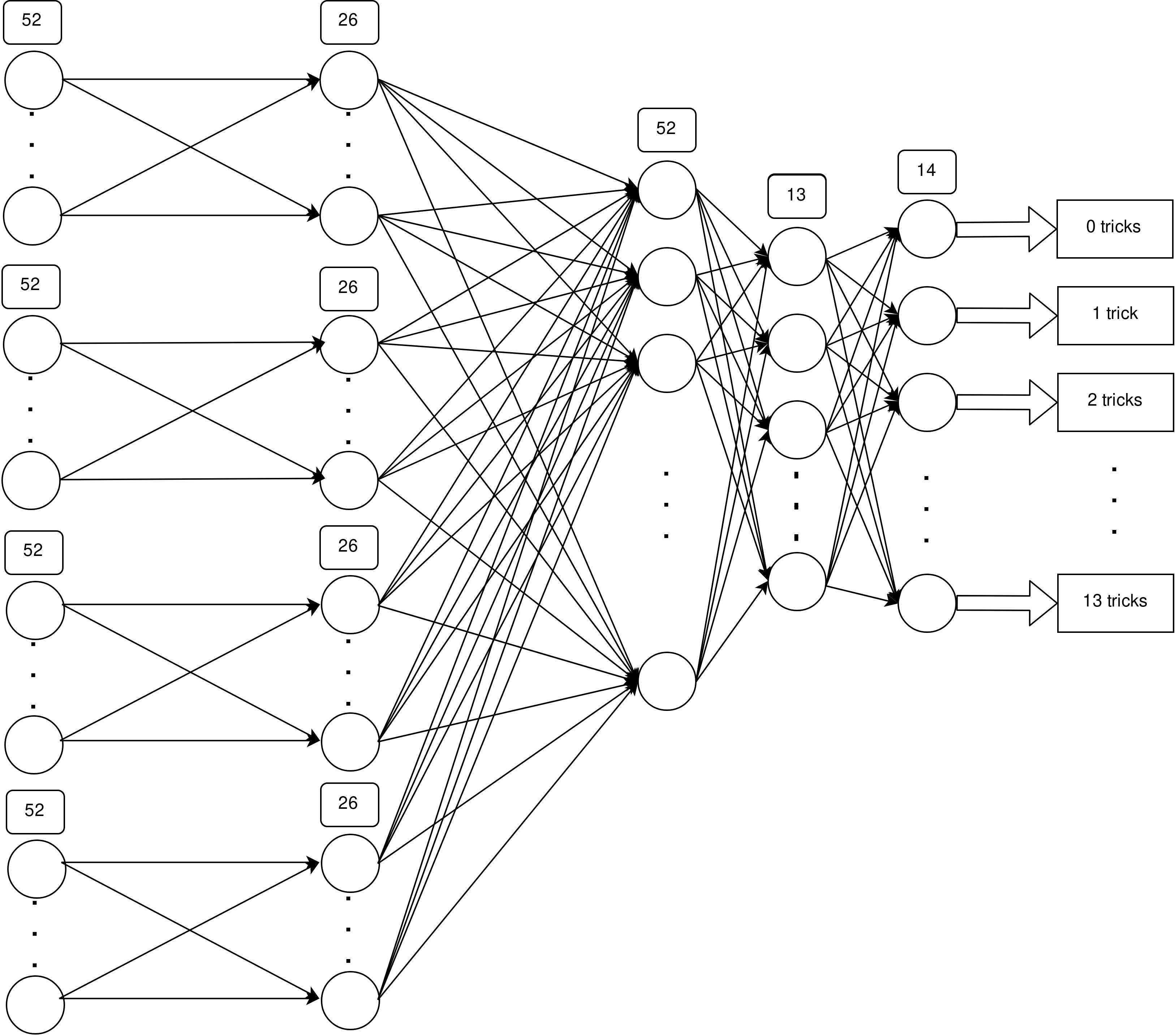
- comparison
This branch contains the code for an experiment with a simple autoencoder. - comparison_fixed
This branch is a further modification of comparision, during the fine tuning phase the weights in the already pretrained autoencoder are frozen and cannot be longer modified.
-
altered_comparison
This experiment is based on the approach described in [1], the network was modified accordingly to use the advantages of the dedicated connections described in the paper. -
altered_comparison_fixed
This branch contains a similar modification as branch comparison_fixed but based on the experiment altered_comparison, the pretrained weights in the encoding layer are no longer modified during the last phase.
In order to run an experiment please ensure you have TensorFlow installed. The version used during the project was TensorFlow 1.7. Then checkout the commit corresponding to the desired experiment:
$ git checkout hash
| Architecture | Neuron count | Fixed | Experiment type | Hash |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dedicated | 104 | No | No trump | 511533f6bfec023990a9ce195092489eb2107a64 |
| dedicated | 104 | No | Trump | a011ead0e055c032ec72c1872cd4885fc818c71e |
| dedicated | 104 | Yes | No trump | 54c3de297e77c2afa8eb552fa2d623b09a0e5393 |
| dedicated | 104 | Yes | Trump | 47af6f0881c58e1c5f6b60f1ff3433638b7041b5 |
| dedicated | 156 | No | No trump | d17cd31b47c0e9283bfd31b9d06a9d22781a4506 |
| dedicated | 156 | No | Trump | 2de6cd452c07cc801a3aa44b7dd4e9786f055788 |
| dedicated | 156 | Yes | No trump | 8f668eba9c178b1f4afacf01a4b531711587f209 |
| dedicated | 156 | Yes | Trump | b9b545f2cf940ce63f35aa0cfad69278d4cc9808 |
| full | 104 | No | No trump | 8dc064ea6303057d53ceac12263376589c1d4f80 |
| full | 104 | No | Trump | 24f63e4dabe9359f2cd3956cbdc6a9321d54b8e3 |
| full | 104 | Yes | No Trump | 71d82d06a73a5d07d777284932fb3f43b9570795 |
| full | 104 | Yes | Trump | 22d3874cd5c48dbd360268d1d67957bb6f724486 |
| full | 156 | No | No trump | 83954aaa8ab0d4722465340c617103dacfb54da8 |
| full | 156 | No | Trump | 5cb485510f4e04bfc6bb3123a022bf5d2bfcb4bc |
| full | 156 | Yes | No trump | 74f897b469e7e0f7a8808cd365ca6476a51edae3 |
| full | 156 | Yes | Trump | 3b30f93a4f939df64c488214cbecbdae195af29d |
Then move to the directory DDBP/DDBP/run and execute the DDBP.py script
$ cd DDBP/DDBP/run
$ python3 DDBP.py
- Amit, A., Markovitch, S.: Learning to bid in bridge. Machine Learning 63(3), 287– 327 (Jun 2006), https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-006-6225-2
- Beling, P.: Partition search revisited. IEEE Transactions on Computational Intelligence and AI in Games 9(1), 76–87 (March 2017)
- David O.E., Netanyahu N.S., W.L.: DeepChess: End-to-End Deep Neural Network for Automatic Learning in Chess. Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning ICANN 2016 9887, 88–96 (2016)
- Dharmalingam, M., Amalraj, R.: Articifial neural network architecture for solving the double dummy bridge problem in contract bridge. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering Vol. 2, Issue 12, December 2013 2, 4683–4691 (2013)
- Dharmalingam, M., Amalraj, R.: A solution to the double dummy contract bridge problem influenced by supervised learning module adapted by artificial neural network. ICTACT Journal on Soft Computing 5, 836–843 (2014)
- Dharmalingam, M., Amalraj, R.: Supervised Elman Neural Network Architecture for Solving Double Dummy Bridge Problem in Contract Bridge. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR) 3, 2745–2750 (2014)
- Francis, H., Truscott, A., Francis, D. (eds.): The Official Encyclopedia of Bridge. American Contract Bridge League Inc, Memphis, TN, fifth edn. (1994)
- Ginsberg, M.L.: http://www.gibware.com
- Ginsberg, M.L.: Library of double-dummy results, http://www.cirl.uoregon. edu/ginsberg/gibresearch.html
- Ho, C.Y., Lin, H.T.: Contract bridge bidding by learning. In: AAAI Workshop: Computer Poker and Imperfect Information (2015)
- Man´dziuk, J., Mossakowski, K.: Example-based estimation of hand’s strength in the game of bridge with or without using explicit human knowledge. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Data Mining (CIDM 2007). pp. 413–420. IEEE Press, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA (2007)
- Man´dziuk, J., Mossakowski, K.: Neural networks compete with expert human players in solving the double dummy bridge problem. In: 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Games. pp. 117–124 (Sept 2009)
- Mossakowski, K., Man´dziuk, J.: Artificial neural networks for solving double dummy bridge problems. In: Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing - ICAISC 2004. LNAI, vol. 3070, pp. 915–921. Springer (2004)
- Mossakowski, K., Man´dziuk, J.: Neural networks and the estimation of hands strength in contract bridge. In: Rutkowski, L., et al. (eds.) Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing ICAISC 2006. Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, vol. 4029, pp. 1189–1198. Springer (2006)
- Mossakowski, K., Man´dziuk, J.: Learning Without Human Expertise: A Case Study of the Double Dummy Bridge Problem. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 20(2), 278–299 (2009)
- Muthusamy, D.: Double Dummy Bridge Problem in Contract Bridge: An Overview. Artificial Intelligence Systems and Machine Learning 10(1), 1–7 (2018)
- Ng, A., Ngiam, J., Foo, C.Y., Mai, Y., Suen, C.: Ufldl tutorial, http://ufldl. stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/UFLDL_Tutorial
- Yegnanarayana, B., Khemani, D., Sarkar, M.: Neural networks for contract bridge bidding. Sadhana 21(3), 395–413 (Jun 1996)