elastic.io iPaaS component to read and write to Google Spreadsheets Component Completeness Matrix
Before building any integration flow you must at first configure the app from inside the Google Developers Console.
- In order to do this you, go to the
API & Servicepage and enable the following:
- Google Drive API
- Google Sheets API
- Go to the
Credentialssection and create a new credential of typeOAuth client ID.
- Set Application type to
Web application - Add Authorized redirect URI as:
https://{your-tenant-address}/callback/oauth2
In case of new domain you may get message like This app isn't verified. Please refer to this doc to check how to proceed:
https://support.google.com/cloud/answer/7454865?hl=en
Here are the environment variables to configure for the component to connect with the Google API:
Following environment variables are required:
OAUTH_CLIENT_ID- oauth App IDOAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET- oauth App Secret
To get these please use the Google Developers Console. As a callback please use https://your-tenant.address/callback/oauth2.
Additional environment variables:
TENANT_DOMAIN- your Google API tenant domain. Defaults toapp.elastic.ioif not providedEIO_REQUIRED_RAM_MB- recommended value of allocated memory is512MB
Google Spreadsheet works with OAuth2 app configured at your Google Developer Console. To Authenticate the component you only need to press the button Authentication and the process would take you to Google to log-in and give permissions to the platform to access your Spreadsheets.
- Enter number of retries (Default: 5)
IMPORTANT!! Please note that Google applies quotas and limitations to their services. You can check the actual values here: https://developers.google.com/sheets/api/limits
In case an API call throws a quota limit exceeded exception (or any other exception, e.g. a connectivity problem, etc.), the component will retry the call based on Exponential backoff algorithm (factor = 2) number of times configured in this field. The default value is 5.
E.g. Setting this to 1 means do a normal call once, then if failed - retry it once.
Please note that you should carefully calculate and plan a strategy to handle an expected load to the component. Note also that Google's quota applies to credentials, not to a step in a flow. This means that if there is a default limit to 60 requests per minute per user per project and there is a component that makes exactly 60 requests per minute, adding a second component with the same user credentials would cause a quota exceeding. This is where careful calculating of number of retries and delay between calls is are very important.
- Max number of calls per second (Default: 5)
If you want to slow down requests to your API you can set a number of requests per second and the component will delay calling the next request after the previous request (1 / number of requests per second * 1000 ms ).
The calculated delay value can not be more than 1140 seconds (19 minutes due to platform limitations).
Note: if result quota restriction will be less than 1 request/min the component Retrieve Sample task won't succeed
Note: If you don't set a value to either Enter number of retries or Max number of calls per second fields, they will remain empty. The component will consider them as the default values (5 in both cases).
The New Spreadsheet Row trigger reads the data in each row of a given Google Spreadsheet and passes it to the next stage of your integration flow.
First, the system reads all the rows from a given Google Spreadsheet and processes it further along with your designed integration flow. It will also create an initial state of your spreadsheet, we call it a snapshot, in order to have something to compare with after your data is updated.
After the initial read, any further requests for an update will be compared to this
snapshot and in case any changes are detected they will be passed along with the integration
flow as well. If Select All Data configuration property has value Yes, the system will read all the rows from a given Google
Spreadsheet whenever flow processes the message.
| Input field | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spreadsheet | true | Spreadsheet which will be used for data reading | MyTestSpreadsheet |
| Worksheet | true | Worksheet of spreadsheet which will be used for data reading | Sheet1 |
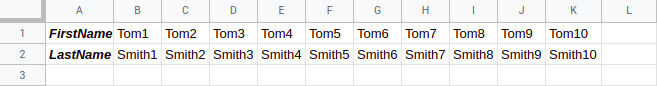
| Dimension | true | The major dimension of the values | ROWS, COLUMNS |
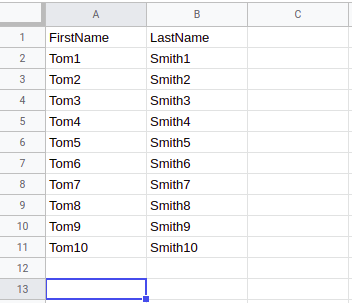
| Use first row/column as header | true | You should specify Yes if your data has a header in the first row/column and you want to use these values as json key in the output message. If you specify No, json key will be taken from row/column index according to A1 notation. Se example below | Yes |
| Select All Data | true | You should specify Yes if you want to fetch all spreadsheet data whenever step starts. If you specify No, a step will be emitting only delta changes (lines which were added after last step runs) | No |
IMPORTANT: Using Use first row/column as header feature, you must be sure that header values are unique.
Values from spreadsheets return as 'UNFORMATTED_VALUE' type
After a trigger execution, data will be extracted from the table above and the following message will be emitted:
{
"FirstName": "Tom1",
"LastName": "Smith1"
}
{
"FirstName": "Tom2",
"LastName": "Smith2"
}
-----------------------
{
"FirstName": "Tom10",
"LastName": "Smith10"
} {
"A": "FirstName",
"B": "LastName"
}
{
"A": "Tom1",
"B": "Smith1"
}
{
"A": "Tom2",
"B": "Smith2"
}
---------------------
{
"A": "Tom10",
"B": "Smith10"
}After a trigger execution, data will be extracted from the table above and the following message will be emitted:
{
"FirstName": "Tom1",
"LastName": "Smith1"
}
{
"FirstName": "Tom2",
"LastName": "Smith2"
}
-----------------------
{
"FirstName": "Tom10",
"LastName": "Smith10"
} {
"1": "FirstName",
"2": "LastName"
}
{
"1": "Tom1",
"2": "Smith1"
}
{
"1": "Tom2",
"2": "Smith2"
}
---------------------
{
"1": "Tom10",
"2": "Smith10"
}Trigger can emit maximum 1000 messages per one execution.
Trigger uses version 4 of Google Sheet API. You can find more information in the Google Sheets API Documentation.
Action to create a new Google spreadsheet. This action is based on Google Spreadsheets API v4. The action needs a JSON instance of a Spreadsheet object in order to create a new spreadsheet. All data structures and limitations are the same to Google API.
| Schema type | Json schema location |
|---|---|
| Input | /schemas/createSpreadsheet.in.json |
| Output | /schemas/createSpreadsheet.out.json |
Action to create a new Google spreadsheet row. This action based on Google Spreadsheets API v4. Adds an array of given values to a spreadsheet as a new row. Data would be inserted in the same order as provided in the input array. Data will be inserted into the last empty line, starting from the first table column. A datatype of inserted values will be the same as for JSON type (string, numeric or boolean). Use "" value to make cell empty.
- Spreadsheet - Spreadsheet name to make changes.
- Worksheet - Worksheet name of selected Spreadsheet to make changes.
- Input Mode - Options: First Row As Headers, Array Based. Default is First Row As Headers
- First Row As Headers (Default): generates input metadata based on values in first row cells.
This method has few limitations:
- There should be at least one value in first row;
- Values in first row cells must be distinct;
- There should be no empty cells in first row;
- Array Based: generates input for array of
values. Array mapped tovaluesis going to be inserted as first row. schema
- First Row As Headers (Default): generates input metadata based on values in first row cells.
This method has few limitations:
- Input Mode: "First Row As Headers" requires first row to have at least one cell with value. - check there are at least one non-empty cell in first row.
- Input Mode: "First Row As Headers" requires cells in first row to be not empty. - check there are no empty cells in between in first row.
- Input Mode: "First Row As Headers" requires cells in first row to be unique. - check values in first row are distinct.
| Schema type | Json schema location |
|---|---|
| Output | /schemas/createSpreadsheetRow.out.json |
Here are some general recommendations to help you avoid potentially confusing cases where you might get unexpected results while using Google Spreadsheets connector.
Depending on your Google Account settings your Google Drive and especially
Google Spreadsheets would have some specific default formatting applicable to
the Account Language/Country Setup in use. By default, Google will assume US
formatting which would mean not only the default currency is US Dollar ($) but
also, the date format will be of MM/DD/YYYY format, not DD/MM/YYYY
which is widely used in European and other countries.
Please note if the data you are planning to write has values in different language/country formatting than your Google Spreadsheets then you are most likely to encounter unexpected results.
Make sure to change it to the desired one in the Google Spreadsheets in advance
by selecting File > Spreadsheet Settings ... menu of your Spreadsheet.
Do NOT change the Spreadsheet structure while your flow is active
If you make structural changes to the Google Spreadsheet while it is being used it will cause a number of Errors and the flow will stop functioning properly.
Decide the structure of your spreadsheet file in advance and avoid making any structural changes during the integration. In particular, avoid adding or removing additional columns since you would need to repeat the flow design process to properly map or link your changes.
If you still wish to change the structure of your Google Spreadsheet then follow these steps:
- Stop the integration flow if it is running;
- Make your changes in the Google Spreadsheet;
- Go through the integration design stage again to ensure that all columns in the modified spreadsheet are properly linked with required fields or values necessary to run your integration flow.
- Activate the flow again.
Do NOT insert a row between the records while your flow is active
If you insert a new row between existing structure the system would fail to recognize it as an update. Instead, this will cause the system to lose the connection between the unique IDs and the records since our unique ID is the row number.
If you wish to insert a row between existing records then you must first stop the integration flow in your Dashboard and then proceed to make the changes in your Google Spreadsheets file. You can activate your flow after you made the necessary changes. However, we recommend not to insert a row between the records even if you have deactivated it.
New inserted row will cause an additional data transfer
Avoid inserting a row in between the records during the integration since it would look different for the system. This would trigger an additional data transfer since not only the newly inserted row will be regarded as a new record but everything after the inserted row would be considered a new data.
Apache-2.0 © elastic.io GmbH