-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 8.3k
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
[Security Solution] [Elastic AI Assistant] LangChain Agents and Tools integration for ES|QL query generation via ELSER #167097
[Security Solution] [Elastic AI Assistant] LangChain Agents and Tools integration for ES|QL query generation via ELSER #167097
Conversation
…ols integration for ES|QL query generation via ELSER This PR integrates [LangChain](https://www.langchain.com/) [Agents](https://js.langchain.com/docs/modules/agents/) and [Tools](https://js.langchain.com/docs/modules/agents/tools/) with the [Elastic AI Assistant](https://www.elastic.co/blog/introducing-elastic-ai-assistant). These abstractions enable the LLM to dynamically choose whether or not to query, via [ELSER](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/machine-learning/current/ml-nlp-elser.html), an [ES|QL](https://www.elastic.co/blog/elasticsearch-query-language-esql) knowledge base. Context from the knowledge base is used to generate `ES|QL` queries, or answer questions about `ES|QL`. Registration of the tool occurs in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.ts`: ```typescript const tools: Tool[] = [ new ChainTool({ name: 'esql-language-knowledge-base', description: 'Call this for knowledge on how to build an ESQL query, or answer questions about the ES|QL query language.', chain, }), ]; ``` The `tools` array above may be updated in future PRs to include, for example, an `ES|QL` query validator endpoint. ### Details The `callAgentExecutor` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.ts`: 1. Creates a `RetrievalQAChain` from an `ELSER` backed `ElasticsearchStore`, which serves as a knowledge base for `ES|QL`: ```typescript // ELSER backed ElasticsearchStore for Knowledge Base const esStore = new ElasticsearchStore(esClient, KNOWLEDGE_BASE_INDEX_PATTERN, logger); const chain = RetrievalQAChain.fromLLM(llm, esStore.asRetriever()); ``` 2. Registers the chain as a tool, which may be invoked by the LLM based on its description: ```typescript const tools: Tool[] = [ new ChainTool({ name: 'esql-language-knowledge-base', description: 'Call this for knowledge on how to build an ESQL query, or answer questions about the ES|QL query language.', chain, }), ]; ``` 3. Creates an Agent executor that combines the `tools` above, the `ActionsClientLlm` (an abstraction that calls `actionsClient.execute`), and memory of the previous messages in the conversation: ```typescript const executor = await initializeAgentExecutorWithOptions(tools, llm, { agentType: 'chat-conversational-react-description', memory, verbose: false, }); ``` Note: Set `verbose` above to `true` to for detailed debugging output from LangChain. 4. Calls the `executor`, kicking it off with `latestMessage`: ```typescript await executor.call({ input: latestMessage[0].content }); ``` ### Changes to `x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistant` A client side change was required to the assistant, because the response returned from the agent executor is JSON. This response is parsed on the client in `x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistant/impl/assistant/api.tsx`: ```typescript return assistantLangChain ? getFormattedMessageContent(result) : result; ``` Client-side parsing of the response only happens when then `assistantLangChain` feature flag is `true`. ## Desk testing Set ```typescript assistantLangChain={true} ``` in `x-pack/plugins/security_solution/public/assistant/provider.tsx` to enable this experimental feature in development environments. Also (optionally) set `verbose` to `true` in the following code in ``x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.ts``: ```typescript const executor = await initializeAgentExecutorWithOptions(tools, llm, { agentType: 'chat-conversational-react-description', memory, verbose: true, }); ``` After setting the feature flag and optionally enabling verbose debugging output, you may ask the assistant to generate an `ES|QL` query, per the example in the next section. ### Example output When the Elastic AI Assistant is asked: ``` From employees, I want to see the 5 earliest employees (hire_date), I want to display only the month and the year that they were hired in and their employee number (emp_no). Format the date as e.g. "September 2019". Only show the query ``` it replies: ``` Here is the query to get the employee number and the formatted hire date for the 5 earliest employees by hire_date: FROM employees | KEEP emp_no, hire_date | EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, "MMMM YYYY") | SORT hire_date | LIMIT 5 ``` Per the screenshot below: 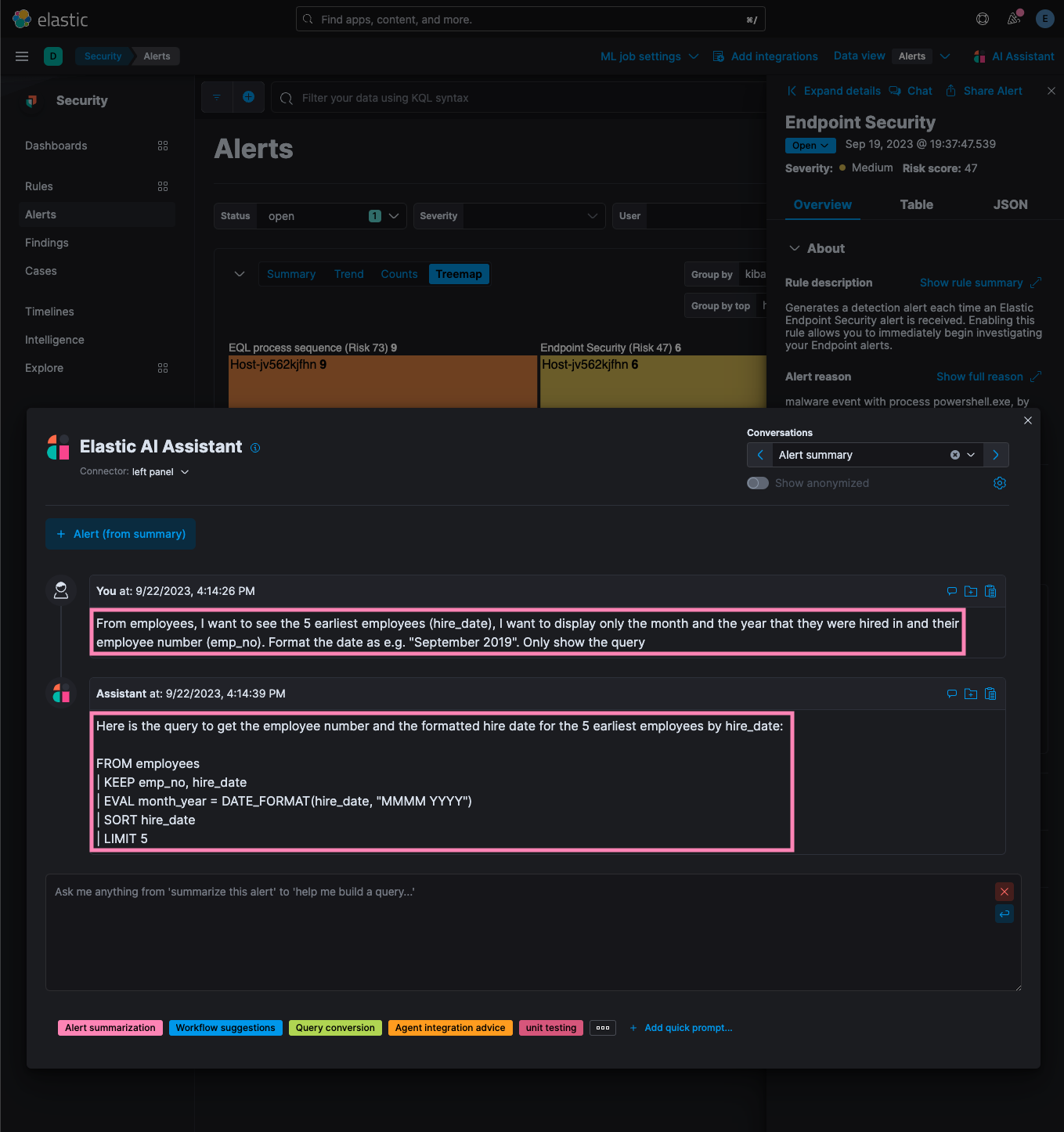 The `verbose: true` output from LangChain logged to the console reveals that the prompt sent to the LLM includes text like the following: ``` Assistant can ask the user to use tools to look up information that may be helpful in answering the users original question. The tools the human can use are:\\n\\nesql-language-knowledge-base: Call this for knowledge on how to build an ESQL query, or answer questions about the ES|QL query language. ``` along with instructions for "calling" the tool like a function. The debugging output also reveals the agent selecting the tool, and returning results from ESLR: ``` [agent/action] [1:chain:AgentExecutor] Agent selected action: { "tool": "esql-language-knowledge-base", "toolInput": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.", "log": "```json\n{\n \"action\": \"esql-language-knowledge-base\",\n \"action_input\": \"Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.\"\n}\n```" } [tool/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool] Entering Tool run with input: "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'." [chain/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain] Entering Chain run with input: { "query": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'." } [retriever/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 6:retriever:VectorStoreRetriever] Entering Retriever run with input: { "query": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'." } [retriever/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 6:retriever:VectorStoreRetriever] [115ms] Exiting Retriever run with output: { "documents": [ { "pageContent": "[[esql-date_format]]\n=== `DATE_FORMAT`\nReturns a string representation of a date in the provided format. If no format\nis specified, the `yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ` format is used.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| KEEP first_name, last_name, hire_date\n| EVAL hired = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"YYYY-MM-dd\")\n----\n", ``` The documents containing `ES|QL` examples, retrieved from ELSER, are sent back to the LLM to answer the original question, per the abridged output below: ``` [llm/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 7:chain:StuffDocumentsChain > 8:chain:LLMChain > 9:llm:ActionsClientLlm] Entering LLM run with input: { "prompts": [ "Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.\n\n[[esql-date_format]]\n=== `DATE_FORMAT`\nReturns a string representation of a date in the provided format. If no format\nis specified, the `yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ` format is used.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| KEEP first_name, last_name, hire_date\n| EVAL hired = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"YYYY-MM-dd\")\n----\n\n\n[[esql-date_trunc]]\n=== `DATE_TRUNC`\nRounds down a date to the closest interval. Intervals can be expressed using the\n<<esql-timespan-literals,timespan literal syntax>>.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| EVAL year_hired = DATE_TRUNC(1 year, hire_date)\n| STATS count(emp_no) BY year_hired\n| SORT year_hired\n----\n\n\n[[esql-from]]\n=== `FROM`\n\nThe `FROM` source command returns a table with up to 10,000 documents from a\ndata stream, index, ``` ### Complete (verbose) LangChain output from the example The following `verbose: true` output from LangChain below was produced via the example in the previous section: ``` [chain/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor] Entering Chain run with input: { "input": "\n\n\n\nFrom employees, I want to see the 5 earliest employees (hire_date), I want to display only the month and the year that they were hired in and their employee number (emp_no). Format the date as e.g. \"September 2019\". Only show the query", "chat_history": [] } [chain/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 2:chain:LLMChain] Entering Chain run with input: { "input": "\n\n\n\nFrom employees, I want to see the 5 earliest employees (hire_date), I want to display only the month and the year that they were hired in and their employee number (emp_no). Format the date as e.g. \"September 2019\". Only show the query", "chat_history": [], "agent_scratchpad": [], "stop": [ "Observation:" ] } [llm/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 2:chain:LLMChain > 3:llm:ActionsClientLlm] Entering LLM run with input: { "prompts": [ "[{\"lc\":1,\"type\":\"constructor\",\"id\":[\"langchain\",\"schema\",\"SystemMessage\"],\"kwargs\":{\"content\":\"Assistant is a large language model trained by OpenAI.\\n\\nAssistant is designed to be able to assist with a wide range of tasks, from answering simple questions to providing in-depth explanations and discussions on a wide range of topics. As a language model, Assistant is able to generate human-like text based on the input it receives, allowing it to engage in natural-sounding conversations and provide responses that are coherent and relevant to the topic at hand.\\n\\nAssistant is constantly learning and improving, and its capabilities are constantly evolving. It is able to process and understand large amounts of text, and can use this knowledge to provide accurate and informative responses to a wide range of questions. Additionally, Assistant is able to generate its own text based on the input it receives, allowing it to engage in discussions and provide explanations and descriptions on a wide range of topics.\\n\\nOverall, Assistant is a powerful system that can help with a wide range of tasks and provide valuable insights and information on a wide range of topics. Whether you need help with a specific question or just want to have a conversation about a particular topic, Assistant is here to assist. However, above all else, all responses must adhere to the format of RESPONSE FORMAT INSTRUCTIONS.\",\"additional_kwargs\":{}}},{\"lc\":1,\"type\":\"constructor\",\"id\":[\"langchain\",\"schema\",\"HumanMessage\"],\"kwargs\":{\"content\":\"TOOLS\\n------\\nAssistant can ask the user to use tools to look up information that may be helpful in answering the users original question. The tools the human can use are:\\n\\nesql-language-knowledge-base: Call this for knowledge on how to build an ESQL query, or answer questions about the ES|QL query language.\\n\\nRESPONSE FORMAT INSTRUCTIONS\\n----------------------------\\n\\nOutput a JSON markdown code snippet containing a valid JSON object in one of two formats:\\n\\n**Option 1:**\\nUse this if you want the human to use a tool.\\nMarkdown code snippet formatted in the following schema:\\n\\n```json\\n{\\n \\\"action\\\": string, // The action to take. Must be one of [esql-language-knowledge-base]\\n \\\"action_input\\\": string // The input to the action. May be a stringified object.\\n}\\n```\\n\\n**Option #2:**\\nUse this if you want to respond directly and conversationally to the human. Markdown code snippet formatted in the following schema:\\n\\n```json\\n{\\n \\\"action\\\": \\\"Final Answer\\\",\\n \\\"action_input\\\": string // You should put what you want to return to use here and make sure to use valid json newline characters.\\n}\\n```\\n\\nFor both options, remember to always include the surrounding markdown code snippet delimiters (begin with \\\"```json\\\" and end with \\\"```\\\")!\\n\\n\\nUSER'S INPUT\\n--------------------\\nHere is the user's input (remember to respond with a markdown code snippet of a json blob with a single action, and NOTHING else):\\n\\n\\n\\n\\n\\nFrom employees, I want to see the 5 earliest employees (hire_date), I want to display only the month and the year that they were hired in and their employee number (emp_no). Format the date as e.g. \\\"September 2019\\\". Only show the query\",\"additional_kwargs\":{}}}]" ] } [llm/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 2:chain:LLMChain > 3:llm:ActionsClientLlm] [3.08s] Exiting LLM run with output: { "generations": [ [ { "text": "```json\n{\n \"action\": \"esql-language-knowledge-base\",\n \"action_input\": \"Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.\"\n}\n```" } ] ] } [chain/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 2:chain:LLMChain] [3.09s] Exiting Chain run with output: { "text": "```json\n{\n \"action\": \"esql-language-knowledge-base\",\n \"action_input\": \"Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.\"\n}\n```" } [agent/action] [1:chain:AgentExecutor] Agent selected action: { "tool": "esql-language-knowledge-base", "toolInput": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.", "log": "```json\n{\n \"action\": \"esql-language-knowledge-base\",\n \"action_input\": \"Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.\"\n}\n```" } [tool/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool] Entering Tool run with input: "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'." [chain/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain] Entering Chain run with input: { "query": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'." } [retriever/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 6:retriever:VectorStoreRetriever] Entering Retriever run with input: { "query": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'." } [retriever/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 6:retriever:VectorStoreRetriever] [115ms] Exiting Retriever run with output: { "documents": [ { "pageContent": "[[esql-date_format]]\n=== `DATE_FORMAT`\nReturns a string representation of a date in the provided format. If no format\nis specified, the `yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ` format is used.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| KEEP first_name, last_name, hire_date\n| EVAL hired = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"YYYY-MM-dd\")\n----\n", "metadata": { "source": "/Users/andrew.goldstein/Projects/forks/spong/kibana/x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/knowledge_base/esql/docs/functions/date_format.asciidoc" } }, { "pageContent": "[[esql-date_trunc]]\n=== `DATE_TRUNC`\nRounds down a date to the closest interval. Intervals can be expressed using the\n<<esql-timespan-literals,timespan literal syntax>>.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| EVAL year_hired = DATE_TRUNC(1 year, hire_date)\n| STATS count(emp_no) BY year_hired\n| SORT year_hired\n----\n", "metadata": { "source": "/Users/andrew.goldstein/Projects/forks/spong/kibana/x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/knowledge_base/esql/docs/functions/date_trunc.asciidoc" } }, { "pageContent": "[[esql-from]]\n=== `FROM`\n\nThe `FROM` source command returns a table with up to 10,000 documents from a\ndata stream, index, or alias. Each row in the resulting table represents a\ndocument. Each column corresponds to a field, and can be accessed by the name\nof that field.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n----\n\nYou can use <<api-date-math-index-names,date math>> to refer to indices, aliases\nand data streams. This can be useful for time series data, for example to access\ntoday's index:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM <logs-{now/d}>\n----\n\nUse comma-separated lists or wildcards to query multiple data streams, indices,\nor aliases:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees-00001,employees-*\n----\n", "metadata": { "source": "/Users/andrew.goldstein/Projects/forks/spong/kibana/x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/knowledge_base/esql/docs/source_commands/from.asciidoc" } }, { "pageContent": "[[esql-where]]\n=== `WHERE`\n\nUse `WHERE` to produce a table that contains all the rows from the input table\nfor which the provided condition evaluates to `true`:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=where]\n----\n\nWhich, if `still_hired` is a boolean field, can be simplified to:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=whereBoolean]\n----\n\n[discrete]\n==== Operators\n\nRefer to <<esql-operators>> for an overview of the supported operators.\n\n[discrete]\n==== Functions\n`WHERE` supports various functions for calculating values. Refer to\n<<esql-functions,Functions>> for more information.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=whereFunction]\n----\n", "metadata": { "source": "/Users/andrew.goldstein/Projects/forks/spong/kibana/x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/knowledge_base/esql/docs/processing_commands/where.asciidoc" } } ] } [chain/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 7:chain:StuffDocumentsChain] Entering Chain run with input: { "question": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.", "input_documents": [ { "pageContent": "[[esql-date_format]]\n=== `DATE_FORMAT`\nReturns a string representation of a date in the provided format. If no format\nis specified, the `yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ` format is used.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| KEEP first_name, last_name, hire_date\n| EVAL hired = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"YYYY-MM-dd\")\n----\n", "metadata": { "source": "/Users/andrew.goldstein/Projects/forks/spong/kibana/x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/knowledge_base/esql/docs/functions/date_format.asciidoc" } }, { "pageContent": "[[esql-date_trunc]]\n=== `DATE_TRUNC`\nRounds down a date to the closest interval. Intervals can be expressed using the\n<<esql-timespan-literals,timespan literal syntax>>.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| EVAL year_hired = DATE_TRUNC(1 year, hire_date)\n| STATS count(emp_no) BY year_hired\n| SORT year_hired\n----\n", "metadata": { "source": "/Users/andrew.goldstein/Projects/forks/spong/kibana/x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/knowledge_base/esql/docs/functions/date_trunc.asciidoc" } }, { "pageContent": "[[esql-from]]\n=== `FROM`\n\nThe `FROM` source command returns a table with up to 10,000 documents from a\ndata stream, index, or alias. Each row in the resulting table represents a\ndocument. Each column corresponds to a field, and can be accessed by the name\nof that field.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n----\n\nYou can use <<api-date-math-index-names,date math>> to refer to indices, aliases\nand data streams. This can be useful for time series data, for example to access\ntoday's index:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM <logs-{now/d}>\n----\n\nUse comma-separated lists or wildcards to query multiple data streams, indices,\nor aliases:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees-00001,employees-*\n----\n", "metadata": { "source": "/Users/andrew.goldstein/Projects/forks/spong/kibana/x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/knowledge_base/esql/docs/source_commands/from.asciidoc" } }, { "pageContent": "[[esql-where]]\n=== `WHERE`\n\nUse `WHERE` to produce a table that contains all the rows from the input table\nfor which the provided condition evaluates to `true`:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=where]\n----\n\nWhich, if `still_hired` is a boolean field, can be simplified to:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=whereBoolean]\n----\n\n[discrete]\n==== Operators\n\nRefer to <<esql-operators>> for an overview of the supported operators.\n\n[discrete]\n==== Functions\n`WHERE` supports various functions for calculating values. Refer to\n<<esql-functions,Functions>> for more information.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=whereFunction]\n----\n", "metadata": { "source": "/Users/andrew.goldstein/Projects/forks/spong/kibana/x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/knowledge_base/esql/docs/processing_commands/where.asciidoc" } } ], "query": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'." } [chain/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 7:chain:StuffDocumentsChain > 8:chain:LLMChain] Entering Chain run with input: { "question": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.", "query": "Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.", "context": "[[esql-date_format]]\n=== `DATE_FORMAT`\nReturns a string representation of a date in the provided format. If no format\nis specified, the `yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ` format is used.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| KEEP first_name, last_name, hire_date\n| EVAL hired = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"YYYY-MM-dd\")\n----\n\n\n[[esql-date_trunc]]\n=== `DATE_TRUNC`\nRounds down a date to the closest interval. Intervals can be expressed using the\n<<esql-timespan-literals,timespan literal syntax>>.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| EVAL year_hired = DATE_TRUNC(1 year, hire_date)\n| STATS count(emp_no) BY year_hired\n| SORT year_hired\n----\n\n\n[[esql-from]]\n=== `FROM`\n\nThe `FROM` source command returns a table with up to 10,000 documents from a\ndata stream, index, or alias. Each row in the resulting table represents a\ndocument. Each column corresponds to a field, and can be accessed by the name\nof that field.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n----\n\nYou can use <<api-date-math-index-names,date math>> to refer to indices, aliases\nand data streams. This can be useful for time series data, for example to access\ntoday's index:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM <logs-{now/d}>\n----\n\nUse comma-separated lists or wildcards to query multiple data streams, indices,\nor aliases:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees-00001,employees-*\n----\n\n\n[[esql-where]]\n=== `WHERE`\n\nUse `WHERE` to produce a table that contains all the rows from the input table\nfor which the provided condition evaluates to `true`:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=where]\n----\n\nWhich, if `still_hired` is a boolean field, can be simplified to:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=whereBoolean]\n----\n\n[discrete]\n==== Operators\n\nRefer to <<esql-operators>> for an overview of the supported operators.\n\n[discrete]\n==== Functions\n`WHERE` supports various functions for calculating values. Refer to\n<<esql-functions,Functions>> for more information.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=whereFunction]\n----\n" } [llm/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 7:chain:StuffDocumentsChain > 8:chain:LLMChain > 9:llm:ActionsClientLlm] Entering LLM run with input: { "prompts": [ "Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.\n\n[[esql-date_format]]\n=== `DATE_FORMAT`\nReturns a string representation of a date in the provided format. If no format\nis specified, the `yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ` format is used.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| KEEP first_name, last_name, hire_date\n| EVAL hired = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"YYYY-MM-dd\")\n----\n\n\n[[esql-date_trunc]]\n=== `DATE_TRUNC`\nRounds down a date to the closest interval. Intervals can be expressed using the\n<<esql-timespan-literals,timespan literal syntax>>.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n| EVAL year_hired = DATE_TRUNC(1 year, hire_date)\n| STATS count(emp_no) BY year_hired\n| SORT year_hired\n----\n\n\n[[esql-from]]\n=== `FROM`\n\nThe `FROM` source command returns a table with up to 10,000 documents from a\ndata stream, index, or alias. Each row in the resulting table represents a\ndocument. Each column corresponds to a field, and can be accessed by the name\nof that field.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees\n----\n\nYou can use <<api-date-math-index-names,date math>> to refer to indices, aliases\nand data streams. This can be useful for time series data, for example to access\ntoday's index:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM <logs-{now/d}>\n----\n\nUse comma-separated lists or wildcards to query multiple data streams, indices,\nor aliases:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\nFROM employees-00001,employees-*\n----\n\n\n[[esql-where]]\n=== `WHERE`\n\nUse `WHERE` to produce a table that contains all the rows from the input table\nfor which the provided condition evaluates to `true`:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=where]\n----\n\nWhich, if `still_hired` is a boolean field, can be simplified to:\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=whereBoolean]\n----\n\n[discrete]\n==== Operators\n\nRefer to <<esql-operators>> for an overview of the supported operators.\n\n[discrete]\n==== Functions\n`WHERE` supports various functions for calculating values. Refer to\n<<esql-functions,Functions>> for more information.\n\n[source,esql]\n----\ninclude::{esql-specs}/docs.csv-spec[tag=whereFunction]\n----\n\n\nQuestion: Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.\nHelpful Answer:" ] } [llm/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 7:chain:StuffDocumentsChain > 8:chain:LLMChain > 9:llm:ActionsClientLlm] [2.23s] Exiting LLM run with output: { "generations": [ [ { "text": "FROM employees\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"MMMM YYYY\")\n| SORT hire_date\n| LIMIT 5" } ] ] } [chain/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 7:chain:StuffDocumentsChain > 8:chain:LLMChain] [2.23s] Exiting Chain run with output: { "text": "FROM employees\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"MMMM YYYY\")\n| SORT hire_date\n| LIMIT 5" } [chain/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain > 7:chain:StuffDocumentsChain] [2.23s] Exiting Chain run with output: { "text": "FROM employees\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"MMMM YYYY\")\n| SORT hire_date\n| LIMIT 5" } [chain/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool > 5:chain:RetrievalQAChain] [2.35s] Exiting Chain run with output: { "text": "FROM employees\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"MMMM YYYY\")\n| SORT hire_date\n| LIMIT 5" } [tool/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 4:tool:ChainTool] [2.35s] Exiting Tool run with output: "FROM employees | KEEP emp_no, hire_date | EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, "MMMM YYYY") | SORT hire_date | LIMIT 5" [chain/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 10:chain:LLMChain] Entering Chain run with input: { "input": "\n\n\n\nFrom employees, I want to see the 5 earliest employees (hire_date), I want to display only the month and the year that they were hired in and their employee number (emp_no). Format the date as e.g. \"September 2019\". Only show the query", "chat_history": [], "agent_scratchpad": [ { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "AIMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "```json\n{\n \"action\": \"esql-language-knowledge-base\",\n \"action_input\": \"Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.\"\n}\n```", "additional_kwargs": {} } }, { "lc": 1, "type": "constructor", "id": [ "langchain", "schema", "HumanMessage" ], "kwargs": { "content": "TOOL RESPONSE:\n---------------------\nFROM employees\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"MMMM YYYY\")\n| SORT hire_date\n| LIMIT 5\n\nUSER'S INPUT\n--------------------\n\nOkay, so what is the response to my last comment? If using information obtained from the tools you must mention it explicitly without mentioning the tool names - I have forgotten all TOOL RESPONSES! Remember to respond with a markdown code snippet of a json blob with a single action, and NOTHING else.", "additional_kwargs": {} } } ], "stop": [ "Observation:" ] } [llm/start] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 10:chain:LLMChain > 11:llm:ActionsClientLlm] Entering LLM run with input: { "prompts": [ "[{\"lc\":1,\"type\":\"constructor\",\"id\":[\"langchain\",\"schema\",\"SystemMessage\"],\"kwargs\":{\"content\":\"Assistant is a large language model trained by OpenAI.\\n\\nAssistant is designed to be able to assist with a wide range of tasks, from answering simple questions to providing in-depth explanations and discussions on a wide range of topics. As a language model, Assistant is able to generate human-like text based on the input it receives, allowing it to engage in natural-sounding conversations and provide responses that are coherent and relevant to the topic at hand.\\n\\nAssistant is constantly learning and improving, and its capabilities are constantly evolving. It is able to process and understand large amounts of text, and can use this knowledge to provide accurate and informative responses to a wide range of questions. Additionally, Assistant is able to generate its own text based on the input it receives, allowing it to engage in discussions and provide explanations and descriptions on a wide range of topics.\\n\\nOverall, Assistant is a powerful system that can help with a wide range of tasks and provide valuable insights and information on a wide range of topics. Whether you need help with a specific question or just want to have a conversation about a particular topic, Assistant is here to assist. However, above all else, all responses must adhere to the format of RESPONSE FORMAT INSTRUCTIONS.\",\"additional_kwargs\":{}}},{\"lc\":1,\"type\":\"constructor\",\"id\":[\"langchain\",\"schema\",\"HumanMessage\"],\"kwargs\":{\"content\":\"TOOLS\\n------\\nAssistant can ask the user to use tools to look up information that may be helpful in answering the users original question. The tools the human can use are:\\n\\nesql-language-knowledge-base: Call this for knowledge on how to build an ESQL query, or answer questions about the ES|QL query language.\\n\\nRESPONSE FORMAT INSTRUCTIONS\\n----------------------------\\n\\nOutput a JSON markdown code snippet containing a valid JSON object in one of two formats:\\n\\n**Option 1:**\\nUse this if you want the human to use a tool.\\nMarkdown code snippet formatted in the following schema:\\n\\n```json\\n{\\n \\\"action\\\": string, // The action to take. Must be one of [esql-language-knowledge-base]\\n \\\"action_input\\\": string // The input to the action. May be a stringified object.\\n}\\n```\\n\\n**Option #2:**\\nUse this if you want to respond directly and conversationally to the human. Markdown code snippet formatted in the following schema:\\n\\n```json\\n{\\n \\\"action\\\": \\\"Final Answer\\\",\\n \\\"action_input\\\": string // You should put what you want to return to use here and make sure to use valid json newline characters.\\n}\\n```\\n\\nFor both options, remember to always include the surrounding markdown code snippet delimiters (begin with \\\"```json\\\" and end with \\\"```\\\")!\\n\\n\\nUSER'S INPUT\\n--------------------\\nHere is the user's input (remember to respond with a markdown code snippet of a json blob with a single action, and NOTHING else):\\n\\n\\n\\n\\n\\nFrom employees, I want to see the 5 earliest employees (hire_date), I want to display only the month and the year that they were hired in and their employee number (emp_no). Format the date as e.g. \\\"September 2019\\\". Only show the query\",\"additional_kwargs\":{}}},{\"lc\":1,\"type\":\"constructor\",\"id\":[\"langchain\",\"schema\",\"AIMessage\"],\"kwargs\":{\"content\":\"```json\\n{\\n \\\"action\\\": \\\"esql-language-knowledge-base\\\",\\n \\\"action_input\\\": \\\"Display the 'emp_no', month and year of the 5 earliest employees by 'hire_date'. Format the date as 'Month Year'.\\\"\\n}\\n```\",\"additional_kwargs\":{}}},{\"lc\":1,\"type\":\"constructor\",\"id\":[\"langchain\",\"schema\",\"HumanMessage\"],\"kwargs\":{\"content\":\"TOOL RESPONSE:\\n---------------------\\nFROM employees\\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \\\"MMMM YYYY\\\")\\n| SORT hire_date\\n| LIMIT 5\\n\\nUSER'S INPUT\\n--------------------\\n\\nOkay, so what is the response to my last comment? If using information obtained from the tools you must mention it explicitly without mentioning the tool names - I have forgotten all TOOL RESPONSES! Remember to respond with a markdown code snippet of a json blob with a single action, and NOTHING else.\",\"additional_kwargs\":{}}}]" ] } [llm/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 10:chain:LLMChain > 11:llm:ActionsClientLlm] [6.47s] Exiting LLM run with output: { "generations": [ [ { "text": "```json\n{\n \"action\": \"Final Answer\",\n \"action_input\": \"Here is the query to get the employee number and the formatted hire date for the 5 earliest employees by hire_date:\\n\\nFROM employees\\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \\\"MMMM YYYY\\\")\\n| SORT hire_date\\n| LIMIT 5\"\n}\n```" } ] ] } [chain/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor > 10:chain:LLMChain] [6.47s] Exiting Chain run with output: { "text": "```json\n{\n \"action\": \"Final Answer\",\n \"action_input\": \"Here is the query to get the employee number and the formatted hire date for the 5 earliest employees by hire_date:\\n\\nFROM employees\\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \\\"MMMM YYYY\\\")\\n| SORT hire_date\\n| LIMIT 5\"\n}\n```" } [chain/end] [1:chain:AgentExecutor] [11.91s] Exiting Chain run with output: { "output": "Here is the query to get the employee number and the formatted hire date for the 5 earliest employees by hire_date:\n\nFROM employees\n| KEEP emp_no, hire_date\n| EVAL month_year = DATE_FORMAT(hire_date, \"MMMM YYYY\")\n| SORT hire_date\n| LIMIT 5" } ```
|
Pinging @elastic/security-solution (Team: SecuritySolution) |
| memory, | ||
| // See `qaChainOptions` from https://js.langchain.com/docs/modules/chains/popular/chat_vector_db | ||
| qaChainOptions: { type: 'stuff' }, | ||
| verbose: false, |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
set this to true for verbose debugging per the PR description
| @@ -78,7 +79,8 @@ export const fetchConnectorExecuteAction = async ({ | |||
|
|
|||
| if (data.choices && data.choices.length > 0 && data.choices[0].message.content) { | |||
| const result = data.choices[0].message.content.trim(); | |||
| return result; | |||
|
|
|||
| return assistantLangChain ? getFormattedMessageContent(result) : result; | |||
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
A client side change was required to the assistant, because the response returned from the agent executor is JSON.
Thoughts on doing this server side as to not leak the agent executor abstraction to the client? Or was there a specific reason this needed to be pushed to the client?
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
A client side change was required to the assistant, because the response returned from the agent executor is JSON.
Thoughts on doing this server side as to not leak the agent executor abstraction to the client? Or was there a specific reason this needed to be pushed to the client?
In summary of our offline discussion:
- Yes, it's possible to do this server side by introducing an additional
JSON.parseof the response from the LLM - In short, the server side code in
x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.tswould look something like the following (psudocode):
await executor.call({ input: latestMessage[0].content });
const rawData = llm.getActionResultData(); // the response from the actions framework
if (rawData.choices && rawData.choices.length > 0 && rawData.choices[0].message.content) {
const result = rawData.choices[0].message.content.trim();
const formatted = getFormattedMessageContent(result);
const data = convertToRecord(formatted);
return {
connector_id: connectorId,
data,
status: 'ok',
};
} else {
throw new Error('Unexpected raw response from the LLM');
}- The psudocode above is very similar to the client side code in
x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistant/impl/assistant/api.tsx - If server-side parsing is implemented, the existing client side code should be extracted into a reusable function (exported by the package), for reuse on the server
In summary, it's possible, but given the above adds an additional server side JSON parse of the LLM response and requires some additional client side refactoring, we'll reconsider the above post FF.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Thank you for taking the time to discuss offline and for summarizing here 🙏 , path forward sounds good to me 👍
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Checked out, tested locally, code reviewed and LGTM! 👍 Thank you for the very detailed (verbose) description, very helpful! 🙂
Note I: Still seeing some wonkiness w/ immediate memory references falling short as we discussed offline. You can just call me CIDR_MATCH from now on... 😅
Note II: Still seeing a SimilaritySearch being kicked off when prompting nothing about ESQL. I don't recall seeing this when we were testing locally, so just curious if you might know why this would be happening even though we're now registering the ESQL tool?
|
@elasticmachine merge upstream |
💚 Build Succeeded
Metrics [docs]Async chunks
History
To update your PR or re-run it, just comment with: |
…eration (RAG) for Alerts This PR implements _Retrieval Augmented Generation_ (RAG) for Alerts in the Security Solution. This feature enables users to ask the assistant questions about the latest and riskiest open alerts in their environment using natural language, for example: - _How many alerts are currently open?_ - _Which alerts should I look at first?_ - _Did we have any alerts with suspicious activity on Windows machines?_ ### More context Previously, the assistant relied solely on the knowledge of the configured LLM and _singular_ alerts or events passed _by the client_ to the LLM as prompt context. This new feature: - Enables _multiple_ alerts to be passed by the _server_ as context to the LLM, via [LangChain tools](elastic#167097) - Applies the user's [anonymization](elastic#159857) settings to those alerts - Only fields allowed by the user will be sent as context to the LLM - Users may enable or disable anonymization for specific fields (via settings) - Click the conversation's `Show anonymized` toggle to see the anonymized values sent to / received from the LLM: 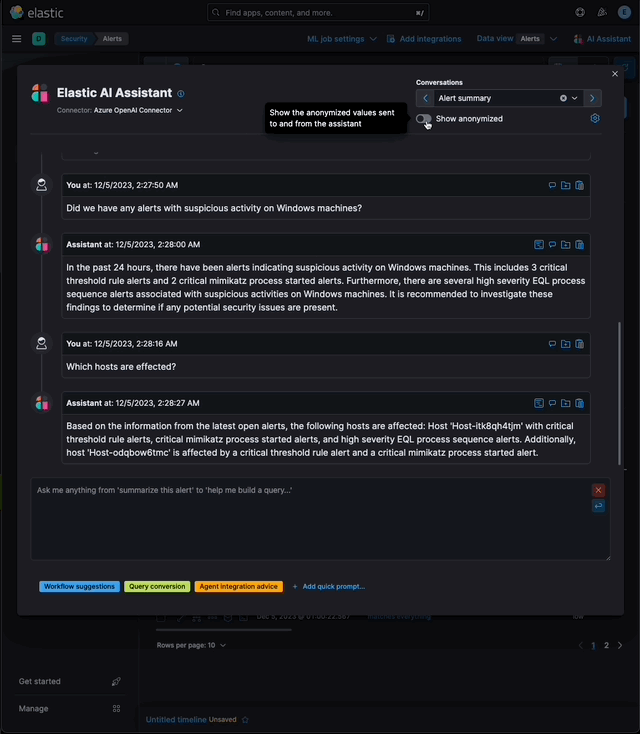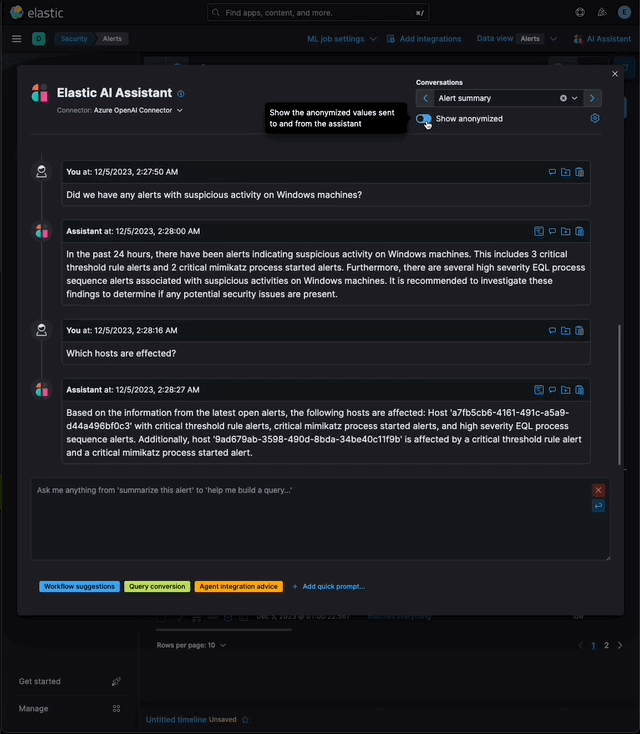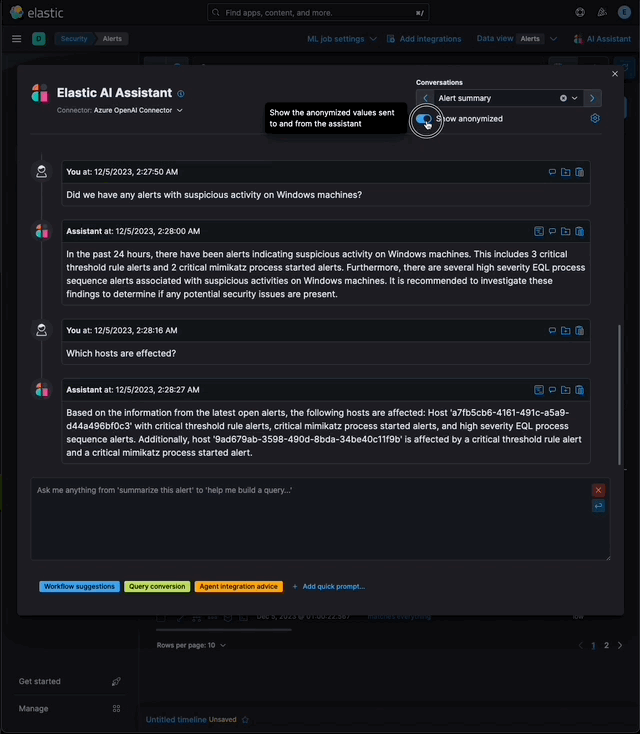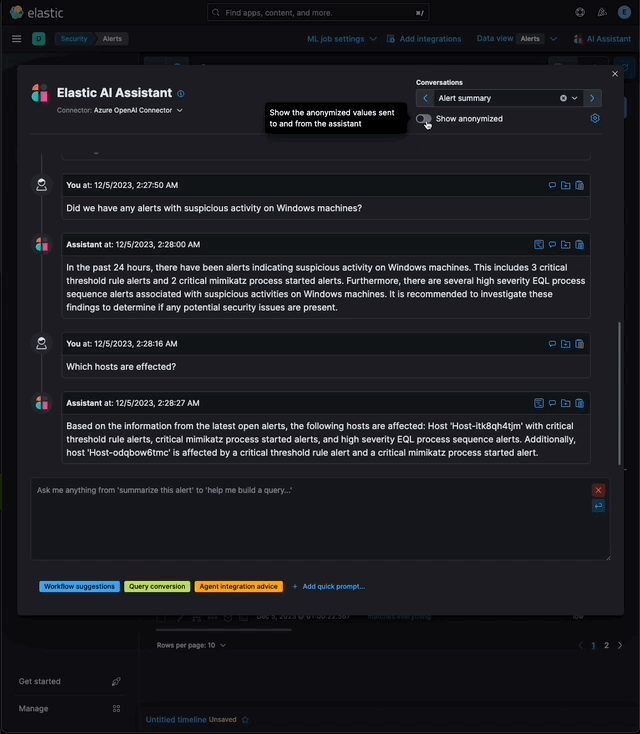 ### Settings This feature is enabled and configured via the `Knowledge Base` > `Alerts` settings in the screenshot below: 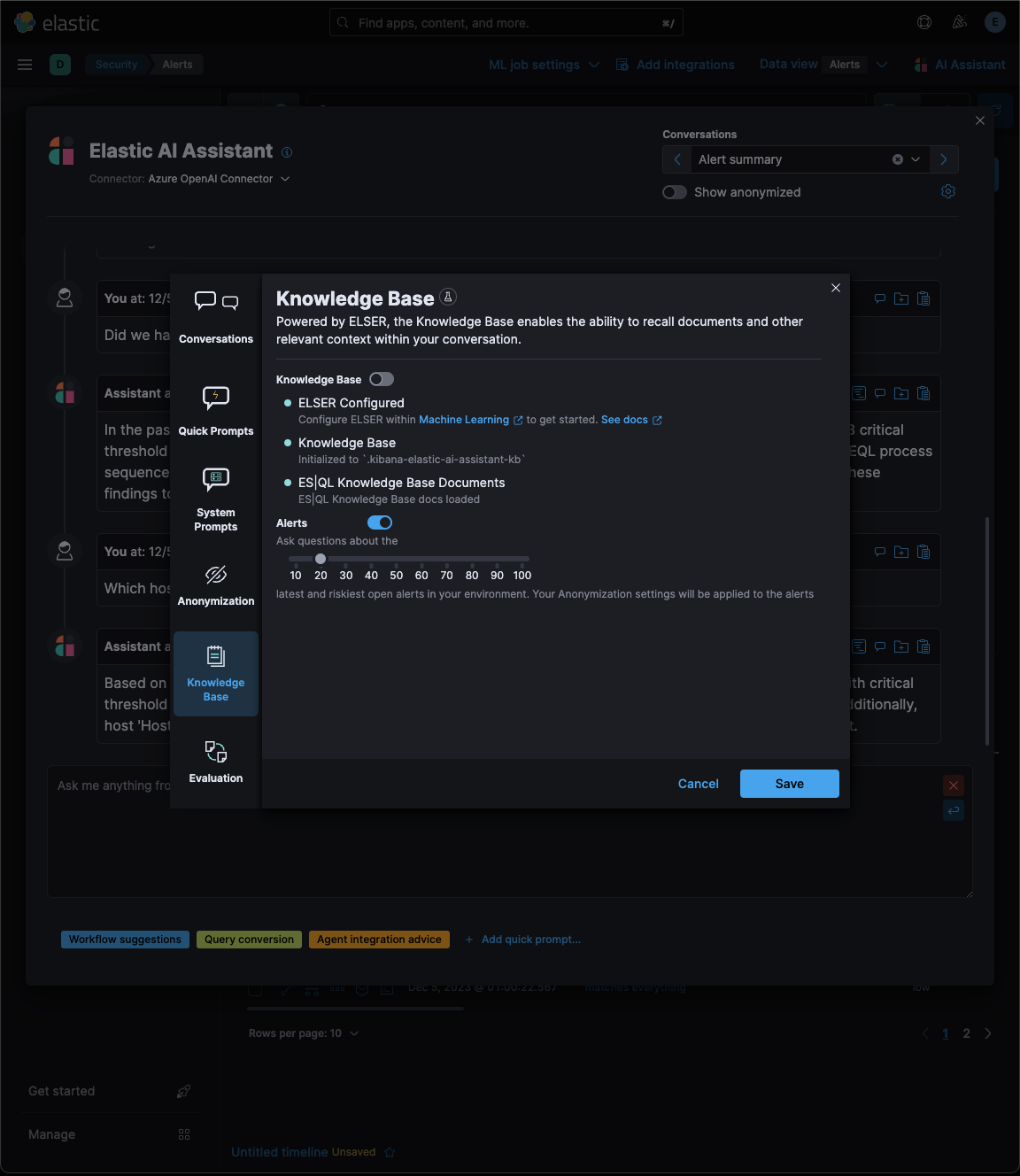 - The `Alerts` toggle enables or disables the feature - The slider has a range of `10` - `100` alerts (default: `20`) When the setting above is enabled, up to `n` alerts (as determined by the slider) that meet the following criteria will be returned: - the `kibana.alert.workflow_status` must be `open` - the alert must have been generated in the last `24 hours` - the alert must NOT be a `kibana.alert.building_block_type` alert - the `n` alerts are ordered by `kibana.alert.risk_score`, to prioritize the riskiest alerts ### Feature flag To use this feature: 1) Add the `assistantRagOnAlerts` feature flag to the `xpack.securitySolution.enableExperimental` setting in `config/kibana.yml` (or `config/kibana.dev.yml` in local development environments), per the example below: ``` xpack.securitySolution.enableExperimental: ['assistantRagOnAlerts'] ``` 2) Enable the `Alerts` toggle in the Assistant's `Knowledge Base` settings, per the screenshot below:  ## How it works - When the `Alerts` settings toggle is enabled, http `POST` requests to the `/internal/elastic_assistant/actions/connector/{id}/_execute` route include the following new (optional) parameters: - `alertsIndexPattern`, the alerts index for the current Kibana Space, e.g. `.alerts-security.alerts-default` - `allow`, the user's `Allowed` fields in the `Anonymization` settings, e.g. `["@timestamp", "cloud.availability_zone", "file.name", "user.name", ...]` - `allowReplacement`, the user's `Anonymized` fields in the `Anonymization` settings, e.g. `["cloud.availability_zone", "host.name", "user.name", ...]` - `replacements`, a `Record<string, string>` of replacements (generated on the server) that starts empty for a new conversation, and accumulates anonymized values until the conversation is cleared, e.g. ```json "replacements": { "e4f935c0-5a80-47b2-ac7f-816610790364": "Host-itk8qh4tjm", "cf61f946-d643-4b15-899f-6ffe3fd36097": "rpwmjvuuia", "7f80b092-fb1a-48a2-a634-3abc61b32157": "6astve9g6s", "f979c0d5-db1b-4506-b425-500821d00813": "Host-odqbow6tmc", // ... }, ``` - `size`, the numeric value set by the slider in the user's `Knowledge Base > Alerts` setting, e.g. `20` - The `postActionsConnectorExecuteRoute` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/routes/post_actions_connector_execute.ts` was updated to accept the new optional parameters, and to return an updated `replacements` with every response. (Every new request that is processed on the server may add additional anonymized values to the `replacements` returned in the response.) - The `callAgentExecutor` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.ts` previously used a hard-coded array of LangChain tools that had just one entry, for the `ESQLKnowledgeBaseTool` tool. That hard-coded array was replaced in this PR with a call to the (new) `getApplicableTools` function: ```typescript const tools: Tool[] = getApplicableTools({ allow, allowReplacement, alertsIndexPattern, assistantLangChain, chain, esClient, modelExists, onNewReplacements, replacements, request, size, }); ``` - The `getApplicableTools` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/index.ts` examines the parameters in the `KibanaRequest` and only returns a filtered set of LangChain tools. If the request doesn't contain all the parameters required by a tool, it will NOT be returned by `getApplicableTools`. For example, if the required anonymization parameters are not included in the request, the `open-alerts` tool will not be returned. - The new `alert-counts` LangChain tool returned by the `getAlertCountsTool` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/alert_counts/get_alert_counts_tool.ts` provides the LLM the results of an aggregation on the last `24` hours of alerts (in the current Kibana Space), grouped by `kibana.alert.severity`. See the `getAlertsCountQuery` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/alert_counts/get_alert_counts_query.ts` for details - The new `open-alerts` LangChain tool returned by the `getOpenAlertsTool` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/open_alerts/get_open_alerts_tool.ts` provides the LLM up to `size` non-building-block alerts generated in the last `24` hours (in the current Kibana Space) with an `open` workflow status, ordered by `kibana.alert.risk_score` to prioritize the riskiest alerts. See the `getOpenAlertsQuery` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/open_alerts/get_open_alerts_query.ts` for details. - On the client, a conversation continues to accumulate additional `replacements` (and send them in subsequent requests) until the conversation is cleared - Anonymization functions that were only invoked by the browser were moved from the (browser) `kbn-elastic-assistant` package in `x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistant/` to a new common package: `x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistant-common` - The new `kbn-elastic-assistant-common` package is also consumed by the `elastic_assistant` (server) plugin: `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant`
…tion (RAG) for Alerts (#172542) ## [Security Solution] [Elastic AI Assistant] Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) for Alerts This PR implements _Retrieval Augmented Generation_ (RAG) for Alerts in the Security Solution. This feature enables users to ask the assistant questions about the latest and riskiest open alerts in their environment using natural language, for example: - _How many alerts are currently open?_ - _Which alerts should I look at first?_ - _Did we have any alerts with suspicious activity on Windows machines?_ ### More context Previously, the assistant relied solely on the knowledge of the configured LLM and _singular_ alerts or events passed _by the client_ to the LLM as prompt context. This new feature: - Enables _multiple_ alerts to be passed by the _server_ as context to the LLM, via [LangChain tools](#167097) - Applies the user's [anonymization](#159857) settings to those alerts - Only fields allowed by the user will be sent as context to the LLM - Users may enable or disable anonymization for specific fields (via settings) - Click the conversation's `Show anonymized` toggle to see the anonymized values sent to / received from the LLM:  ### Settings This feature is enabled and configured via the `Knowledge Base` > `Alerts` settings in the screenshot below:  - The `Alerts` toggle enables or disables the feature - The slider has a range of `10` - `100` alerts (default: `20`) When the setting above is enabled, up to `n` alerts (as determined by the slider) that meet the following criteria will be returned: - the `kibana.alert.workflow_status` must be `open` - the alert must have been generated in the last `24 hours` - the alert must NOT be a `kibana.alert.building_block_type` alert - the `n` alerts are ordered by `kibana.alert.risk_score`, to prioritize the riskiest alerts ### Feature flag To use this feature: 1) Add the `assistantRagOnAlerts` feature flag to the `xpack.securitySolution.enableExperimental` setting in `config/kibana.yml` (or `config/kibana.dev.yml` in local development environments), per the example below: ``` xpack.securitySolution.enableExperimental: ['assistantRagOnAlerts'] ``` 2) Enable the `Alerts` toggle in the Assistant's `Knowledge Base` settings, per the screenshot below:  ## How it works - When the `Alerts` settings toggle is enabled, http `POST` requests to the `/internal/elastic_assistant/actions/connector/{id}/_execute` route include the following new (optional) parameters: - `alertsIndexPattern`, the alerts index for the current Kibana Space, e.g. `.alerts-security.alerts-default` - `allow`, the user's `Allowed` fields in the `Anonymization` settings, e.g. `["@timestamp", "cloud.availability_zone", "file.name", "user.name", ...]` - `allowReplacement`, the user's `Anonymized` fields in the `Anonymization` settings, e.g. `["cloud.availability_zone", "host.name", "user.name", ...]` - `replacements`, a `Record<string, string>` of replacements (generated on the server) that starts empty for a new conversation, and accumulates anonymized values until the conversation is cleared, e.g. ```json "replacements": { "e4f935c0-5a80-47b2-ac7f-816610790364": "Host-itk8qh4tjm", "cf61f946-d643-4b15-899f-6ffe3fd36097": "rpwmjvuuia", "7f80b092-fb1a-48a2-a634-3abc61b32157": "6astve9g6s", "f979c0d5-db1b-4506-b425-500821d00813": "Host-odqbow6tmc", // ... }, ``` - `size`, the numeric value set by the slider in the user's `Knowledge Base > Alerts` setting, e.g. `20` - The `postActionsConnectorExecuteRoute` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/routes/post_actions_connector_execute.ts` was updated to accept the new optional parameters, and to return an updated `replacements` with every response. (Every new request that is processed on the server may add additional anonymized values to the `replacements` returned in the response.) - The `callAgentExecutor` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.ts` previously used a hard-coded array of LangChain tools that had just one entry, for the `ESQLKnowledgeBaseTool` tool. That hard-coded array was replaced in this PR with a call to the (new) `getApplicableTools` function: ```typescript const tools: Tool[] = getApplicableTools({ allow, allowReplacement, alertsIndexPattern, assistantLangChain, chain, esClient, modelExists, onNewReplacements, replacements, request, size, }); ``` - The `getApplicableTools` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/index.ts` examines the parameters in the `KibanaRequest` and only returns a filtered set of LangChain tools. If the request doesn't contain all the parameters required by a tool, it will NOT be returned by `getApplicableTools`. For example, if the required anonymization parameters are not included in the request, the `open-alerts` tool will not be returned. - The new `alert-counts` LangChain tool returned by the `getAlertCountsTool` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/alert_counts/get_alert_counts_tool.ts` provides the LLM the results of an aggregation on the last `24` hours of alerts (in the current Kibana Space), grouped by `kibana.alert.severity`. See the `getAlertsCountQuery` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/alert_counts/get_alert_counts_query.ts` for details - The new `open-alerts` LangChain tool returned by the `getOpenAlertsTool` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/open_alerts/get_open_alerts_tool.ts` provides the LLM up to `size` non-building-block alerts generated in the last `24` hours (in the current Kibana Space) with an `open` workflow status, ordered by `kibana.alert.risk_score` to prioritize the riskiest alerts. See the `getOpenAlertsQuery` function in `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/tools/open_alerts/get_open_alerts_query.ts` for details. - On the client, a conversation continues to accumulate additional `replacements` (and send them in subsequent requests) until the conversation is cleared - Anonymization functions that were only invoked by the browser were moved from the (browser) `kbn-elastic-assistant` package in `x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistant/` to a new common package: `x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistant-common` - The new `kbn-elastic-assistant-common` package is also consumed by the `elastic_assistant` (server) plugin: `x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant`





[Security Solution] [Elastic AI Assistant] LangChain Agents and Tools integration for ES|QL query generation via ELSER
This PR integrates LangChain Agents and Tools with the Elastic AI Assistant.
These abstractions enable the LLM to dynamically choose whether or not to query, via ELSER, an ES|QL knowledge base. Context from the knowledge base is used to generate
ES|QLqueries, or answer questions aboutES|QL.Registration of the tool occurs in
x-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.ts:The
toolsarray above may be updated in future PRs to include, for example, anES|QLquery validator endpoint.Details
The
callAgentExecutorfunction inx-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.ts:RetrievalQAChainfrom anELSERbackedElasticsearchStore, which serves as a knowledge base forES|QL:toolsabove, theActionsClientLlm(an abstraction that callsactionsClient.execute), and memory of the previous messages in the conversation:Note: Set
verboseabove totrueto for detailed debugging output from LangChain.executor, kicking it off withlatestMessage:Changes to
x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistantA client side change was required to the assistant, because the response returned from the agent executor is JSON. This response is parsed on the client in
x-pack/packages/kbn-elastic-assistant/impl/assistant/api.tsx:Client-side parsing of the response only happens when then
assistantLangChainfeature flag istrue.Desk testing
Set
in
x-pack/plugins/security_solution/public/assistant/provider.tsxto enable this experimental feature in development environments.Also (optionally) set
verbosetotruein the following code inx-pack/plugins/elastic_assistant/server/lib/langchain/execute_custom_llm_chain/index.ts:After setting the feature flag and optionally enabling verbose debugging output, you may ask the assistant to generate an
ES|QLquery, per the example in the next section.Example output
When the Elastic AI Assistant is asked:
it replies:
Per the screenshot below:
The
verbose: trueoutput from LangChain logged to the console reveals that the prompt sent to the LLM includes text like the following:along with instructions for "calling" the tool like a function.
The debugging output also reveals the agent selecting the tool, and returning results from ESLR:
The documents containing
ES|QLexamples, retrieved from ELSER, are sent back to the LLM to answer the original question, per the abridged output below:Complete (verbose) LangChain output from the example
The following
verbose: trueoutput from LangChain below was produced via the example in the previous section: