Spring Cloud Sleuth implements a distributed tracing solution for Spring Cloud.
Spring Cloud Sleuth borrows Dapper’s terminology.
Span: The basic unit of work. For example, sending an RPC is a new span, as is sending a response to an RPC. Span’s are identified by a unique 64-bit ID for the span and another 64-bit ID for the trace the span is a part of. Spans also have other data, such as descriptions, timestamped events, key-value annotations (tags), the ID of the span that caused them, and process ID’s (normally IP address).
Spans are started and stopped, and they keep track of their timing information. Once you create a span, you must stop it at some point in the future.
Trace: A set of spans forming a tree-like structure. For example, if you are running a distributed big-data store, a trace might be formed by a put request.
Annotation: is used to record existence of an event in time. Some of the core annotations used to define the start and stop of a request are:
-
cs - Client Sent - The client has made a request. This annotation depicts the start of the span.
-
sr - Server Received - The server side got the request and will start processing it. If one subtracts the cs timestamp from this timestamp one will receive the network latency.
-
ss - Server Sent - Annotated upon completion of request processing (when the response got sent back to the client). If one subtracts the sr timestamp from this timestamp one will receive the time needed by the server side to process the request.
-
cr - Client Received - Signifies the end of the span. The client has successfully received the response from the server side. If one subtracts the cs timestamp from this timestamp one will receive the whole time needed by the client to receive the response from the server.
Visualization of what Span and Trace will look in a system together with the Zipkin annotations:
Each color of a note signifies a span (7 spans - from A to G). If you have such information in the note:
Trace Id = X
Span Id = D
Client SentThat means that the current span has Trace-Id set to X, Span-Id set to D. It also has emitted Client Sent event.
This is how the visualization of the parent / child relationship of spans would look like:
In the following sections the example from the image above will be taken into consideration.
Altogether there are 10 spans . If you go to traces in Zipkin you will see this number:
However if you pick a particular trace then you will see 7 spans:
|
Note
|
When picking a particular trace you will see merged spans. That means that if there were 2 spans sent to Zipkin with Server Received and Server Sent / Client Received and Client Sent annotations then they will presented as a single span. |
In the image depicting the visualization of what Span and Trace is you can see 20 colorful labels. How does it happen that in Zipkin 10 spans are received?
-
2 span A labels signify span started and closed. Upon closing a single span is sent to Zipkin.
-
4 span B labels are in fact are single span with 4 annotations. However this span is composed of two separate instances. One sent from service 1 and one from service 2. So in fact two span instances will be sent to Zipkin and merged there.
-
2 span C labels signify span started and closed. Upon closing a single span is sent to Zipkin.
-
4 span B labels are in fact are single span with 4 annotations. However this span is composed of two separate instances. One sent from service 2 and one from service 3. So in fact two span instances will be sent to Zipkin and merged there.
-
2 span E labels signify span started and closed. Upon closing a single span is sent to Zipkin.
-
4 span B labels are in fact are single span with 4 annotations. However this span is composed of two separate instances. One sent from service 2 and one from service 4. So in fact two span instances will be sent to Zipkin and merged there.
-
2 span G labels signify span started and closed. Upon closing a single span is sent to Zipkin.
So 1 span from A, 2 spans from B, 1 span from C, 2 spans from D, 1 span from E, 2 spans from F and 1 from G. Altogether 10 spans.
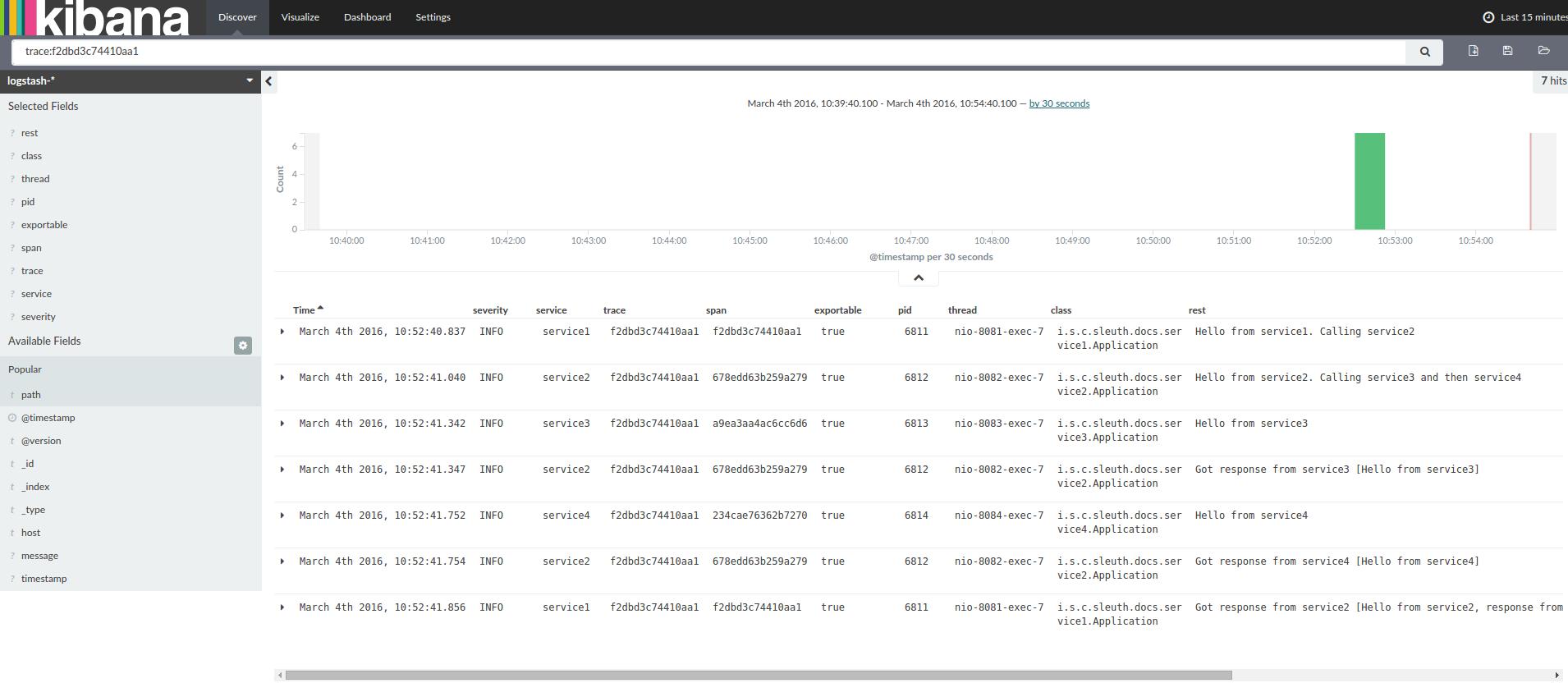
When grepping the logs of those four applications by trace id equal to e.g. 2485ec27856c56f4 one would get the following:
service1.log:2016-02-26 11:15:47.561 INFO [service1,2485ec27856c56f4,2485ec27856c56f4,true] 68058 --- [nio-8081-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service1.Application : Hello from service1. Calling service2
service2.log:2016-02-26 11:15:47.710 INFO [service2,2485ec27856c56f4,9aa10ee6fbde75fa,true] 68059 --- [nio-8082-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service2.Application : Hello from service2. Calling service3 and then service4
service3.log:2016-02-26 11:15:47.895 INFO [service3,2485ec27856c56f4,1210be13194bfe5,true] 68060 --- [nio-8083-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service3.Application : Hello from service3
service2.log:2016-02-26 11:15:47.924 INFO [service2,2485ec27856c56f4,9aa10ee6fbde75fa,true] 68059 --- [nio-8082-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service2.Application : Got response from service3 [Hello from service3]
service4.log:2016-02-26 11:15:48.134 INFO [service4,2485ec27856c56f4,1b1845262ffba49d,true] 68061 --- [nio-8084-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service4.Application : Hello from service4
service2.log:2016-02-26 11:15:48.156 INFO [service2,2485ec27856c56f4,9aa10ee6fbde75fa,true] 68059 --- [nio-8082-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service2.Application : Got response from service4 [Hello from service4]
service1.log:2016-02-26 11:15:48.182 INFO [service1,2485ec27856c56f4,2485ec27856c56f4,true] 68058 --- [nio-8081-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service1.Application : Got response from service2 [Hello from service2, response from service3 [Hello from service3] and from service4 [Hello from service4]]If you’re using a log aggregating tool like Kibana, Splunk etc. you can order the events that took place. An example of Kibana would look like this:
If you want to use Logstash here is the Grok pattern for Logstash:
filter {
# pattern matching logback pattern
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:timestamp}\s+%{LOGLEVEL:severity}\s+\[%{DATA:service},%{DATA:trace},%{DATA:span},%{DATA:exportable}\]\s+%{DATA:pid}---\s+\[%{DATA:thread}\]\s+%{DATA:class}\s+:\s+%{GREEDYDATA:rest}" }
}
}|
Note
|
If you want to use Grok together with the logs from Cloud Foundry you have to use this pattern: |
filter {
# pattern matching logback pattern
grok {
match => { "message" => "(?m)OUT\s+%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:timestamp}\s+%{LOGLEVEL:severity}\s+\[%{DATA:service},%{DATA:trace},%{DATA:span},%{DATA:exportable}\]\s+%{DATA:pid}---\s+\[%{DATA:thread}\]\s+%{DATA:class}\s+:\s+%{GREEDYDATA:rest}" }
}
}-
Adds trace and span ids to the Slf4J MDC, so you can extract all the logs from a given trace or span in a log aggregator. Example logs:
2016-02-02 15:30:57.902 INFO [bar,6bfd228dc00d216b,6bfd228dc00d216b,false] 23030 --- [nio-8081-exec-3] ... 2016-02-02 15:30:58.372 ERROR [bar,6bfd228dc00d216b,6bfd228dc00d216b,false] 23030 --- [nio-8081-exec-3] ... 2016-02-02 15:31:01.936 INFO [bar,46ab0d418373cbc9,46ab0d418373cbc9,false] 23030 --- [nio-8081-exec-4] ...
notice the
[appname,traceId,spanId,exportable]entries from the MDC:-
spanId - the id of a specific operation that took place
-
appname - the name of the application that logged the span
-
traceId - the id of the latency graph that contains the span
-
exportable - whether the log should be exported to Zipkin or not
-
-
Provides an abstraction over common distributed tracing data models: traces, spans (forming a DAG), annotations, key-value annotations. Loosely based on HTrace, but Zipkin (Dapper) compatible.
-
Sleuth records timing information to aid in latency analysis. Using sleuth, you can pinpoint causes of latency in your applications. Sleuth is written to not log too much, and to not cause your production application to crash.
-
propagates structural data about your call-graph in-band, and the rest out-of-band.
-
includes opinionated instrumentation of layers such as HTTP
-
includes sampling policy to manage volume
-
can report to a Zipkin system for query and visualization
-
-
Instruments common ingress and egress points from Spring applications (servlet filter, async endpoints, rest template, scheduled actions, message channels, zuul filters, feign client).
-
Provides simple metrics of accepted / dropped spans.
-
If
spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkinthen the app will generate and collect Zipkin-compatible traces. By default it sends them via HTTP to a Zipkin server on localhost (port 9411). Configure the location of the service usingspring.zipkin.baseUrl. -
If
spring-cloud-sleuth-streamthen the app will generate and collect traces via Spring Cloud Stream. Your app automatically becomes a producer of tracer messages that are sent over your broker of choice (e.g. RabbitMQ, Apache Kafka, Redis).
|
Important
|
If using Zipkin or Stream, configure the percentage of spans exported using spring.sleuth.sampler.percentage
(default 0.1, i.e. 10%). Otherwise you might think that Sleuth is not working cause it’s omitting some spans.
|
|
Note
|
the SLF4J MDC is always set and logback users will immediately see the trace and span ids in logs per the example
above. Other logging systems have to configure their own formatter to get the same result. The default is
logging.pattern.level set to %clr(%5p) %clr([${spring.application.name:},%X{X-Trace-Id:-},%X{X-Span-Id:-},%X{X-Span-Export:-}]){yellow}
(this is a Spring Boot feature for logback users).
This means that if you’re not using SLF4J this pattern WILL NOT be automatically applied.
|
There are a few samples with slightly different features. You can run all of them from an IDE via the main method, or on the command line with mvn spring-boot:run. They all log trace and span data on the console by default. Here’s a list:
-
spring-cloud-sleuth-sample: vanilla (no zipkin) web app that calls back to itself on various endpoints ("/", "/call", "/async") -
spring-cloud-sleuth-sample-zipkin: same as vanilla sample but with zipkin (setsample.zipkin.enabled=trueif you have a collector running) -
spring-cloud-sleuth-sample-stream: same as vanilla sample, but exports span data to RabbitMQ using Spring Cloud Stream -
spring-cloud-sleuth-sample-stream-zipkin: a consumer for the span data on RabbitMQ that pushes it into a Zipkin span store, so it can be queried and visualized using the standard Zipkin UI. -
spring-cloud-sleuth-sample-messaging: a Spring Integration application with two HTTP endpoints ("/" and "/xform") -
spring-cloud-sleuth-sample-ribbon: two endpoints ("/" and "/call") that make calls to the "zipkin" sample via Ribbon. Also has `@EnableZUulProxy" so if the other samples are running they are proxied at "/messaging", "/zipkin", "/vanilla" (see "/routes" for a list).
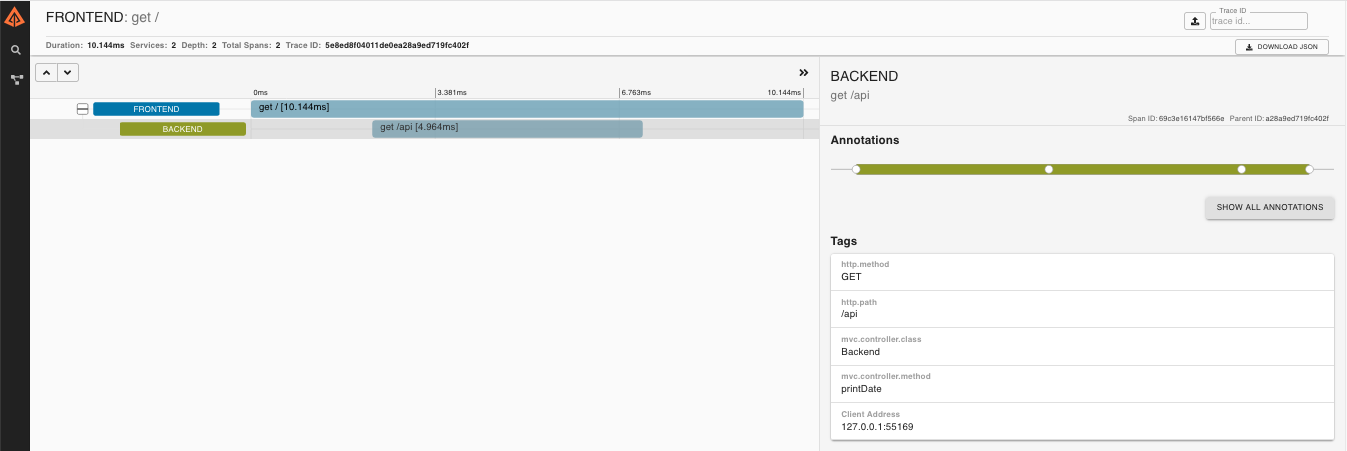
The Ribbon sample makes an interesting demo or playground for learning about zipkin. In the screenshot below you can see a trace with 3 spans - it starts in the "testSleuthRibbon" app and crosses to "testSleuthMessaging" for the next 2 spans.
-
Optionally run the Zipkin UI, e.g. via docker compose (there’s a
docker-compose.ymlin Spring Cloud Sleuth, or in Docker Zipkin -
Run the zipkin sample application (set
sample.zipkin.enabled=falseif you have no Zipkin running). If you are using a VM to run docker you might need to tunnel port 9411 to localhost, or change thespring.zipkin.baseUrl. -
Hit
http://localhost:3380,http://localhost:3380/call,http://localhost:3380/asyncfor some interesting sample traces (the app callas back to itself). -
Goto
http://localhost:8080for zipkin web (if you are using boot2docker the host will be different)
|
Note
|
You can see the zipkin spans without the UI (in logs) if you run the sample with sample.zipkin.enabled=false.
|
The fact that the first trace in says "testSleuthMessaging" seems to be a bug in the UI (it has some annotations from that service, but it originates in the "testSleuthRibbon" service).
Instead of POSTing trace data directly to a Zipkin server, you can export them over Spring Cloud Stream.
-
Build the Zipkin Stream sample with Maven and run it via its
docker-compose.yml(which also starts the required middleware and the Zipkin UI). -
Run the
spring-cloud-sleuth-sample-streamapp and interact with it in a browser, just like the vanilla sample. If you are using a VM to run docker you might need to tunnel port 5672 to localhost, or change thespring.rabbbitmq.host. -
Goto
http://localhost:8080for zipkin web (if you are using a VM to run docker the host will be different).
The UI should look like the screenshot above.
To build the source you will need to install JDK 1.8.
Spring Cloud uses Maven for most build-related activities, and you should be able to get off the ground quite quickly by cloning the project you are interested in and typing
$ ./mvnw install
|
Note
|
You can also install Maven (>=3.3.3) yourself and run the mvn command
in place of ./mvnw in the examples below. If you do that you also
might need to add -P spring if your local Maven settings do not
contain repository declarations for spring pre-release artifacts.
|
|
Note
|
Be aware that you might need to increase the amount of memory
available to Maven by setting a MAVEN_OPTS environment variable with
a value like -Xmx512m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m. We try to cover this in
the .mvn configuration, so if you find you have to do it to make a
build succeed, please raise a ticket to get the settings added to
source control.
|
For hints on how to build the project look in .travis.yml if there
is one. There should be a "script" and maybe "install" command. Also
look at the "services" section to see if any services need to be
running locally (e.g. mongo or rabbit). Ignore the git-related bits
that you might find in "before_install" since they’re related to setting git
credentials and you already have those.
The projects that require middleware generally include a
docker-compose.yml, so consider using
Docker Compose to run the middeware servers
in Docker containers. See the README in the
scripts demo
repository for specific instructions about the common cases of mongo,
rabbit and redis.
|
Note
|
If all else fails, build with the command from .travis.yml (usually
./mvnw install).
|
The spring-cloud-build module has a "docs" profile, and if you switch
that on it will try to build asciidoc sources from
src/main/asciidoc. As part of that process it will look for a
README.adoc and process it by loading all the includes, but not
parsing or rendering it, just copying it to ${main.basedir}
(defaults to ${basedir}, i.e. the root of the project). If there are
any changes in the README it will then show up after a Maven build as
a modified file in the correct place. Just commit it and push the change.
If you don’t have an IDE preference we would recommend that you use Spring Tools Suite or Eclipse when working with the code. We use the m2eclipe eclipse plugin for maven support. Other IDEs and tools should also work without issue.
We recommend the m2eclipe eclipse plugin when working with eclipse. If you don’t already have m2eclipse installed it is available from the "eclipse marketplace".
Unfortunately m2e does not yet support Maven 3.3, so once the projects
are imported into Eclipse you will also need to tell m2eclipse to use
the .settings.xml file for the projects. If you do not do this you
may see many different errors related to the POMs in the
projects. Open your Eclipse preferences, expand the Maven
preferences, and select User Settings. In the User Settings field
click Browse and navigate to the Spring Cloud project you imported
selecting the .settings.xml file in that project. Click Apply and
then OK to save the preference changes.
|
Note
|
Alternatively you can copy the repository settings from .settings.xml into your own ~/.m2/settings.xml.
|
If you prefer not to use m2eclipse you can generate eclipse project metadata using the following command:
$ ./mvnw eclipse:eclipse
The generated eclipse projects can be imported by selecting import existing projects
from the file menu.
|
Important
|
There are 2 different versions of language level used in Spring Cloud Sleuth. Java 1.7 is used for main sources and
Java 1.8 is used for tests. When importing your project to an IDE please activate the ide Maven profile to turn on
Java 1.8 for both main and test sources. Of course remember that you MUST NOT use Java 1.8 features in the main sources. If you do
so your app will break during the Maven build.
|
Spring Cloud is released under the non-restrictive Apache 2.0 license, and follows a very standard Github development process, using Github tracker for issues and merging pull requests into master. If you want to contribute even something trivial please do not hesitate, but follow the guidelines below.
Before we accept a non-trivial patch or pull request we will need you to sign the contributor’s agreement. Signing the contributor’s agreement does not grant anyone commit rights to the main repository, but it does mean that we can accept your contributions, and you will get an author credit if we do. Active contributors might be asked to join the core team, and given the ability to merge pull requests.
This project adheres to the Contributor Covenant code of conduct. By participating, you are expected to uphold this code. Please report unacceptable behavior to [email protected].
None of these is essential for a pull request, but they will all help. They can also be added after the original pull request but before a merge.
-
Use the Spring Framework code format conventions. If you use Eclipse you can import formatter settings using the
eclipse-code-formatter.xmlfile from the Spring Cloud Build project. If using IntelliJ, you can use the Eclipse Code Formatter Plugin to import the same file. -
Make sure all new
.javafiles to have a simple Javadoc class comment with at least an@authortag identifying you, and preferably at least a paragraph on what the class is for. -
Add the ASF license header comment to all new
.javafiles (copy from existing files in the project) -
Add yourself as an
@authorto the .java files that you modify substantially (more than cosmetic changes). -
Add some Javadocs and, if you change the namespace, some XSD doc elements.
-
A few unit tests would help a lot as well — someone has to do it.
-
If no-one else is using your branch, please rebase it against the current master (or other target branch in the main project).
-
When writing a commit message please follow these conventions, if you are fixing an existing issue please add
Fixes gh-XXXXat the end of the commit message (where XXXX is the issue number).