https://github.com/NagleZhang/Binary-Bomb
该实验是书籍深入理解计算机操作系统中可以说是最有趣的实验之一,主要是使用 gdb,来拆解二进制(或者说程序)的一个文件,了解其运行逻辑。我们对这个程序的了解有:
- 有六个关卡,分别是 phase_1 - phase_6(不常规,应该从0开始的)
- 每一步都会要求你输入一个内容,就好像是密码,但是密码需要自己通过技术手段获取。
- 程序是 C 写的。
- bomb.c 是程序的总逻辑,可以看到每一个关卡都是调用一个 phase 开头的函数。
- bomb.c 是程序的总逻辑,可以看到每一个关卡都是调用一个 phase 开头的函数。
- Linux 系统,我是在云上面买了一台 Ubuntu 操作系统,你也可以自己去买
- gdb: 调试的基本工具
- Git: 克隆代码
| 寄存器名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| rax | 存储返回值 |
| rbx | 存储调用函数的地址 |
| rcx | 存储参数 |
| rdx | 存储参数 |
| rsi | 存储参数 |
| rdi | 存储参数 |
| rbp | 存储调用函数的地址 |
| rsp | 栈寄存器 |
| r8 | 存储参数 |
| r9 | 存储参数 |
| ... | ... |
mov: 数据搬迁指令
mov s, d move d to s
movb move byte
movw move word
movl move long
movq move quad word
leaq: Load Effective Address
leaq s,d move &d to s
inc: increment dec: decrement neg: negate not: complement
| 符号 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| r1 | 获取寄存器存储的内容. |
| $Imm | 立即数, 或者说直接使用展示的数据. |
| Imm | 内存中对应的 Imm 地址里面的内容. |
| (r1) | 根据寄存器里面存储的内容作为地址. |
| Imm(r1) | 根据寄存器里面存储的内容加上 Imm 作为地址. |
| (r1, r2) | 两个寄存器的内容相加作为地址. |
| Imm(r1,r2) | Imm + r1 + r2 内容相加,作为地址. |
| (,r1,4) | r1的内容乘以4,作为地址. |
| Imm(,r1,4) | Imm + r1 x 4, 作为地址. |
| (r1, r2, 4) | r1 + r2 x 4, 作为地址. |
| Imm(r1,r2,4) | Imm + r1 + r2 x 4, 作为地址. |
比如说,内存中有一群数据如下表所示
| Address | Value |
|---|---|
| 0x100 | 0xFF |
| 0x104 | 0xAB |
| 0x108 | 0x13 |
| 0x10C | 0x11 |
| Register | Value |
|---|---|
| rax | 0x100 |
| rcx | 0x1 |
| rdx | 0x3 |
以下是对应的指令以及寻址的结果
| 指令 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| rax | 0x100 |
| 0x104 | 0xAB |
| $0x108 | 0x108 |
| (rax) | 0xFF |
| 4(rax) | 0xAB |
| 9(rax,rdx) | 0x11 |
| 260(rcx,rdx) | 0x13 |
| 0xFC(,rcx,4) | 0xFF |
| (rax,rdx,4) | 0x11 |
| 位名称 | 位作用 |
|---|---|
| CF | Carry Flag. 判断最近的一条指令执行结果是否产生进位 |
| ZF | Zero Flag. 判断最近的一条指令的结果是否为零 |
| SF | Sign Flag. 判断最近的一条指令执行的结果是否为复数 |
| OF | Overflow Flag. 判断最近一条指令执行的结果是否产生符号位扩展(实际上就是有符号的产生进位) |
已C语言中, t = a+b (a,b,t 都为整数)为例。
CF 为 1: unsigned t < unsigned a (解释:因为a,b,t 为无符号数, a+b = t , 所以 a 肯定小于 t,如果不是,则肯定产生进位, cf 为 1)
ZF 为 1: t == 0
SF 为 1: t < 0
OF 为 1: (a < 0 == b < 0) && ( t < 0 != a < 0) (解释:前面的表达式的意思是,a 与 b的符号位相同,但是 t 与 a 的符号位不同。这个只有一个原因, a+b 溢出,产生进位)
- jmp 跳转
- je/jne: 上一条指令执行结果是否等于0
- js/jns: 上一条指令的执行结果是否为负数
- jg/jge: 上一条执行指令,是否符合大于/大于等于(无符号位)
- jl/jle: 上一条执行指令,是否符合小于/小于等于(无符号位)
- ja/jae: 上一条执行指令,是否符合大于/大于等于(有符号位)
- jb/jbe: 上一条执行指令,是否符合小于/小于等于(有符号位)
| 命令 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| quit | 退出 |
| run | 开始程序 |
| kill | 停止程序 |
| break | 断点 |
| break functionname | 在functionname 处打断点 |
| break *0x111111 | 在 0x111111 处打断点 |
| delete 1 | 删除 1号断点 |
| delete | 删除所有断点 |
| stepi | 单步调试(汇编级) |
| stepi 4 | 单步调试4次 |
| nexti | 程序级别下一条指令 |
| continue | 继续执行 |
| finish | 运行直到程序返回 |
| disas | 反汇编当前函数 |
| disas functionname | 反汇编functionname函数 |
| disas 0x11111111 | 反汇编0x11111111的函数 |
| disas 0x11111111, 0x22222222 | 反汇编两个地址范围的函数 |
| print /x $rip | 十六进制打印程序计数器 |
| print $rax | 打印$rax寄存器的内容 |
| print /x $rax | 十六进制打印$rax的内容 |
| print /t $rax | 二进制形式打印 $rax 的内容 |
| print 0x100 | 打印0x100的十进制 |
| print /x 555 | 16进制打印 555 |
| print /x ($rsp+8) | 十六进制打印 $rsp+8 地址的内容 |
| print *(long *) 0x11111111 | long 整型形式打印 0x11111111 地址的内容 |
| print *(long *) ($rsp + 8) | long 整形形式打印 $rsp +8 地址的内容 |
| x/2g 0x11111111 | 输出从 0x11111111地址 开始 2 word 长度的内容 |
| x/20b functioname | 输出从 functionname 地址开始的 20 byte 的内容 |
| info frame | 当前栈帧的信息 |
| info registers | 当前寄存器信息 |
| help | 帮助 |
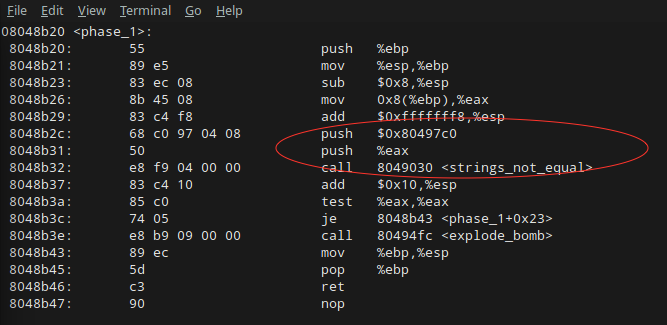
- 既然是 c 程序,必然会有一个 main 函数,我们可以通过这个地方入手,先通过 gdb 在 main 函数处打断点。
- 然后就是开始执行程序,把程序反汇编,形成汇编代码,找到第一关的地方,也就是 phase_1, 在 phase_1 处断点。
- 接下来我们运行到 phase_1 的断点处,再次查看 phase_1 的汇编代码,找到其相应逻辑,查看在哪一步进行了对比操作。
- 跟踪到对比的这一步。如果执行对比,那么肯定是有两个寄存器会需要存储需要对比的两个值。
- 我们可以查看寄存器里面的内容,然后直接拿到寄存器指定地址的内容。
- 破解问题
- 执行 git clone https://github.com/zhangnianlin/Binary-Bomb.git
- cd Binary-Bomb/Training
- chmod +x bomb: 给 bomb 执行权限
- gdb bomb: gdb 调试 bomb
- break main: 给main下端点,运行到到该处暂停
- break phase_1: 给 phase_1 下断点,运行到该处时候暂停。
- run: 开始运行
- disas: 反汇编
- 多次 stepi: 单步执行汇编代码
- info registers: 展示各个寄存器的状态
- x /d $registers: 显示寄存器所执行的内容
- This is lab assignments taken from my course on Programming Systems with Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective text book in use.
- The purpose of this lab assignment is to familiarize yourself with machine-level programs and the tools that you can use to understand them. You will do this by defusing a Binary Bomb produced by Dr. Evil, a nefarious Canadian.
- I take no credit on making this possible All credit goes to those people who have written the books. Some Solutions are my friends'
============
This is a very hard exercise with few resources on Google or whatever-web-search-tool out there, but it is awesome.
It is so hard at first that I almost cry solving this. However, by solving this you will sharpen your skill in understanding machine code (Assembly code).
At the end of the series you would've seen how several aspects of a C program are represented in machine code, for example: local variables, registers, conditionals, loops, switch statements, arrays, recursion, structs, etc.
Also, this is not where you find solutions to your homework if you are taking an equivalent course at your College, or happen to come accross here by Google search. This is where I provide you with numerous bombs to challenge you. This is not made to compromise the value of the exercise for both instructors and students using CS:APP.
=============
Read the bomblab-instructions.pdf file. Skip step 1.
You will see more than 30 folders with identical numbers (1551xxx). Don't panic. These numbers are my classmates' student IDs. Each of the folder contains a unique bomb. Although the solving technique is the same for all bombs, this was done to make sure no one can copy others' solutions. It is therefore very good for you to pratice.
My folder is 1551020.
In each of the folder, we have 3 files :
- bomb.c
this is the bomb in C code - bomb
an executable file for you to run and debug from - solution.txt
me and my friend's solution to defuse the bomb - Report folder
Explanation for solution in pdf file inside
You will need to take a look at the bomb.c .That file tells you that how they are making the bomb. Nevertheless, they hid the necessary source code for you to defuse the bomb, but leave you only the name of the phase that you need to by pass ( from phase_1 to phase_6 ).
What you need to do is : debug the code through the executable file bomb using a debugger (gdb, or IDA). It is crucial that you know how to use a debugger and understand Assembly Code.
Helpful Link for gdb : here. Pay close attention on : how to run a executable file, how to debug it, how to set breakpoints, how to disassemble, how to view register and their value...
That's all. Happy defusing.