rate.sx — console service for exploring (crypto)currencies exchange rates
- realtime¹ currencies and cryptocurrencies exchange rates information
- (crypto)currencies converter and calculator
- historical² exchange rates graphical representation
- clean, concise and very fast³ interface
- available everywhere, no installation needed
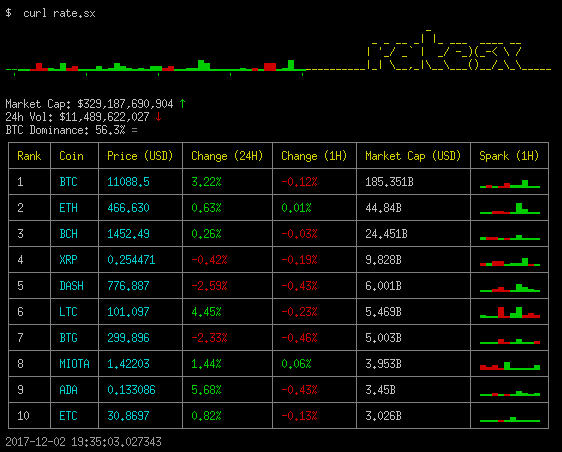
To get information about current exchange rates and market capitalization of the top ten cryptocoins in shell:
$ curl rate.sx
By default, all rates are represented in USD. To use some other currency, specify it in the domain name (lower-, upper- or mixed-case):
$ curl eur.rate.sx
Also, you can use rate.sx as (crypto)currency converter/calculator.
To convert some amount of (crypto)currencies into other (crypto)currency,
you have to specify the amount in the query line, after rate.sx/.
For example, to convert 10 Bitcoins (BTC) into US Dollars do:
$ curl rate.sx/10BTC
(WARNING: This feature is currently not supported. See #70) You can also combine different currencies and cryptocurrencies in the same query:
$ curl eur.rate.sx/1BTC+1BCH+1BTG # convert sum of the Bitcoins (BTC, BCH and BTG) into Euro (EUR)
$ curl rub.rate.sx/100ETH # convert 100 ETH into Russian ruble (RUB)
$ curl rate.sx/1BTC-10ETH # compare what is more: 1 BTC or 10 ETH
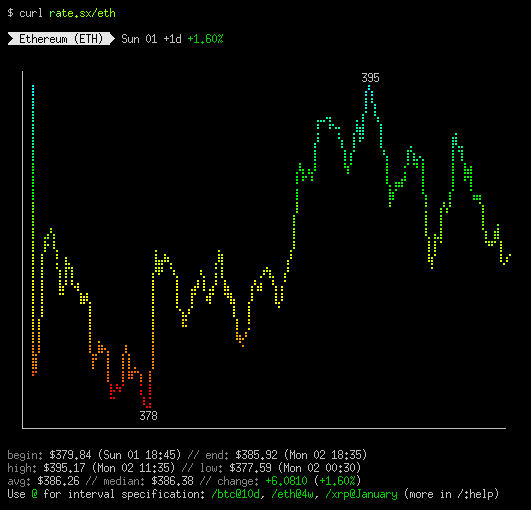
To show how cryptocurrency exchange rate was changing in time, specify name of the cryptocurrency in the URL.
For example, for Ethereum (ETH):
$ curl rate.sx/eth
By default, data for the last 24 hours is displayed, but you can specify
any³ other interval, using the @range notation (more on it below, in the Interval specification section).
To display output in some other currency (USD is used by default) or to compare a cryptocurrency
with another cryptocurrency, specify it in the domain name or after / in the query:
$ curl rate.sx/eth@30d # Ethereum to USD rate for the last 30 days
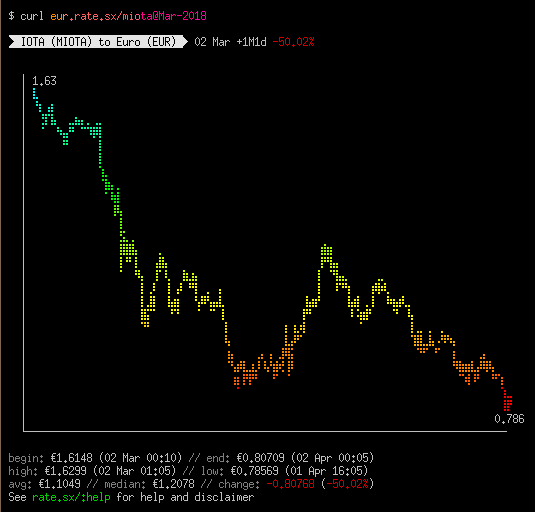
$ curl eur.rate.sx/btc@february # How Bitcoin (BTC) price in EUR changed in February
$ curl xlm.rate.sx/xrp@01-Feb-2018.. # Is it true that 1 XRP (Ripple) costs 3 XLM (Stellar) since Feb 1?
The time interval can be specified in many various ways. Though, most of them are intuitively clear, consult the Interval specification section just to see what interval formats are supported.
You can get the service in a web browser (though it is not its primary user interface), just type rate.sx in the location bar for that.
You can find actual list of the supported currencies in /:currencies and cryptocurrencies in /:coins.
32 different currencies and 500 most popular crypto currencies are supported at the moment.
For the list of all supported options see /:help:
$ curl rate.sx/:help
The most important options:
n=NUMBER number of cryptocurrencies to show (10 by default)
Options are specified after the ? sign in the URL.
They can be separated using the & sign (don't forget to escape or to quote it in the shell, because
it is a special shell symbol).
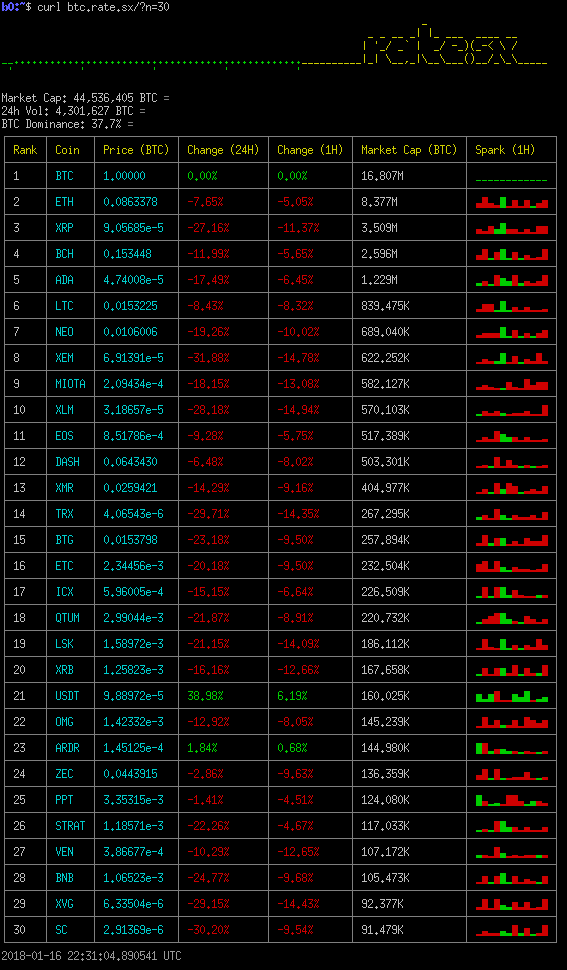
$ curl btc.rate.sx/?n=30
When showing exchange rates historical data, data for the last 24 hours is displayed by default.
To use other time interval you have to specify it in the url after coin name, separated with the @ sign.
For example, to get info for the last 4 days, add @4d:
$ curl rate.sx/eth@4d
The following time intervals specfiers are supported:
s Second
m Minute
h Hour
d Day (24 hours)
w Week
M Month (30 days)
y Year (365 days)
The specifiers have to be prefixed with an integer number (even if it is equal to 1) and can be combined together:
10d # 10 days
2w4d # 2 weeks and 4 days
1h30m # 1 hour and 30 minutes
In all these cases you specify the starting point of the interval, and the end is always the current time. That means, that information for the last time is shown.
You can specify some range in the past. There are three options for that:
- You specify the starting and the stopping date (and/or if needed time) separated with
..(the stopping date can be omited):
10d..5d # from 10 days ago to 5 days ago
2018-01-10..2018-01-20 # from 2018-01-10 to 2018-01-20
2018-03-15+12:00.. # from 2018-03-15 12:00 till now
- You specify the starting (or stopping) date/time and the delta separated with
+,-or+-:
2018-03-01+-3d # March 01 and +- 3 days around it
2018-03-15+1w # one week starting from 2018-03-15
2018-03-25-2w # two weeks to 2018-03-25
- You can specify some time range, and rate.sx try to guess what do you mean:
February # the whole February (this year)
02-Feb # the whole day, February 2 (this year)
Март # you can even use other languages (Март is March in Russian)
Don't afraid to be too inventive. If rate.sx can't parse your date, it will say about it. The toplevel interval grammar is summarized below.
Interval specifications grammar:
LENGTH
DATETIME
DATETIME..[DATETIME]
DATETIME+LENGTH
DATETIME-LENGTH
DATETIME+-LENGTH
By default, rate.sx shows rates of cryptocurrencies to USD (or any other currency if it is specified in the query as show above). It is possible to use a crypto currency as the unit. Keep in mind, that in the changes columns (and in the sparklines) difference to the historical rates is displayed, and not to the current rate. That is obviously the reason why spark for the rate currency to the same currency is always 1 (and change is 0).
This mode can be used to compare some cryptocurrency with the rest. Say, if we want to see, what cryptocurrencies are falling not so fast comparing to BTC (picture is done during the January 2018 correction):
We see here that nothing (except ARDR) from the top 30 (because we use ?n=30 here)
is falling slower than BTC (USDT is obviously an exception).
If we would use normal USD/EUR/GBP output, we could not find this out (at least not instantly).
Though rate.sx synchronizes with online cryptocurrencies exchanges every five minutes, we cannot guarantee absolute accuracy of the displayed exchange rates. You should always confirm current rates before making any transactions that could be affected by changes in the exchange rates. Cryptocurrency rates based on the data provided by exchanges APIs. All rates are for information purposes only and are subject to change without prior notice. Since rates for actual transactions may vary, we are not offering to enter into any transaction at any rate displayed. Displayed rates are composite prices and not intended to be used for investment purposes.
rate-sx.el — rate.sx in Emacs (courtesy of Dave Pearson @davep)
- Data update interval is 5 minutes (300 seconds)
- Historical data covers the range starting on 07 Jan 2018
- 99.9% of all queries are processed within 150ms
If you want to install the rate.sx server, you can do it. Keep in mind that you need some data datasource. A server without data is useless (of course, you can always use rate.sx as the datasource, though the point of such a strange configuration is not clear).
git clone github.com/chubin/rate.sx
cd rate.sx
virtualenv ve
ve/bin/pip install -r requirements.txt
ve/bin/python bin/srv.py
Configure the web server, that will be used to access the service (if you want to use a web frontend; it's recommended):
server {
listen [::]:80;
server_name rate.sx *.rate.sx;
access_log /var/log/nginx/rate.sx-access.log main;
error_log /var/log/nginx/rate.sx-error.log;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8004;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
proxy_send_timeout 90;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
proxy_buffers 4 32k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k;
expires off;
}
}