BlinkCard SDK is a delightful component for quick and easy scanning of payment cards. The SDK is powered with Microblink's industry-proven and world leading OCR, and offers:
- integrated camera management
- layered API, allowing everything from simple integration to complex UX customizations.
- lightweight and no internet connection required
- enteprise-level security standards
BlinkCard is a part of family of SDKs developed by Microblink for optical text recognition, barcode scanning, ID document, payment card scanning and many others.
You can start by watching our step-by-step tutorial, in which you’ll find out how to make BlinkCard SDK a part of your iOS app.
- Requirements
- Quick Start
- Advanced BlinkCard integration instructions
MBCRecognizerand available recognizers- List of available recognizers
- Localization
- Troubleshooting
- Size Report
- Additional info
SDK package contains BlinkCard framework and one or more sample apps which demonstrate framework integration. The framework can be deployed in iOS 13.0 or later. NOTE: The SDK doesn't contain bitcode anymore.
This Quick Start guide will get you up and performing OCR scanning as quickly as possible. All steps described in this guide are required for the integration.
This guide closely follows the BlinkCard-Sample app in the Samples folder of this repository. We highly recommend you try to run the sample app. The sample app should compile and run on your device, and in the iOS Simulator.
The source code of the sample app can be used as the reference during the integration.
- Download and install/update Cocopods version 1.10.0 or newer
- Since the libraries are stored on Git Large File Storage, you need to install git-lfs by running these commands:
brew install git-lfs
git lfs install-
Be sure to restart your console after installing Git LFS
-
Note: if you already did try adding SDK using cocoapods and it's not working, first install the git-lfs and then clear you cocoapods cache. This should be sufficient to force cocoapods to clone BlinkCard SDK, if it still doesn't work, try deinitializing your pods and installing them again.
-
Project dependencies to be managed by CocoaPods are specified in a file called
Podfile. Create this file in the same directory as your Xcode project (.xcodeproj) file. -
If you don't have podfile initialized run the following in your project directory.
pod init
- Copy and paste the following lines into the TextEdit window:
platform :ios, '13.0'
target 'Your-App-Name' do
pod 'MBBlinkCard', '~> 2.10.0'
end- Install the dependencies in your project:
$ pod install- From now on, be sure to always open the generated Xcode workspace (
.xcworkspace) instead of the project file when building your project:
open <YourProjectName>.xcworkspaceBlinkCard SDK is available via Carthage. Please check out Carthage documentation if you are new to Carthage.
- Install Carthage. Check out Installing Carthage guide. Please make sure you have Carthage => v0.38.0 installed.
- Create a Cartfile in the same directory where your .xcodeproj or .xcworkspace is.
- Add BlinkCard as a dependency to this Cartfile:
binary "https://github.com/BlinkCard/blinkcard-ios/blob/master/blinkcard-ios.json"- Run
carthage update --use-xcframeworks. - If successful, a Cartfile.resolved file and a Carthage directory will appear in the same directory as your Xcode project.
- Drag the binaries from
Carthage/Build/<platform>into your application’s Xcode project.
BlinkCard SDK is available as Swift Package. Please check out Swift Package Manager documentation if you are new to Swift Package Manager.
We provide a URL to the public package repository that you can add in Xcode:
https://github.com/blinkcard/blinkcard-swift-package-
Choose Swift package version
Download latest release (Download .zip or .tar.gz file starting with BlinkCard. DO NOT download Source Code as GitHub does not fully support Git LFS)
OR
Clone this git repository:
- Since the libraries are stored on Git Large File Storage, you need to install git-lfs by running these commands:
brew install git-lfs
git lfs install-
Be sure to restart your console after installing Git LFS
-
To clone, run the following shell command:
git clone [email protected]:BlinkCard/blinkcard-ios.git-
Copy BlinkCard.xcframework to your project folder.
-
In your Xcode project, open the Project navigator. Drag the BlinkCard.xcframework file to your project, ideally in the Frameworks group, together with other frameworks you're using. When asked, choose "Create groups", instead of the "Create folder references" option.
- Since BlinkCard.xcframework is a dynamic framework, you also need to add it to embedded binaries section in General settings of your target and choose option
Embed & Sign.
-
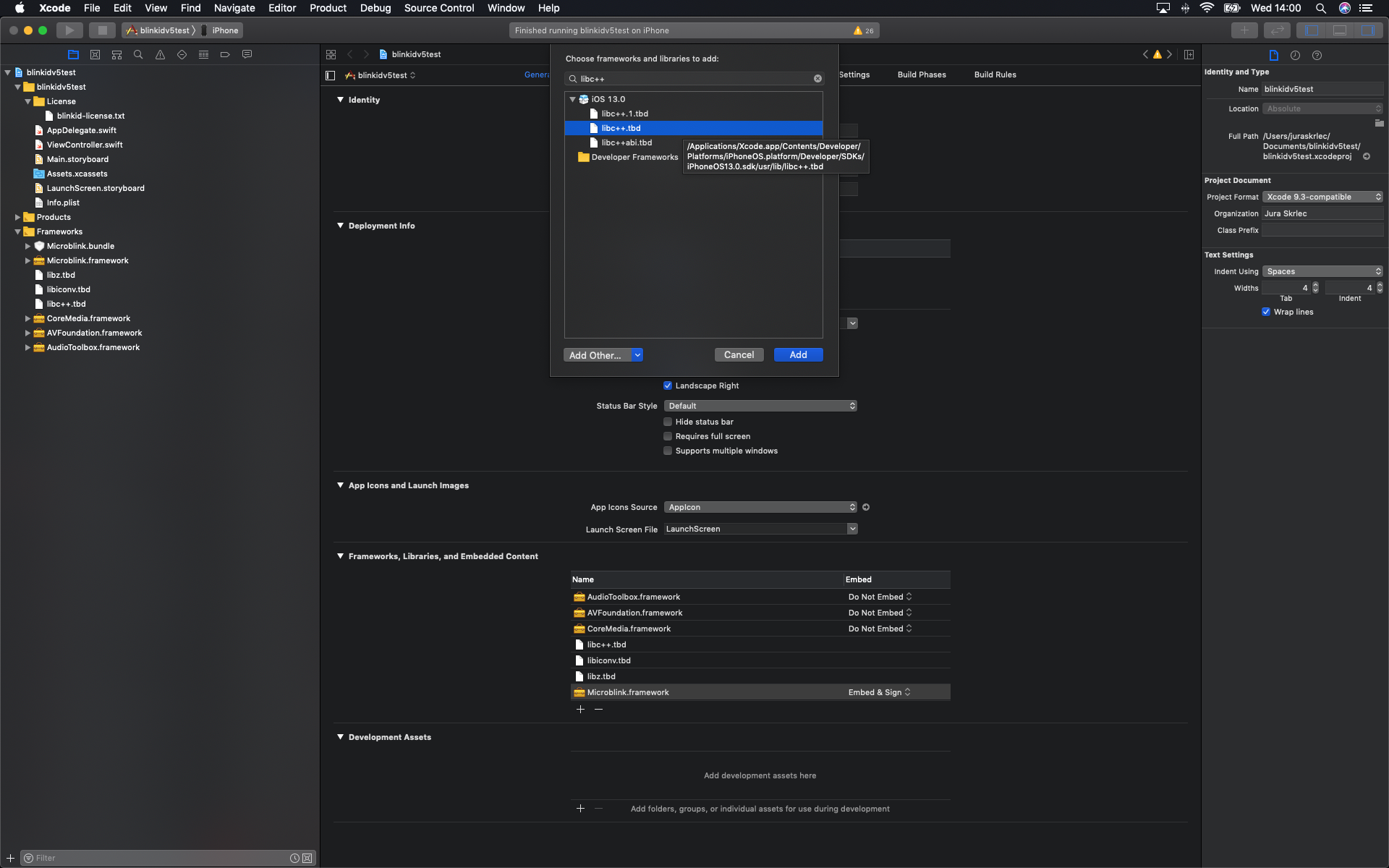
Include the additional frameworks and libraries into your project in the "Linked frameworks and libraries" section of your target settings.
- libc++.tbd
- libiconv.tbd
- libz.tbd
In files in which you want to use scanning functionality place import directive.
Swift
import BlinkCardObjective-C
#import <BlinkCard/BlinkCard.h>To initiate the scanning process, first decide where in your app you want to add scanning functionality. Usually, users of the scanning library have a button which, when tapped, starts the scanning process. Initialization code is then placed in touch handler for that button. Here we're listing the initialization code as it looks in a touch handler method.
Swift
class ViewController: UIViewController, MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewControllerDelegate {
var blinkCardRecognizer : MBCBlinkCardRecognizer?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
}
@IBAction func didTapScan(_ sender: AnyObject) {
/** Create BlinkCard recognizer */
blinkCardRecognizer = MBCBlinkCardRecognizer()
/** Create BlinkCard settings */
let settings : MBCBlinkCardOverlaySettings = MBCBlinkCardOverlaySettings()
/** Crate recognizer collection */
let recognizerList = [blinkCardRecognizer!]
let recognizerCollection : MBCRecognizerCollection = MBCRecognizerCollection(recognizers: recognizerList)
/** Create your overlay view controller */
let blinkCardOverlayViewController = MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController(settings: settings, recognizerCollection: recognizerCollection, delegate: self)
/** Create recognizer view controller with wanted overlay view controller */
let recognizerRunneViewController : UIViewController = MBCViewControllerFactory.recognizerRunnerViewController(withOverlayViewController: blinkCardOverlayViewController)
/** Present the recognizer runner view controller. You can use other presentation methods as well (instead of presentViewController) */
self.present(recognizerRunneViewController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
}Objective-C
@interface ViewController () <MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewControllerDelegate>
@property (nonatomic, strong) MBCBlinkCardRecognizer *blinkCardRecognizer;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[MBCMicroblinkSDK.sharedInstance setLicenseResource:@"blinkid-license" withExtension:@"key" inSubdirectory:@"" for:Bundle.main errorCallback:block];
}
- (IBAction)didTapScan:(id)sender {
/** Create BlinkCard recognizer */
self.blinkCardRecognizer = [[MBCBlinkCardRecognizer alloc] init];
/** Create BlinkCard settings */
MBCBlinkCardOverlaySettings* settings = [[MBCBlinkCardOverlaySettings alloc] init];
/** Create recognizer collection */
MBCRecognizerCollection *recognizerCollection = [[MBCRecognizerCollection alloc] initWithRecognizers:@[self.blinkCardRecognizer]];
/** Create your overlay view controller */
MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController *blinkCardOverlayViewController = [[MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController alloc] initWithSettings:settings recognizerCollection:recognizerCollection delegate:self];
/** Create recognizer view controller with wanted overlay view controller */
UIViewController<MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController>* recognizerRunnerViewController = [MBCViewControllerFactory recognizerRunnerViewControllerWithOverlayViewController: blinkCardOverlayViewController];
/** Present the recognizer runner view controller. You can use other presentation methods as well (instead of presentViewController) */
[self presentViewController:recognizerRunnerViewController animated:YES completion:nil];
}
@endA valid license key is required to initialize scanning. You can request a free trial license key, after you register, at Microblink Developer Hub.
You can include the license key in your app by passing a string or a file with license key.
Note that you need to set the license key before intializing scanning. Ideally in AppDelegate or viewDidLoad before initializing any recognizers.
You can pass the license key as a string, the following way:
Swift
MBCMicroblinkSDK.shared().setLicenseKey("LICENSE-KEY", errorCallback: block)Objective-C
[[MBCMicroblinkSDK sharedInstance] setLicenseKey:@"LICENSE-KEY" errorCallback:block];Or you can include the license key, with the code below. Please make sure that the file that contains the license key is included in your project and is copied during Copy Bundle Resources build phase.
Swift
MBCMicroblinkSDK.shared().setLicenseResource("license-key-file", withExtension: "key", inSubdirectory: "directory-to-license-key", for: Bundle.main, errorCallback: block)Objective-C
[[MBCMicroblinkSDK sharedInstance] setLicenseResource:@"license-key-file" withExtension:@"key" inSubdirectory:@"" forBundle:[NSBundle mainBundle] errorCallback:block];If the licence is invalid or expired then the methods above will throw an exception.
In the previous step, you instantiated MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController object with a delegate object. This object gets notified on certain events in scanning lifecycle. In this example we set it to self. The protocol which the delegate has to implement is MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewControllerDelegate protocol. It is necessary to conform to that protocol. We will discuss more about protocols in Advanced integration section. You can use the following default implementation of the protocol to get you started.
Swift
func blinkCardOverlayViewControllerDidFinishScanning(_ blinkCardOverlayViewController: MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController, state: MBCRecognizerResultState) {
// this is done on background thread
// check for valid state
if state == .valid {
// first, pause scanning until we process all the results
blinkCardOverlayViewController.recognizerRunnerViewController?.pauseScanning()
DispatchQueue.main.async(execute: {() -> Void in
// All UI interaction needs to be done on main thread
})
}
}
func blinkCardOverlayViewControllerDidTapClose(_ blinkCardOverlayViewController: MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController) {
// Your action on cancel
}Objective-C
- (void)blinkCardOverlayViewControllerDidFinishScanning:(MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController *)blinkCardOverlayViewController state:(MBCRecognizerResultState)state {
// this is done on background thread
// check for valid state
if (state == MBCRecognizerResultStateValid) {
// first, pause scanning until we process all the results
[blinkCardOverlayViewController.recognizerRunnerViewController pauseScanning];
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
// All UI interaction needs to be done on main thread
});
}
}
- (void)blinkCardOverlayViewControllerDidTapClose:(nonnull MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController *)blinkCardOverlayViewController {
// Your action on cancel
}This section covers more advanced details of BlinkCard integration.
- First part will cover the possible customizations when using UI provided by the SDK.
- Second part will describe how to embed
MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController's delegatesinto yourUIViewControllerwith the goal of creating a custom UI for scanning, while still using camera management capabilites of the SDK. - Third part will describe how to use the
MBCRecognizerRunner(Direct API) for recognition directly fromUIImagewithout the need of camera or to recognize camera frames that are obtained by custom camera management. - Fourth part will describe recognizer concept and available recognizers.
Within BlinkCard SDK there are several built-in overlay view controllers and scanning subview overlays that you can use to perform scanning.
MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController is overlay view controller best suited for performing scanning of payment cards for both front and back side. It has MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewControllerDelegate delegate which can be used out-of-the-box to perform scanning using the default UI. Here is an example how to use and initialize MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController:
Swift
/** Create your overlay view controller */
let blinkCardViewController : MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController = MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController(settings: blinkCardSettings, recognizerCollection: recognizerCollection, delegate: self)
/** Create recognizer view controller with wanted overlay view controller */
let recognizerRunneViewController : UIViewController = MBCViewControllerFactory.recognizerRunnerViewController(withOverlayViewController: blinkCardViewController)
/** Present the recognizer runner view controller. You can use other presentation methods as well (instead of presentViewController) */
self.present(recognizerRunneViewController, animated: true, completion: nil)Objective-C
MBCDocumentVerificationOverlayViewController *overlayVC = [[MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController alloc] initWithSettings:settings recognizerCollection: recognizerCollection delegate:self];
UIViewController<MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController>* recognizerRunnerViewController = [MBCViewControllerFactory recognizerRunnerViewControllerWithOverlayViewController:overlayVC];
/** Present the recognizer runner view controller. You can use other presentation methods as well (instead of presentViewController) */
[self presentViewController:recognizerRunnerViewController animated:YES completion:nil];As you can see, when initializing MBCDocumentVerificationOverlayViewController, we are sending delegate property as self. To get results, we need to conform to MBCDocumentVerificationOverlayViewControllerDelegate protocol.
SDK also provides an overlay view controller that allows users to edit scanned results and input data that wasn't scanned. Note that this view controller works only with MBCBlinkCardRecognizer.
Enable edit screen by setting property enableEditScreen = YES/true on MBCBlinkCardOverlaySettings. It is enabled by default.
If edit screen is enabled, you must implement blinkCardOverlayViewControllerDidFinishEditing delegate method from MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewControllerDelegate protocol to get edited results. It returns MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewController and MBCBlinkCardEditResult object. You can still get original results and images from MBCBlinkCardRecognizerResult.
Edit results view controller can be customised in several ways:
- to configure which fields should be displayed use
fieldConfigurationproperty of typeMBCBlinkCardEditFieldConfiguration - set your custom theme with
MBCBlinkCardEditOverlayTheme - for setting custom strings, please check out our Localization guide
SDK also provides options to use MBCBlinkCardEditViewController with Custom UI. Initalize it and, add it to { class_prefix }}BlinkCardEditNavigationController and present it.
let blinkCardEditViewController = MBCBlinkCardEditViewController(delegate: self)
let navigationController = MBCBlinkCardEditNavigationController(rootViewController: blinkCardEditViewController)self.blinkCardEditViewController = [[MBCBlinkCardEditViewController alloc] initWithDelegate:self];
self.navigationController = [[MBCBlinkCardEditNavigationController alloc] initWithRootViewController:self.blinkCardEditViewController];Please check our Samples for custom implementation of overlay view controller.
Overlay View Controller is an abstract class for all overlay views.
Its responsibility is to provide meaningful and useful interface for the user to interact with.
Typical actions which need to be allowed to the user are:
- intuitive and meaniningful way to guide the user through scanning process. This is usually done by presenting a "viewfinder" in which the user need to place the scanned object
- a way to cancel the scanning, typically with a "cancel" or "back" button
- a way to power on and off the light (i.e. "torch") button
BlinkCard SDK always provides it's own default implementation of the Overlay View Controller for every specific use. Your implementation should closely mimic the default implementation as it's the result of thorough testing with end users. Also, it closely matches the underlying scanning technology.
For example, the scanning technology usually gives results very fast after the user places the device's camera in the expected way above the scanned object. This means a progress bar for the scan is not particularly useful to the user. The majority of time the user spends on positioning the device's camera correctly. That's just an example which demonstrates careful decision making behind default camera overlay view.
To use your custom overlay with Microblink's camera view, you must first subclass MBCCustomOverlayViewController and implement the overlay behaviour conforming wanted protocols.
There are five MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController protocols and one overlay protocol MBCBlinkCardOverlayViewControllerDelegate.
Five RecognizerRunnerViewController protocols are:
MBCScanningRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBCDetectionRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBCOcrRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBCDebugRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegateMBCRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegate
In viewDidLoad, other protocol conformation can be done and it's done on recognizerRunnerViewController property of MBCOverlayViewController, for example:
Swift and Objective-C
self.scanningRecognizerRunnerViewControllerDelegate = self;In Quick Start guide it is shown how to use a default overlay view controller. You can now swap default view controller with your implementation of CustomOverlayViewController
Swift
let recognizerRunnerViewController : UIViewController = MBCViewControllerFactory.recognizerRunnerViewController(withOverlayViewController: CustomOverlayViewController)Objective-C
UIViewController<MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController>* recognizerRunnerViewController = [MBCViewControllerFactory recognizerRunnerViewControllerWithOverlayViewController:CustomOverlayViewController];This guide will in short present you how to process UIImage objects with BlinkCard SDK, without starting the camera video capture.
With this feature you can solve various use cases like: - recognizing text on images in Camera roll - taking full resolution photo and sending it to processing - scanning barcodes on images in e-mail etc.
DirectAPI-sample demo app here will present UIImagePickerController for taking full resolution photos, and then process it with BlinkCard SDK to get scanning results using Direct processing API.
Direct processing API is handled with MBCRecognizerRunner. That is a class that handles processing of images. It also has protocols as MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController.
Developer can choose which protocol to conform:
MBCScanningRecognizerRunnerDelegateMBCDetectionRecognizerRunnerDelegateMBCDebugRecognizerRunnerDelegateMBCOcrRecognizerRunnerDelegate
In example, we are conforming to MBCScanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate protocol.
To initiate the scanning process, first decide where in your app you want to add scanning functionality. Usually, users of the scanning library have a button which, when tapped, starts the scanning process. Initialization code is then placed in touch handler for that button. Here we're listing the initialization code as it looks in a touch handler method.
Swift
func setupRecognizerRunner() {
var recognizers = [MBCRecognizer]()
recognizer = MBCBlinkCardRecognizer()
recognizers.append(recognizer!)
let recognizerCollection = MBCRecognizerCollection(recognizers: recognizers)
recognizerRunner = MBCRecognizerRunner(recognizerCollection: recognizerCollection)
recognizerRunner?.scanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate = self
}
func processImageRunner(_ originalImage: UIImage) {
var image: MBCImage? = nil
if let anImage = originalImage {
image = MBCImage(uiImage: anImage)
}
image?.cameraFrame = true
image?.orientation = MBCProcessingOrientation.left
let _serialQueue = DispatchQueue(label: "com.microblink.DirectAPI-sample-swift")
_serialQueue.async(execute: {() -> Void in
self.recognizerRunner?.processImage(image!)
})
}
func recognizerRunner(_ recognizerRunner: MBCRecognizerRunner, didFinishScanningWith state: MBCRecognizerResultState) {
if recognizer.result.resultState == MBCRecognizerResultStateValid {
// Handle result
}
}Objective-C
- (void)setupRecognizerRunner {
NSMutableArray<MBCRecognizer *> *recognizers = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
self. recognizer = [[MBCBlinkCardRecognizer alloc] init];
[recognizers addObject: self.recognizer];
MBCRecognizerCollection *recognizerCollection = [[MBCRecognizerCollection alloc] initWithRecognizers:recognizers];
self.recognizerRunner = [[MBCRecognizerRunner alloc] initWithRecognizerCollection:recognizerCollection];
self.recognizerRunner.scanningRecognizerRunnerDelegate = self;
}
- (void)processImageRunner:(UIImage *)originalImage {
MBCImage *image = [MBCImage imageWithUIImage:originalImage];
image.cameraFrame = YES;
image.orientation = MBCProcessingOrientationLeft;
dispatch_queue_t _serialQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.microblink.DirectAPI-sample", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_async(_serialQueue, ^{
[self.recognizerRunner processImage:image];
});
}
- (void)recognizerRunner:(nonnull MBCRecognizerRunner *)recognizerRunner didFinishScanningWithState:(MBCRecognizerResultState)state {
if (self.recognizer.result.resultState == MBCRecognizerResultStateValid) {
// Handle result
}
}Now you've seen how to implement the Direct processing API.
In essence, this API consists of two steps:
- Initialization of the scanner.
- Call of
- (void)processImage:(MBCImage *)image;method for each UIImage or CMSampleBufferRef you have.
Some recognizers support recognition from NSString. They can be used through Direct API to parse given NSString and return data just like when they are used on an input image. When recognition is performed on NSString, there is no need for the OCR. Input NSString is used in the same way as the OCR output is used when image is being recognized.
Recognition from String can be performed in the same way as recognition from image.
The only difference is that user should call - (void)processString:(NSString *)string; on MBCRecognizerRunner.
The MBCRecognizer is the basic unit of processing within the SDK. Its main purpose is to process the image and extract meaningful information from it. As you will see later, the SDK has lots of different MBCRecognizer objects that have various purposes.
Each MBCRecognizer has a MBCRecognizerResult object, which contains the data that was extracted from the image. The MBCRecognizerResult object is a member of corresponding MBCRecognizer object its lifetime is bound to the lifetime of its parent MBCRecognizer object. If you need your MBCRecognizerResult object to outlive its parent MBCRecognizer object, you must make a copy of it by calling its method copy.
While MBCRecognizer object works, it changes its internal state and its result. The MBCRecognizer object's MBCRecognizerResult always starts in Empty state. When corresponding MBCRecognizer object performs the recognition of given image, its MBCRecognizerResult can either stay in Empty state (in case MBCRecognizerfailed to perform recognition), move to Uncertain state (in case MBCRecognizer performed the recognition, but not all mandatory information was extracted) or move to Valid state (in case MBCRecognizer performed recognition and all mandatory information was successfully extracted from the image).
As soon as one MBCRecognizer object's MBCRecognizerResult within MBCRecognizerCollection given to MBCRecognizerRunner or MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController changes to Valid state, the onScanningFinished callback will be invoked on same thread that performs the background processing and you will have the opportunity to inspect each of your MBCRecognizer objects' MBCRecognizerResult to see which one has moved to Valid state.
As soon as onScanningFinished method ends, the MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController will continue processing new camera frames with same MBCRecognizer objects, unless paused. Continuation of processing or reset recognition will modify or reset all MBCRecognizer objects's MBCRecognizerResult. When using built-in activities, as soon as onScanningFinished is invoked, built-in activity pauses the MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController and starts finishing the activity, while saving the MBCRecognizerCollection with active MBCRecognizer.
The MBCRecognizerCollection is is wrapper around MBCRecognizer objects that has array of MBCRecognizer objects that can be used to give MBCRecognizer objects to MBCRecognizerRunner or MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController for processing.
The MBCRecognizerCollection is always constructed with array [[MBCRecognizerCollection alloc] initWithRecognizers:recognizers] of MBCRecognizer objects that need to be prepared for recognition (i.e. their properties must be tweaked already).
The MBCRecognizerCollection manages a chain of MBCRecognizer objects within the recognition process. When a new image arrives, it is processed by the first MBCRecognizer in chain, then by the second and so on, iterating until a MBCRecognizer object's MBCRecognizerResult changes its state to Valid or all of the MBCRecognizer objects in chain were invoked (none getting a Valid result state).
You cannot change the order of the MBCRecognizer objects within the chain - no matter the order in which you give MBCRecognizer objects to MBCRecognizerCollection, they are internally ordered in a way that provides best possible performance and accuracy. Also, in order for SDK to be able to order MBCRecognizer objects in recognition chain in a best way possible, it is not allowed to have multiple instances of MBCRecognizer objects of the same type within the chain. Attempting to do so will crash your application.
This section will give a list of all MBCRecognizer objects that are available within BlinkCard SDK, their purpose and recommendations how they should be used to get best performance and user experience.
The MBCFrameGrabberRecognizer is the simplest recognizer in SDK, as it does not perform any processing on the given image, instead it just returns that image back to its onFrameAvailable. Its result never changes state from empty.
This recognizer is best for easy capturing of camera frames with MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController. Note that MBCImage sent to onFrameAvailable are temporary and their internal buffers all valid only until the onFrameAvailable method is executing - as soon as method ends, all internal buffers of MBCImage object are disposed. If you need to store MBCImage object for later use, you must create a copy of it by calling copy.
The MBCSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer is a special MBCecognizer that wraps some other MBCRecognizer and impersonates it while processing the image. However, when the MBCRecognizer being impersonated changes its MBCRecognizerResult into Valid state, the MBCSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer captures the image and saves it into its own MBCSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizerResult object.
Since MBCSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer impersonates its slave MBCRecognizer object, it is not possible to give both concrete MBCRecognizer object and MBCSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer that wraps it to same MBCRecognizerCollection - doing so will have the same result as if you have given two instances of same MBCRecognizer type to the MBCRecognizerCollection - it will crash your application.
This recognizer is best for use cases when you need to capture the exact image that was being processed by some other MBCRecognizer object at the time its MBCRecognizerResult became Valid. When that happens, MBCSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizer's MBCSuccessFrameGrabberRecognizerResult will also become Valid and will contain described image.
Payment card recognizers are used to scan payment cards.
The MBCBlinkCardRecognizer extracts the card number (PAN), expiry date, owner information (name or company title), IBAN, and CVV, from a large range of different card layouts.
MBCBlinkCardRecognizer is a Combined recognizer, which means it's designed for scanning both sides of a card. However, if all required data is found on the first side, we do not wait for second side scanning. We can return the result early. A set of required fields is defined through the recognizer's settings.
"Front side" and "back side" are terms more suited to ID scanning. We start the scanning process with the side containing the card number. This makes the UX easier for users with cards where all data is on the back side.
The MBCLegacyBlinkCardRecognizeris used for scanning the front and back side of Payment / Debit card.
The MBCLegacyBlinkCardEliteRecognizer scans back side of elite Payment / Debit card after scanning the front side and combines data from both sides.
The SDK is localized on following languages: Arabic, Chinese simplified, Chinese traditional, Croatian, Czech, Dutch, Filipino, French, German, Hebrew, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Malay, Portuguese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Thai, Vietnamese.
If you would like us to support additional languages or report incorrect translation, please contact us at help.microblink.com.
If you want to add additional languages yourself or change existing translations, you need to set customLocalizationFileName property on MBCMicroblinkApp object to your strings file name.
For example, let's say that we want to change text "Scan the front side of a document" to "Scan the front side" in BlinkID sample project. This would be the steps:
- Find the translation key in en.strings file inside BlinkCard.framework
- Add a new file MyTranslations.strings to the project by using "Strings File" template
- With MyTranslations.string open, in File inspector tap "Localize..." button and select English
- Add the translation key "blinkid_generic_message" and the value "Scan the front side" to MyTranslations.strings
- Finally in AppDelegate.swift in method
application(_:, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)addMBCMicroblinkApp.instance()?.customLocalizationFileName = "MyTranslations"
In case of problems with integration of the SDK, first make sure that you have tried integrating it into Xcode by following integration instructions.
If you have followed Xcode integration instructions and are still having integration problems, please contact us at help.microblink.com.
In case of problems with using the SDK, you should do as follows:
If you are getting "invalid licence key" error or having other licence-related problems (e.g. some feature is not enabled that should be or there is a watermark on top of camera), first check the console. All licence-related problems are logged to error log so it is easy to determine what went wrong.
When you have determine what is the licence-relate problem or you simply do not understand the log, you should contact us help.microblink.com. When contacting us, please make sure you provide following information:
- exact Bundle ID of your app (from your
info.plistfile) - licence that is causing problems
- please stress out that you are reporting problem related to iOS version of BlinkCard SDK
- if unsure about the problem, you should also provide excerpt from console containing licence error
If you are having problems with scanning certain items, undesired behaviour on specific device(s), crashes inside BlinkCard SDK or anything unmentioned, please do as follows:
- Contact us at help.microblink.com describing your problem and provide following information:
- log file obtained in previous step
- high resolution scan/photo of the item that you are trying to scan
- information about device that you are using
- please stress out that you are reporting problem related to iOS version of BlinkCard SDK
Here is a list of frequently asked questions and solutions for them and also a list of known problems in the SDK and how to work around them.
In demo everything worked, but after switching to production license I get NSError with MBCMicroblinkSDKRecognizerErrorDomain and MBCRecognizerFailedToInitalize code as soon as I construct specific MBCRecognizer object
Each license key contains information about which features are allowed to use and which are not. This NSError indicates that your production license does not allow using of specific MBCRecognizer object. You should contact support to check if provided licence is OK and that it really contains all features that you have purchased.
I get NSError with MBCMicroblinkSDKRecognizerErrorDomain and MBCRecognizerFailedToInitalize code with trial license key
Whenever you construct any MBCRecognizer object or, a check whether license allows using that object will be performed. If license is not set prior constructing that object, you will get NSError with MBCMicroblinkSDKRecognizerErrorDomain and MBCRecognizerFailedToInitalize code. We recommend setting license as early as possible in your app.
Make sure you link your app with iconv and Accelerate frameworks as shown in Quick start.
If you are using Cocoapods, please be sure that you've installed git-lfs prior to installing pods. If you are still getting this error, go to project folder and execute command git-lfs pull.
SDK crashes on armv7 devices if bitcode is enabled. We are working on it.
In my didFinish callback I have the result inside my MBCRecognizer, but when scanning activity finishes, the result is gone
This usually happens when using MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController and forgetting to pause the MBCRecognizerRunnerViewController in your didFinish callback. Then, as soon as didFinish happens, the result is mutated or reset by additional processing that MBCRecognizer performs in the time between end of your didFinish callback and actual finishing of the scanning activity. For more information about statefulness of the MBCRecognizer objects, check this section.
BlinkCard.framework is a dynamic framework which contains slices for all architectures - device and simulator. If you intend to extract .ipa file for ad hoc distribution, you'll need to preprocess the framework to remove simulator architectures.
Ideal solution is to add a build phase after embed frameworks build phase, which strips unused slices from embedded frameworks.
Build step is based on the one provided here: http://ikennd.ac/blog/2015/02/stripping-unwanted-architectures-from-dynamic-libraries-in-xcode/
APP_PATH="${TARGET_BUILD_DIR}/${WRAPPER_NAME}"
# This script loops through the frameworks embedded in the application and
# removes unused architectures.
find "$APP_PATH" -name '*.framework' -type d | while read -r FRAMEWORK
do
FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_NAME=$(defaults read "$FRAMEWORK/Info.plist" CFBundleExecutable)
FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH="$FRAMEWORK/$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_NAME"
echo "Executable is $FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH"
EXTRACTED_ARCHS=()
for ARCH in $ARCHS
do
echo "Extracting $ARCH from $FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_NAME"
lipo -extract "$ARCH" "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH" -o "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH-$ARCH"
EXTRACTED_ARCHS+=("$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH-$ARCH")
done
echo "Merging extracted architectures: ${ARCHS}"
lipo -o "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH-merged" -create "${EXTRACTED_ARCHS[@]}"
rm "${EXTRACTED_ARCHS[@]}"
echo "Replacing original executable with thinned version"
rm "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH"
mv "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH-merged" "$FRAMEWORK_EXECUTABLE_PATH"
doneLogging can be disabled by calling disableMicroblinkLogging method on MBCLogger instance.
We are delivering complete size report of our BlinkCard SDK based on our BlinkCard-sample-Swift sample project. You can check that here.
Complete API reference can be found here.
For any other questions, feel free to contact us at help.microblink.com.