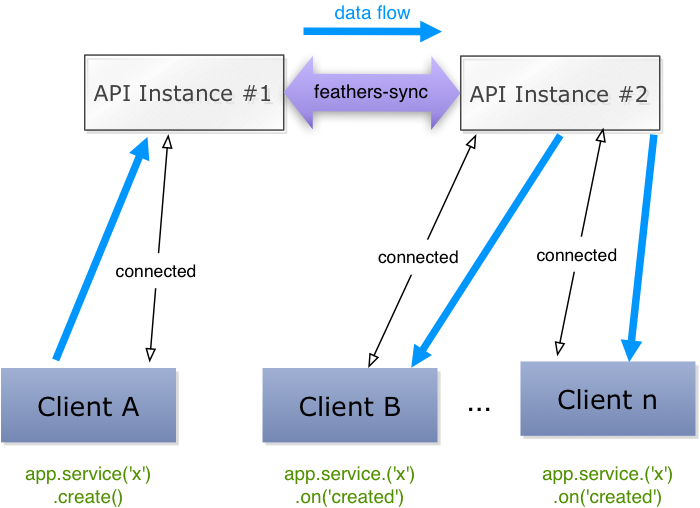
Synchronize service events between application instances
When running multiple instances of your Feathers application (e.g. on several Heroku Dynos), service events (created, updated, patched, removed) do not get propagated to other instances.
feathers-sync uses a messaging mechanism to propagate all events to all application instances. It currently supports:
This allows to scale real-time websocket connections to any number of clients.
The application initialized in the following example will use the local feathers-sync database and sync collection and share service events with every other instance connected to the same database:
const feathers = require('@feathers/feathers');
const sync = require('feathers-sync');
const app = feathers();
app.configure(sync({
uri: 'mongodb://localhost:27017/sync',
collection: 'events'
}));
app.use('/todos', todoService);When set up, app.sync will contain the following information:
type- The adapter type (e.g.mongodborredis)ready- A promise that resolves when the synchronization mechanism is ready
app.sync.ready.then(() => {
// Do things here
});feathers-sync can be disabled on the service method call level in a hook by setting the require('feathers-sync').SYNC property on the hook context to false:
const { SYNC } = require('feathers-sync');
app.service('messages').hooks({
after: {
create(context) {
// Don't synchronize if more than 1000 items were created at once
if(context.result.length > 1000) {
context[SYNC] = false;
}
return context;
}
}
});feathers-sync can be initialized either by specifying the type of adapter through the uri (e.g. mongodb://localhost:27017/sync) or using e.g. sync.mongodb directly:
// Configure MongoDB
app.configure(sync({
uri: 'mongodb://localhost:27017/sync',
collection: 'events'
}));
// Configure MongoDB with an existing connection
app.configure(sync.mongodb({
db: existingConnection
collection: 'events'
}));
// Configure Redis
app.configure(sync({
uri: 'redis://localhost:6379'
}));
app.configure(sync.redis({
db: redisInstance
}));uri- The connection string (must start withmongodb://)db- The MongoDB database object or connection string (alias foruri)collection(default:events) - The name of the capped event collectionmubsub- Settings to be passed to mubsub (e.g.{authSource:'admin'})channel- Mubsub channel synchronization options:size(default:5mb) - Max size of the collection in bytesmax- Max amount of documents in the collectionretryInterval(default:200ms) - Time in ms to wait if no docs are foundrecreate(default:true) - Recreate the tailable cursor when an error occurs (default istrue)
uri- The connection string (must start withredis://)db- The Redis database object or connection string (e.g.redis://localhost:6379)key- The key under which all synchronization events will be stored (default:feathers-sync)
uri- The AMQP connection string (e.g.amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672).key(default:feathers-sync) - The name exchange where sync messages will be publishedamqpConnectionOptions- AMQP connection options
When listening to service events with feathers-sync, all events are going to get propagated to all clients. This means, that your event listeners should not perform any actions that change the global state (e.g. write something into the database) because every server instance will perform the same action.
Instead, event listeners should only be used to update the local state (e.g. a local cache) and send real-time updates to all its clients.
If you need to perform actions, for example setting up a first blog post after a new user has been created, add it to the service method itself (which will only run on its own instance) or use a Feathers after hook.
feathers-sync allows to implement custom adapters using the sync-in and sync-out events on the application:
const { core } = require('feathers-sync');
const myMessagingService = {
publish(data) {
// send data here
},
subscribe(callback) {
// subscribe to message queue and emit data
}
}
module.exports = config => {
return app => {
app.configure(core);
app.sync = {
type: 'custom',
ready: new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// resolve when client is ready
// reject on connection error
})
};
// Sent every time a service
app.on('sync-out', data => {
// Publish `data` to the message queue
myMessagingService.publish(data);
});
myMessagingService.subscribe(data => {
// Send the synchronization event to the application
app.emit('sync-in', data);
});
};
};The data for the sync-in event should be in the same form as the one that is sent by sync-out (currently it includes { event, path, data, context }).
Copyright (c) 2018 Feathers contributors
Licensed under the MIT license.