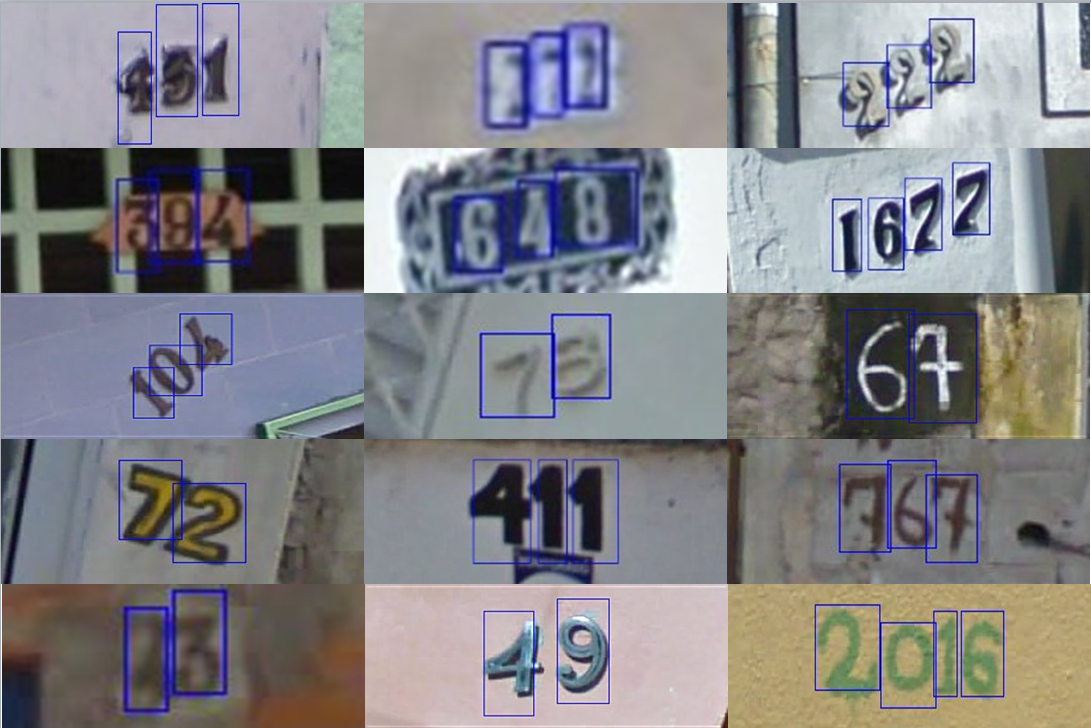Localizing the the digits in images from the Google SVHN dataset. Link to dataset: http://ufldl.stanford.edu/housenumbers/
Please cite our work if Google-Street-View-House-Numbers-Digit-Localization and our approach helps your research.
@Misc{SVHNLocalization,
author = {{Dhall*}, A. and {Chandak*} Y.}
title = "{Google-Street-View-House-Numbers-Digit-Localization}",
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/ankitdhall/Google-Street-View-House-Numbers-Digit-Localization}},
year = {2015}
}
Recall:0.6955
Precision:0.6024
F-score:0.6456
img_num num_of_boxes x1 y1 w1 h1 x2 y2 w2 h2 . . . xn yn wn hn
Each line contains an image number followed by the number of bounding boxes in the image and 4-tuple of top x co-ordinate, y co-ordinate, width and height
The above format is for both groundtruth as well as CPU generated bounding boxes.
intersectionOverUnion.txt contains the ratios of the intersection of CPU and groundtruth boxes to that of their union for each digit.
We prepared the dataset for training by segregating individual digits into 10 classes. To generate negative data for training we cropped random samples from images where digits were absent. The training data was prepared by padding 10% of the height and resizing the digits to 20x30 pixels.
Data was trained by means of Linear Binary Pattern classifier on OpenCV in C++. The classifier ran for 15 levels of training on 2500 instances of each of the ten digits with 3000 negative examples in the data set.
We trained 10 separated binary classifiers for each of the digits 0 through 9. Each binary classifier detected presence or absence of a particular digit. This group of binary classifiers was cascaded on the image with windows. We ran multi-scale classification with both resizing and rescaling images by various factors.
The ten classifiers gave numerous bounding boxes; sometimes as many as 130 on a single image! Some of these boxes were irregular in size. Assuming that the actual digits have a similar aspect ratio and the order of the area is similar we removed smaller and larger boxes. This was done by considering those whose areas were closer to the mean area in terms of standard deviations. Such processing helped improve accuracy and removal of boxes that would have been false positives.
Still there were very many bounding boxes around the digits. To reduce the number of redundant detections we used the idea of clustering. We took a running mean of bounding boxes and considered merging boxes if the overlapped at least 50% onto the current cluster box (obtained from averaging bounding rectangles currently in the cluster). When this criterion failed to meet we closed the current cluster and started with a new one. This ensured that redundant boxes generated were the bounding boxes were kept to a minimal.
We measured the results on the first 100 images of the SVHN dataset.
Total number of images: 100
Total number of individual digits: 220
Number of digits detected by CPU algorithm: 254
Number of bounding boxes with intersection over union ratio > 0.50: 153
Recall:0.6955
Precision:0.6024
F-score:0.6456
The accuracy was measured using the intersection area over union area of ground truth and CPU generated results. If this ratio is greater than 0.5 we consider that the digit has been localized.
The description of the format in which results are stored is as follows:
Please see the /results folder for more information and specific details.
img_num num_of_boxes x1 y1 w1 h1 x2 y2 w2 h2 . . . xn yn wn hn
img_num num_of_boxes x1 y1 w1 h1 confidenceScore1 x2 y2 w2 h2 confidenceScore2 . . . xn yn wn hn confidenceScoren
Each line contains an image number followed by the number of bounding boxes in the image and 4-tuple of top x co-ordinate, y co-ordinate, width and height
The above format is for both groundtruth as well as CPU generated bounding boxes.
contains the ratios of the intersection of CPU and groundtruth boxes to that of their union for each digit.
the confidence here is the number of boxes that were clustered together to get the box on the current digit in question. The confidence is an integer.
this has confidence in terms of a ratio = clustersize of this digit/max clustersize in the image. Confidence is a float value belonging to (0,1]