The AerisWeather Android SDK allows a developer to quickly and easily add weather content and functionality to their android applications. It utilizes the AerisWeather API backend for data loading and is built on top of an object mapping system that efficiently loads requested weather content into third-party Android applications, greatly reducing the amount of code and development needed on the developer end.
View the latest installation and implementation details at AerisWeather under the AerisWeather Android SDK toolkit documentation.
Before you can begin using the AerisWeather Android SDK in your project, you will need to download the latest version of the SDK and ensure that you have the required AerisWeather API keys for your application.
Step 1: Get the files. Download the latest version of the AerisWeather Android SDK.
Step 2: Get access to the AerisWeather API.
To use the AerisWeather API, you will need to have valid access keys. Access keys are obtained by registering your application/namespace. To register your application, log in to AerisWeather with your account and look for "APPS". Don't have an AerisWeather account? You can get one for free here.
Step 3: Determine which components of the AerisWeather Android SDK you need for your project:
This is the base library for accessing the AerisWeather API. If you are planning to use the AerisWeather API for data without a map component, this is all you need.
This library provides access to AerisWeather mapping features such as radar, satellite, warnings, etc. The map library includes a dependency on the AerisWeather Core library, so you won't need to download the Core library separately. If you are planning to use AerisWeather to create weather maps for your Android project, this is the library for you. Step 4: Include the AerisWeather Android SDK files in your project's Gradle.build file(s).
The SDK includes a demo app to help get you started. To allow the demo project to access data using the AerisWeather API, you will need to configure the AerisWeather Demo project to use your unique credentials. Just sign up for a free developer account and register yourself and your application with AerisWeather, to get your unique client Id and secret.
Log in to your account to register your application for an API access key. Each application requires its own unique access key. Check out the API docs for more info.*
Add the client_id and the secret_key to the res/values/strings.xml of the Demo application. Specifically, the aeris_client_id and aeris_client_secret values.
- The DemoApp namespace/package name can be found around line 3 of the manifest.xml file and will look similar to: com.example.demoaerisproject
The AerisWeather Maps library project currently supports only Google maps. To use the Google Maps API, you'll need to register for an API key in the Google Maps API Console. Visit the Google Maps Android API page and click the "GET A KEY" button for detailed instructions on getting your Google Maps key.
Once you have your Google Maps API account set up:
On the Services page, verify that the “Google Maps Android API v2” is enabled. In the left navigation bar, click API Access. On the resulting page, click Create New Android Key. In the resulting dialog, enter the SHA-1 fingerprint, then a semicolon, then The Demo project’s package name. For example: FE:6D:DC:73:D5:22:C1:43:67:71:9F:65:93:AE:A6:66:6D:44:5A:75;com.example.demoaerisproject The Google API Console responds by displaying a Key for Android apps (with certificates) followed by a forty-character API key.
In your Android project, update the meta tag in the Demo Project’s Manifest:
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.maps.v2.API_KEY"
android:value="your_api_key" />
Note: Your SHA1 can be obtained in Android Studio by running the "signingReport" task under the "Gradle projects" section.
The following permissions are required in order to use the AerisWeather Android SDK in the application. Please add these to your AndroidManifest.xml:
<manifest>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COURSE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
</manifest>
The AerisWeather Core and AerisWeather Maps libraries are available through Maven Central. To add these dependencies to your project add these lines to your build.gradle file.
AerisWeather Core:
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
+ implementation 'com.aerisweather:aeris-core-lib:#.#.#@aar' // kotlin
- compile 'com.aerisweather:aeris-core-lib:#.#.#@aar' // java
}AerisWeather Maps:
(Note: you do not need to add AerisWeather Core seperately if you are using AerisWeather Maps - the core lib is referenced in the maps lib)
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
+ implementation ('com.aerisweather:aeris-maps-lib:#.#.#@aar') { // kotlin
- compile ('com.aerisweather:aeris-maps-lib:#.#.#@aar') { // java
transitive true
}
+ implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-maps:#.#.#' // kotlin
- compile 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-maps:#.#.#' // java
- compile 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.4.1'
}Specify other locations (under Search) for alternates from your Android system default.


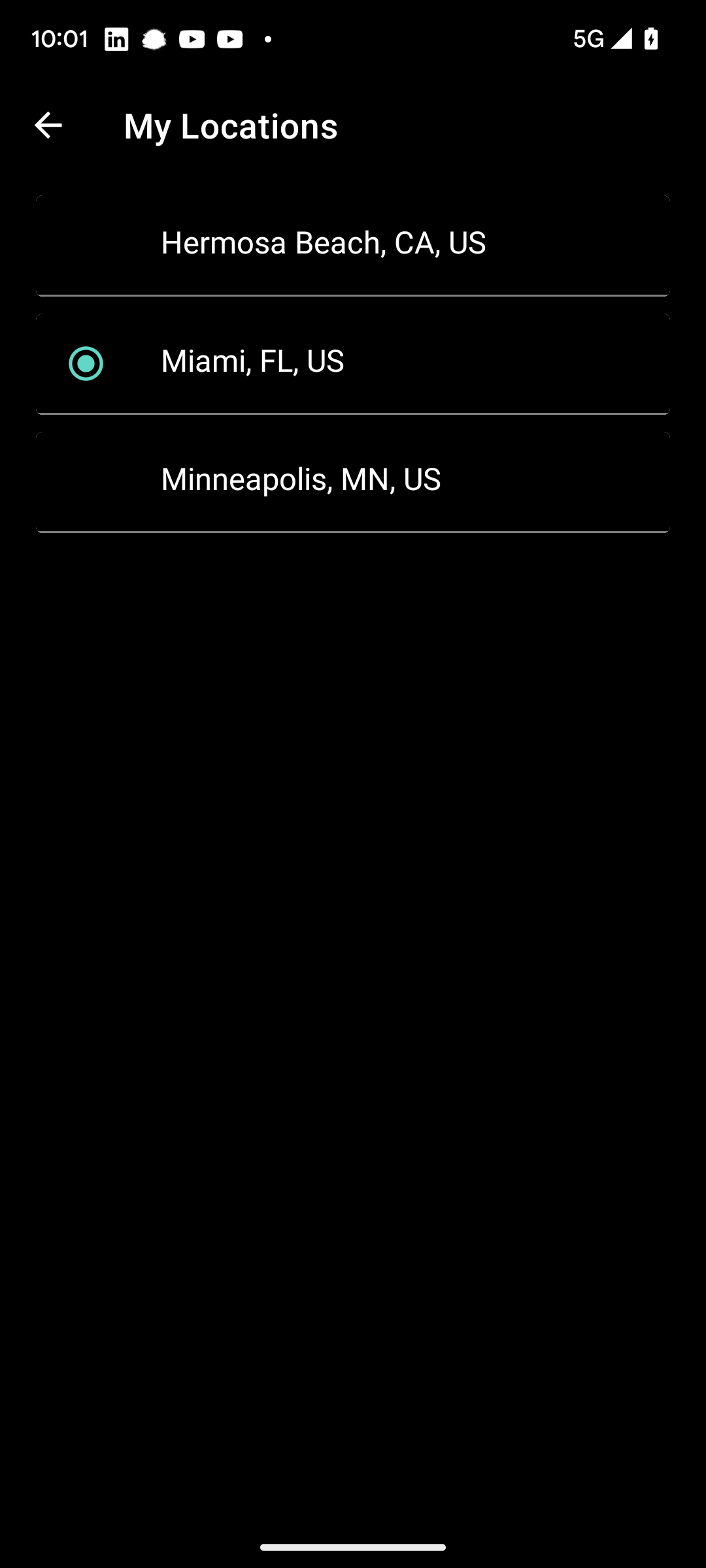

Enable notification or use metrics under the settings panel.

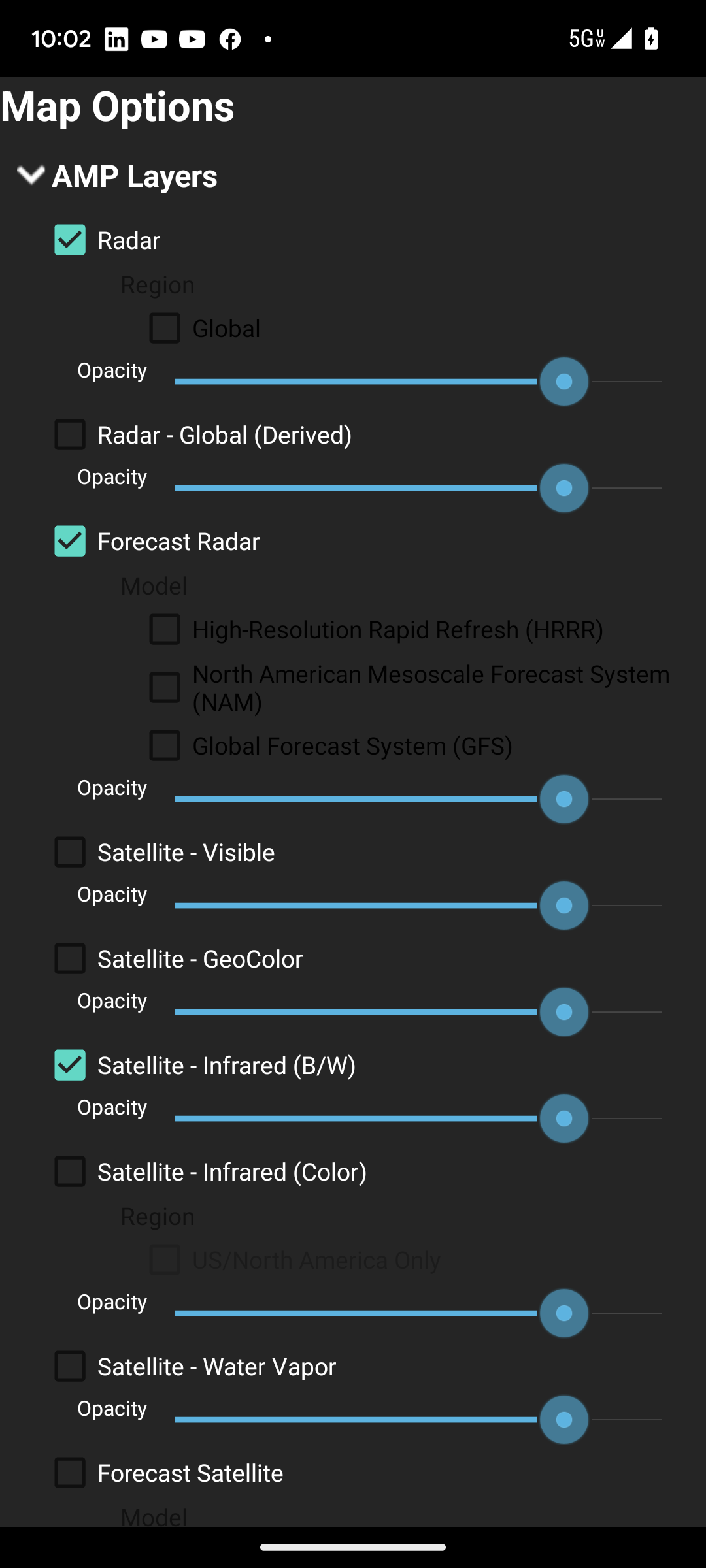
Specify layers (under the menu) to customize the interactive map.

Version: Chipmunk|2021.2.1 Patch2 or later
Android Gradle Plugin Version 7.2.2
Gradle Version 7.5.1.
AerisWeather API Docs.
AerisWeather API Signup.
AerisWeather Android SDK.
AerisWeather Android Core Library Javadocs.
AerisWeather Android Maps.
AerisWeather Android Maps Library Javadocs.