-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Developing New Tasks in SAMOA
A task is a machine learning related activity such as a specific evaluation for a classifier. Example of a task is the prequential evaluation task i.e. a task that uses each instance for testing and training a model built using a specific classification algorithm. A task corresponds to a topology in SAMOA.
In this tutorial, we will develop a simple Hello World task which will be explained below.
The Hello World task consists of a source processor, a stream and a destination processor with a parallelism hint setting. The source processor will generate a random integer which will be send into the destination processors. Figure below shows the layout of Hello World task.
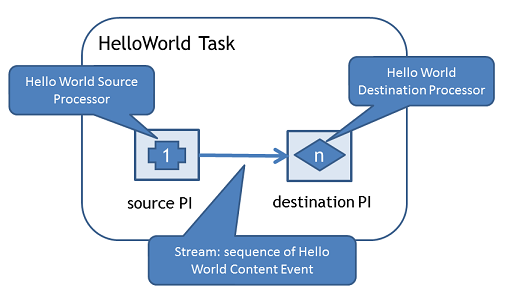
To develop the task, create a new class that extends samoa.tasks.Task and net.samoaproject.javacliparser.Configurable.
init method is where we instantiate the necessary ProcessingItems, instantiate the necessary Streams and connect the source processor with the destination processor.
Using current API, we need two classes to start a task in SAMOA. They are a source processor which implements Processor and a topology starter which implements TopologyStarter. In this tutorial, the source processor is HelloWorldSourceProcessor with its associated HelloWorldTopologyStarter.
SAMOA runtime invokes start method of TopologyStarter and this start method contains the specific method/portions of source processor to send content events through the stream. In this tutorial, HelloWorldSourceProcessor exposes sendInstance method to send HelloWorldContentEvent via HelloWorldStream. Moving forward, these two classes could be refactored to only use one class to start the topology.
Here is sendInstance method in HelloWorldSourceProcessor:
public void sendInstance(){
int count = 0;
while(count < maxInst){
this.helloWorldStream.put(new HelloWorldContentEvent(rnd.nextInt(), false));
count++;
}
this.helloWorldStream.put(new HelloWorldContentEvent(-1, true));
}
Here is the corresponding HelloWorldTopologyStarter:
public static class HelloWorldTopologyStarter implements TopologyStarter{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5445314667316145715L;
private final HelloWorldSourceProcessor hwsp;
public HelloWorldTopologyStarter(HelloWorldSourceProcessor hwsp){
this.hwsp = hwsp;
}
@Override
public void start() {
this.hwsp.sendInstance();
}
}
We also need to create a new type of content event called HelloWorldContentEvent and this content event contains helloWorldData which is just an integer.
public class HelloWorldContentEvent implements ContentEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2406968925730298156L;
private final boolean isLastEvent;
private final int helloWorldData;
public HelloWorldContentEvent(int helloWorldData, boolean isLastEvent){
this.isLastEvent = isLastEvent;
this.helloWorldData = helloWorldData;
}
@Override
public String getKey() {
return null; //do nothing it's key-less content event
}
@Override
public void setKey(String str) {
//do nothing, it's key-less content event
}
@Override
public boolean isLastEvent() {
return isLastEvent;
}
public int getHelloWorldData(){
return helloWorldData;
}
}
The Hello World Source Processor and its associated Topology Starter can be found here. Moreover, the Hello World Content Event can be found here.
The destination processor for SAMOA is pretty straightforward and it will print the HelloWorldData from HelloWorldContentEvent.
class HelloWorldDestinationProcessor implements Processor {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6042613438148776446L;
private int processorId;
@Override
public boolean process(ContentEvent event) {
if(event instanceof HelloWorldContentEvent){
HelloWorldContentEvent hwce = (HelloWorldContentEvent) event;
System.out.println(processorId + ", HelloWorldData: " + hwce.getHelloWorldData());
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(int id) {
this.processorId = id;
}
@Override
public Processor newProcessor(Processor p) {
return new HelloWorldDestinationProcessor();
}
}
The Hello World destination processor can be found here.
To put all the components together, we need to back to class HelloWorldTask. The most important part is in the init method. Since SAMOA does not contain dynamic binding yet, we need to explicitly instantiate TopologyBuilder in the beginning of init method.
if(builder == null){
builder = new TopologyBuilder();
logger.debug("Sucessfully instantiating TopologyBuilder");
builder.initTopology(evaluationNameOption.getValue());
logger.debug("Sucessfully initializing SAMOA topology with name {}", evaluationNameOption.getValue());
}
Next step is to instantiate the source processor and the topology starter. Once these two objects are instantiated, TopologyBuilder creates an entrance processor based on the two objects. Note that the topology starter should be exposed via getTopologyStarter method so that the underlying components could start the topology properly.
//create sourceProcesor
sourceProcessor = new HelloWorldSourceProcessor(instanceLimitOption.getValue());
starter = new HelloWorldTopologyStarter(sourceProcessor);
builder.addEntranceProcessor(sourceProcessor, starter);
After adding the entrance processor to the topology, we want to create a stream that is originated from it. We should use create stream method of TopologyBuilder and after that, we need to set explicitly the corresponding stream of HelloWorldSourceProcessor by using setHelloWorldStream method.
//create Stream
Stream stream = builder.createStream(sourceProcessor);
sourceProcessor.setHelloWorldStream(stream);
Now it's time to create the HelloWorld destination processor and connect it to the stream.
//create Destination Processor
destProcessor = new HelloWorldDestinationProcessor();
builder.addProcessor(destProcessor, helloWorldParallelismOption.getValue());
builder.connectInputShuffleStream(stream, destProcessor);
Once we create all the components, we should use the builder to build the topology. We should expose this topology by using getTopology method.
//build the topology
helloWorldTopology = builder.build();
logger.debug("Sucessfully building the topology");
The complete HelloWorldTask could be found here.