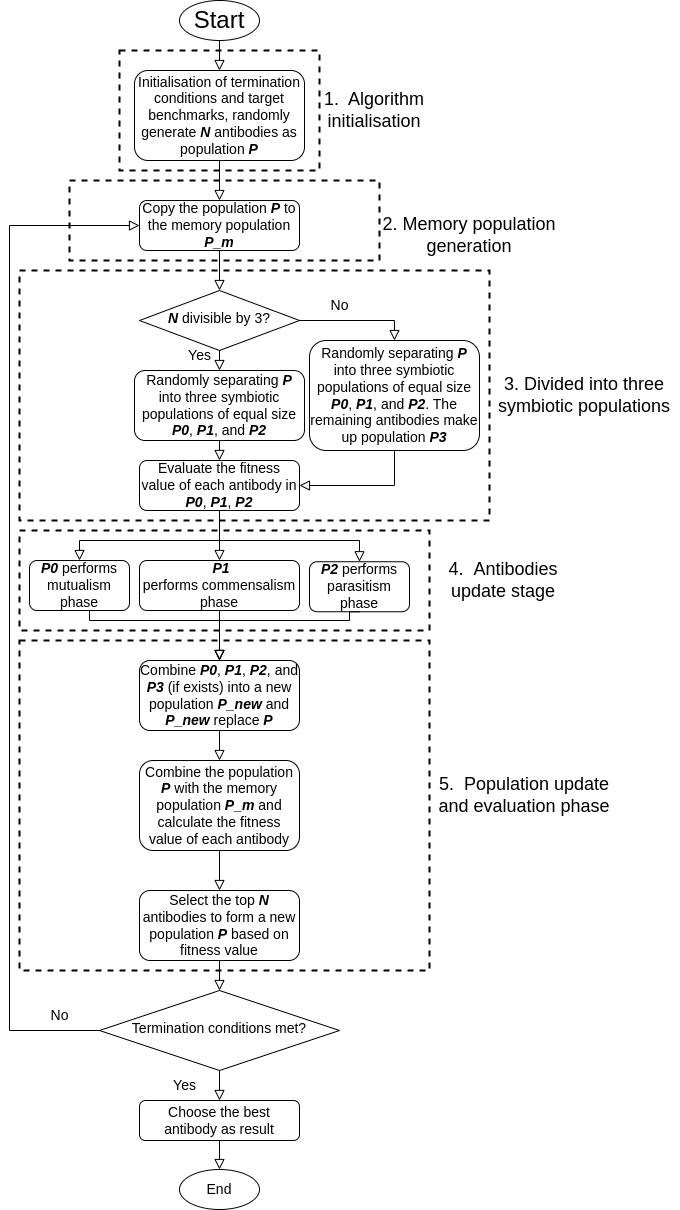
SAIS (Symbiotic Artificial Immune Systems) is a novel Artificial Immune System inspired by symbiotic relationships observed in biology. It leverages the three key stages of symbiotic relationships—mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism—for population updating, as seen in the Symbiotic Organisms Search (SOS) algorithm. This approach effectively tackles the challenges associated with large population sizes and enhances population diversity, issues that traditional AIS and SOS algorithms struggle to address efficiently. This project aims to provide an open-source implementation of the SAIS algorithm to foster innovation and research in bio-inspired computing and immune-inspired algorithms.
📦 Official Python Package Index (PyPI) Package: SAIS.
📚 The paper has been published in the 'ACM Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO '24 Companion)'🎉.
🎊 The preprint is available on arXiv.
- Implementation of the Symbiotic Artificial Immune Systems algorithm.
- Easy to calculate the objective value of the function.
- Customizable for different optimisation needs.
- Support for multiple benchmark functions.
Ensure the following dependencies are installed on your system:
- Python 3.x
- numpy
📥 Install sais using pip:
pip install sais🔥 Example usage, here’s how to use SAIS to optimise a function:
from sais import run
# define your benchmark number and population size
population_size = 2000
# number from Benchmarks List
benchmark_number = 1
run(population_size, benchmark_number)📌 Example output:
Starting SAIS for benchmark 1 with population size 2000.
Iterations Number: 8
Running Time: 0.18377017974853516 Secounds
Best Fitness: 4.523554492464579e-10
Best Antibody: [2.9999822 0.49999976]🎯 Function evaluation, get the function’s value at a given point:
import numpy as np
from sais import benchmark_result
x = np.random.uniform(np.pi, np.pi, 2)
y = sais.benchmark_result(x, 2)
print(x, y)### Benchmarks (Name, Range, Global Minimum)
# F1 = Beale [-4.5; 4.5]; 0
# F2 = Easom [-100,100]; -1
# F3 = Matyas [-10,10]; 0
# F4 = Bochachvesky 1 [-100,100]; 0
# F5 = Booth [-10, 10]; 0
# F6 = Michalewicz 2[0,pi]; -1.8013
# F7 = Schaffer [-100; 100]; 0
# F8 = Six Hump Camel Back [-5; 5]; -1.03163
# F9 = Bochachvesky 2 [-100,100]; 0
# F10 = Bochachvesky 3 [-100,100]; 0
# F11 = Shubert [-10,10]; -186.73
# F12 = Colville [-10,10]; 0
# F13 = Michalewicz 5 [0,pi]; -4.6877
# F14 = Zakharov[-5,10]; 0
# F15 = Michalewicz 10 [0,pi]; -4.6877
# F16 = Step [-5.12; 5.12]; 0
# F17 = Sphere [-100,100]; 0
# F18 = SumSquares [-10, 10]; 0
# F19 = Quartic [-1.28,1.28]; 0
# F20 = Schwefel 2.22 [-10,10]; 0
# F21 = Schwefel 1.2 [-10,10]; 0
# F22 = Rosenbrock [-30,30]; 0
# F23 = Dixon-Price [-10, 10]; 0
# F24 = Rastrigin [-5.12; 5.12];
# F25 = Griewank [-600,600]; 0
# F26 = Ackley [-600; 600]; 0
For any questions or suggestions, please contact us via:
This project is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.
@inproceedings{song2024sais,
title={SAIS: A Novel Bio-Inspired Artificial Immune System Based on Symbiotic Paradigm},
author={Song, Junhao and Yuan, Yingfang and Pang, Wei},
booktitle={Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion},
pages={2115--2118},
year={2024}
}
We extend our sincere thanks to 🏛️ Imperial College London & Heriot-Watt University for their support and the academic environment that facilitated our research.