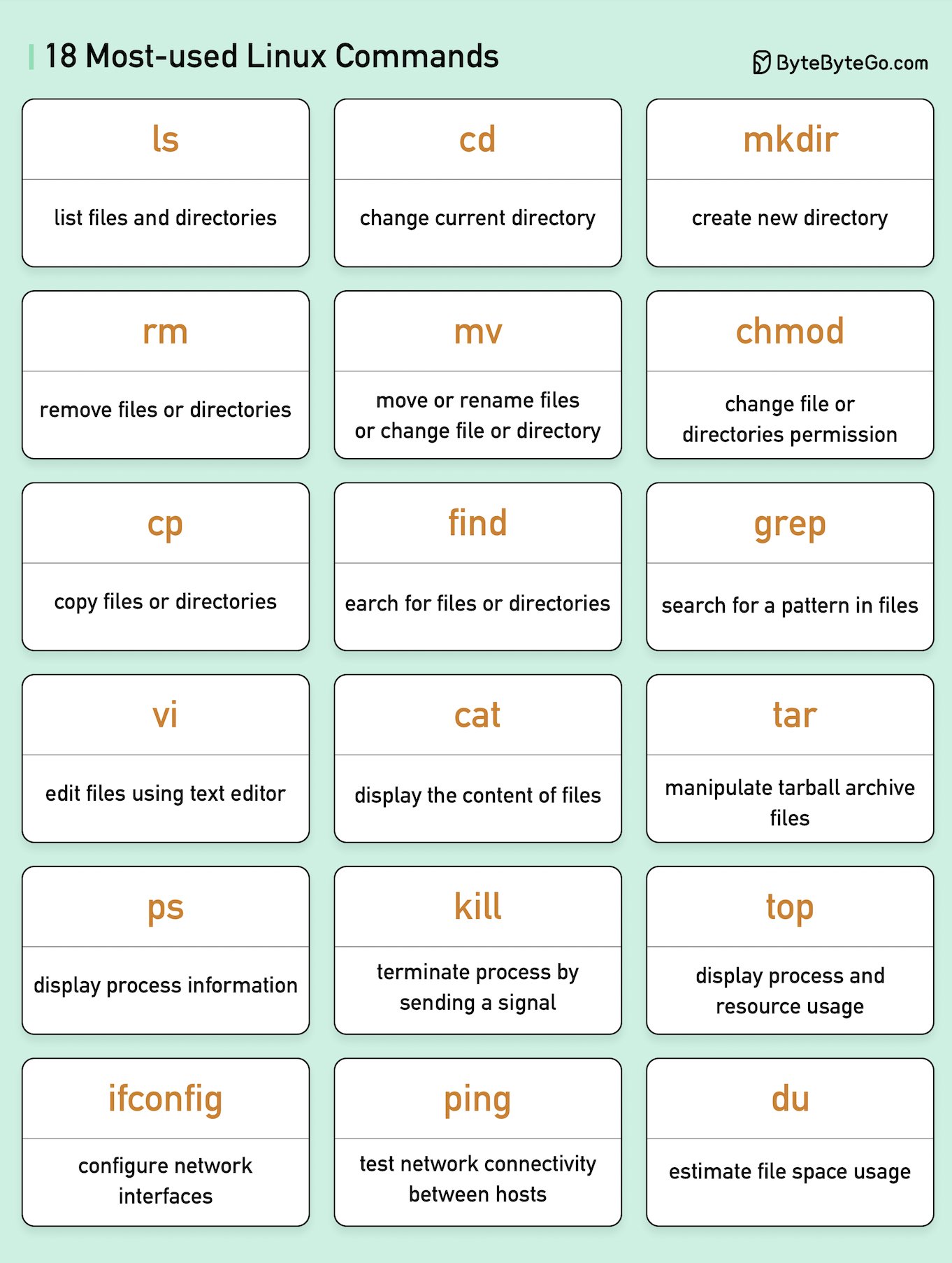
1.DESKTOP--> Desktop mainly divided into three parts- 1. Computation 2.Storage 3. Network
2.SOME TERMS -
CPU-central processing unit
GPU-graphic processing unit
DPU-data processing unit
TPU-tensor processing unit
3.SOC(SYSTEM ON A CHIP)-A System on Chip or an SoC is an integrated circuit that incorporates a majority of components present on a computer. As the name suggests, it is an entire system fabricated on a silicon chip. The beauty of an SoC is that it integrates all the components on a single substrate. In semiconductors, a substrate is a thin film of silicon used to fabricate integrated circuits. In contrast to the traditional motherboard, SoC integrates the replaceable components onto a single chip, thereby reducing the size and increasing efficiency.
4.CISC[complex instruction set computer]--closed source like intel and AMD(advanced micro devices).It develop X-86 series under ISA[intruction set arichtecture] in 1978.
5.RISC[reduced instruction set computer]--close source like ARM[Adavnce risc machine] .It has specific intruction,very fast and efficient.
6.RISC-V--it is based on RISC principles and develop in 2023 and which is a free open source. it also have a project called SHAKTI.
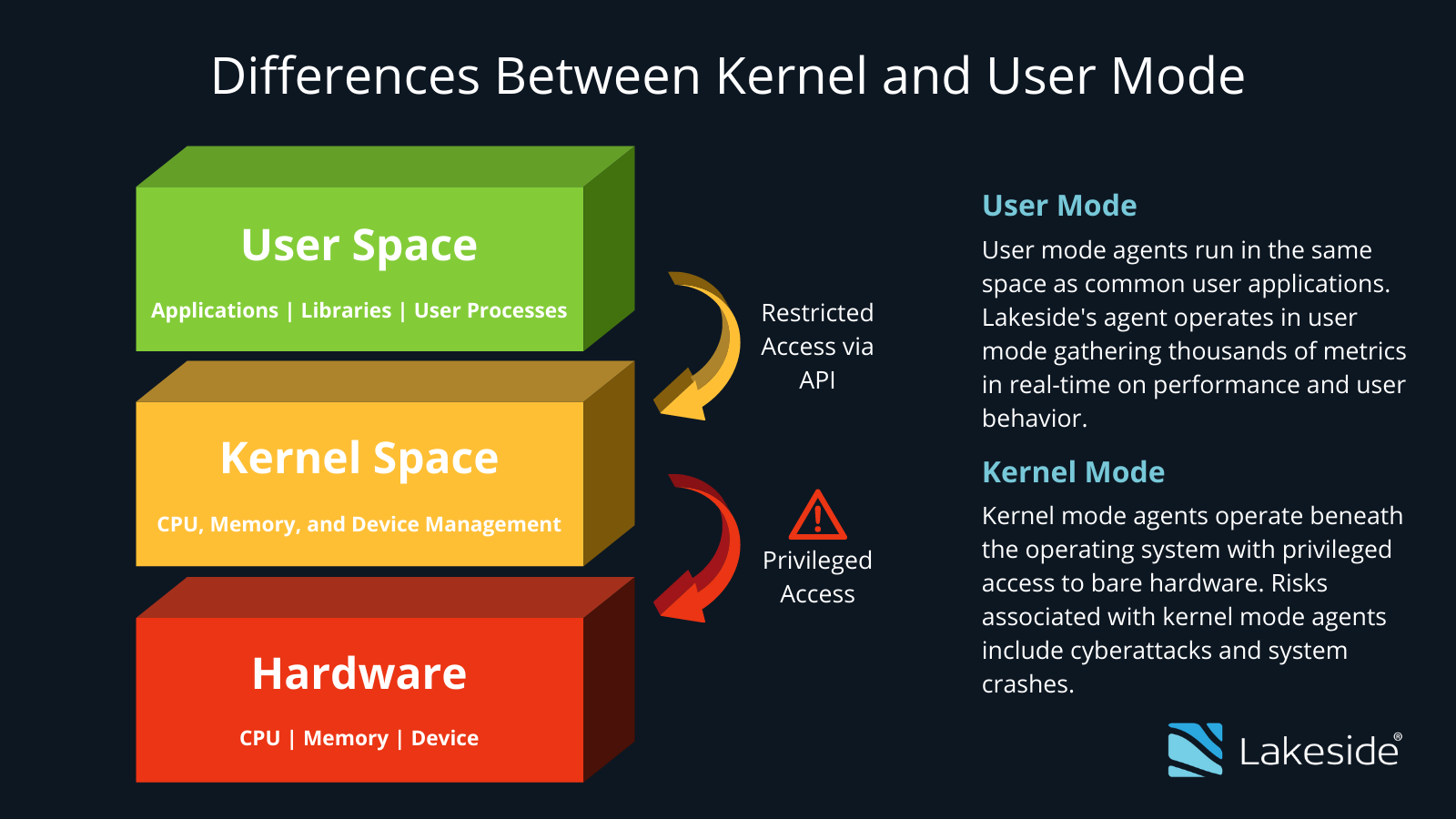
7.KERNEL--that manages operations between computer and hardware.
C,C++,rust
8.OPERATING SYSTEM- a.Windows b.MacOS
9.LINUX-It is open source operting system made by linus torvalds.Came under UNIX[uniplexed information computer system].
LINUX has two types of family-
a.Debian-It contain OPERATING SYSTEM like UBUNTU[open source,developed by CANONICAL],KALI LINUX.
b.RHEL[red hat enterprise linux]-It contain OPERATING SYSTEM likre centOS,oracle,fedora,red hat.
Packing manager: Yum
It is owned by IBM[international business machine] at 40 billon dollor.
10.NETWORK There are two types of network- 1.Internet[(WAN-wide area network) and it is a public network] 2.Intranet[(LAN-local area network) and it is a private network]
11.CLOUD COMPUTING CLOUD means internet which is a public network[distributed over multiple location]. a.AWS[amazon web services]-by amazon b.AZURE-by microsoft c.GCP[Google Cloud Platform]-by goggle
12.Ip address[internet protocol]-a unique address which identify the device on internet or on local internet .There are three types of ip address-
Private-ex:starts with 10. ,172. ,192. .
Public- ex:starts with 11..
Local-ex:starts with 127.0.00[a specific number]
like JIO-ipv6, airtel-ipv4.
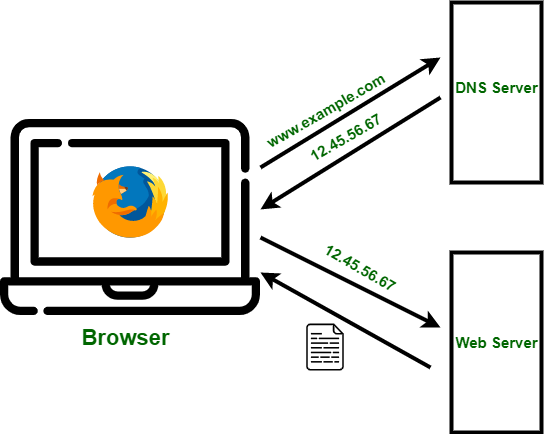
13.DNS[domain name server]- turns domain names into IP Address. ex:google.com
14.Routing-the process of path selection in any network.
15.BARE METAL -fresh server[which has no operating system]
16.DUAL BOOT-2 operating system
17.HYPERVISOR -A program used to run and manage two or more virtual machine.hypervisor for Windows by Microsoft
There are two type of hypervisor-
a.type-1
b.type-2
18.type-1 -- there is no need to install operating system. Bare metal-->hypervisor type-1-->VM1,VM2,VM3..
19.type2--there is a need to install operating system . bare metal-->install operating system-->VM1,VM2,VM3-->type 2[VM1,VM2,VM3..,Virtual box,work station,VM Ware]
20.VM WARE(virtual machine)-it is a company of cloud computing and a open source(oracle),owned by broad com(62 billon$)
21.GDPR--general data protection regulation
22.FAANG,MAANG,MERN- a group of big tech stocks that are tradtionally made up of Facebook (Meta Platforms), Amazon, Apple, Netflix, and Google.
The acronym MAANG stands for Meta, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, and Google.
MERN stands for MongoDB, Express, React, Node
23.FPGA(field programmable gate array)-A field-programmable gate array is a type of integrated circuit that can be programmed or reprogrammed after manufacturing. It consists of an array of programmable logic block and interconnects that can be configured to perform various digital functions.This feature sets FPGAs apart from Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs). The latter is explicitly made for a given goal, which one cannot change later.
24.ASIC'S(Application-specific integrated circuit)- It is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficiency video codec.
25.Photonic-Photonics also includes research on photonic systems.
#QRNG-Quantum random number generators (QRNGs) are a special case of TRNG ( True random number generators ), that generate randomness by measuring quantum processes, which are, by nature non-deterministic.
#PRNG( Pseudo random number generators )-computer follows the given instructions blindly and is therefore completely predictable. It is not possible to generate truly random numbers from deterministic thing like computers so PRNG is a technique developed to generate random numbers using a computer(RANDOMNESS).A pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) is a program written for, and used in, probability and statistics applications when large quantities of random digits are needed.
26.Company only make silicon chip(SoCs)
a.taiwan b.intel c.samsung
27.Cryptography-The prefix “crypt” means “hidden” and suffix “graphy” means “writing”.it is technique of securing information and communications through use of codes so that only those person for whom the information is intended can understand it and process it.
28.post-cryptography-it ia technology which is trend now a day .Post-quantum cryptography aims to develop new cryptographic algorithms that are secure against attacks from both classical and quantum computers.
29.https-s means secure socket layer(SSL)
30.SSL[secure socket layer]-ip address[layer3]+ port number[layer4]
31.Port number-a way to indentify a specific process to which an internet or other network message is to be forwarded when it arrives at a server.
eg:
HTTP-80
HTTPS-443
FTP-20,21
SMTP-25
TELMET-23
SSH[secure shell]-22
32.SEVEN LAYER OF OSI[OPEN SYSTEM INTERCONNECTION]
~layer7-application/protocol
~layer6-presentation
~layer5-cryptography
~layer4-port number[16 bits]
~layer3-IP ADDRESS[32 bits]
~layer2-hardware address-NIC,MAC
~layer1-digital(1 and 0)
33.TCP/IP(TRANSMISION CONTROL PROTOCOL)-layer5+layer6+layer7
34.eth0(Ethernet adapter)-(physical NIC) use to in and out the data packages
DPDK(data plane development kit)- it is an open source software project managed by the Linux Foundation. It provides a set of data plane libraries and network interface controller polling-mode drivers for offloading TCP packet processing from the operating system kernel to processes running in user space. DPDK facilitates the quicker expansion of high-speed data packet networking applications.
SR-IOV(single root)-In virtualization, single root input/output virtualization (SR-IOV) is a specification that allows the isolation of PCI Express resources for manageability and performance reasons.SR-IOV allows a device, such as a network adapter, to separate access to its resources among various PCIe hardware functions.
CNDP-Cloud Native Data Plane (CNDP) is a collection of user space libraries to accelerate packet processing for cloud applications using AF_XDP sockets as the primary I/O..
PTP-The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol used to synchronize clocks throughout a computer network. On a local area network, it achieves clock accuracy in the sub-microsecond range, making it suitable for measurement and control systems.
NTP-The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use.
35.URL-(uniform resource locator) is a unique identifier used to locate a resource on the Internet. It is also referred to as a web address.
36.cache-it is a high-speed data storage layer which stores a subset of data [temporary memory]
37.Switch - connects device in network to each other, enabling them to each other, enabling them to talk by exchanging data packets.
38.Virtual Machine - created by using Hyperviser
-
Protocol - It is a standardized set of rules for formatting and processing data.
-
Firmware- It is micro code or program that is embedded into memory of hardware device to help them operate.
-
TLS - Transport layer security encrypts data send over the internet.
-
Stack - Stack is a linear data structure that follows a particular order in which the operation are peroformed. LIFO(Last In First Output).
-
IAM(Identity and access management)-centrally manage permissions that control which AWS resources users can access.
44.nginx - proxy server
45.proxy server-A proxy server is a system or router that provides a gateway between users and the internet. Therefore, it helps prevent cyber attackers from entering a private network. It is a server, referred to as an “intermediary” because it goes between end-users and the web pages they visit online.
46.apache- client server - uses httpd(d stands for dameon: continuously runs in background) that creates a pool of child processes or threads to handle requestes. The purpose of the daemon is to respond to network, hardware, or system requests to perform certain tasks.
47.UDP- User datagram protocol, is a commuincation protocol used across the internet for especially time- sensitive transimission
48.Packets- Its a small segment of a large message. Data send over computer networks, such as internt, is divided into packets, recombined by client computer
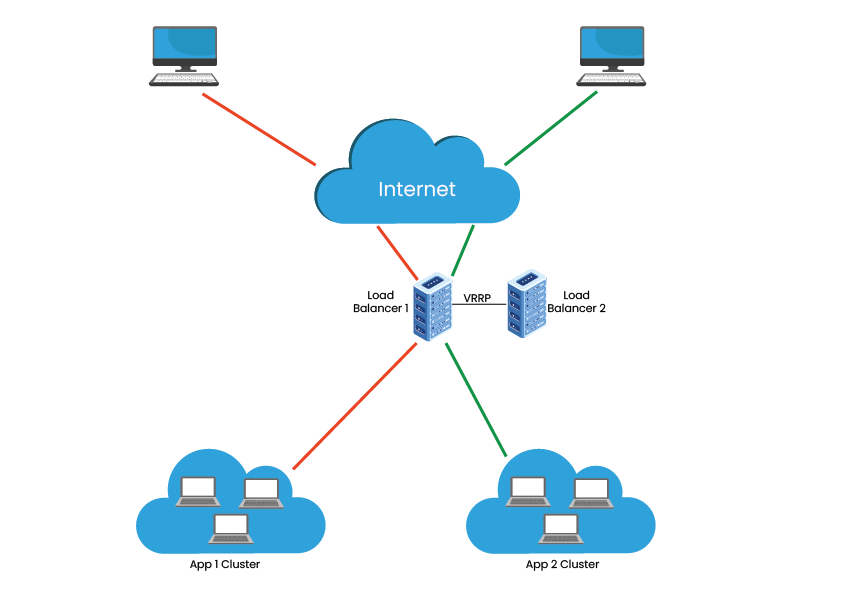
49.Load balancer- It is the method of distributing network traffic eqaully across a pull of resources that support an application.
50.Von Neumann architecture and harvard architecture -The term "von Neumann architecture" has evolved to refer to any stored-program computer in which an instruction fetch and a data operation cannot occur at the same time
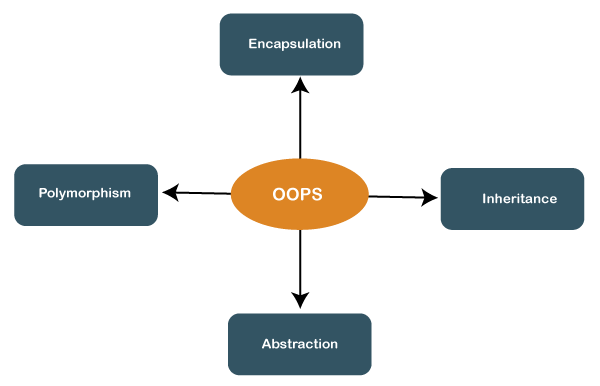
52.OOPS[object-oriented programming system]--> C + OOPS=C++.
53.OOPS contain--
a.class b.object c.reference d.construction
encapsulation (or OOP Encapsulation) refers to the bundling of data, along with the methods that operate on that data, into a single unit.Encapsulation is a way to achieve “information hiding” so, you don’t “need to know the internal workings of the mobile phone to operate” with it.
abstruction-Abstraction on the other side can be explained as the capability to use the same interface for different objects. Different implementations of the same interface can exist. Details are hidden by encapsulation.
Polymorphism-Polymorphism is a concept, which allows us to redefine the way something works, by either changing how it is done or by changing the parts used to get it done.
Inheritance-Inheritance is a feature of object-oriented programming that allows code reusability when a class includes property of another class. Considering HumanBeing a class, that has properties like hands, legs, eyes, mouth, etc, and functions like walk, talk, eat, see, etc.**
55.IDE-INTEGRATED DEVELOPMENT ENVIROMENT
a.IAAS (infrastructure as a service): Amazon web service(AWS),Google computer engine (GCE),Microsoft AZURE.
b.SAAS (software as a service): dropbox,google workspace,and salesforce.
c.PAAS (platform as a service): VM Ware,oracle cloud platform(OCP),adobe commerce.
57.TYPES OF CLOUD -
a.Public Cloud - It is cloud computing that`s delivered via the internet and shared accross thr organisation.
b.Private Cloud -it is a cloud computing that is dedicated solely to your organisation.
c.Hybrid Cloud-it is any environment that uses both public and private cloud.
58.Benefits of cloud computing-
a.scalability
b.accessibility
c.redundancy
d.efficiency
e.security
f.go global in minutes
61.COMPUTER BASICS-
a.SSL CERTIFICATE-An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a website's identity and enables an encrypted connection. SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, a security protocol that creates an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser.standard form of certificate is X.509.
b.NAT-Network address translation (NAT) is a method of mapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device.
62.BLOCKCHAIN-a system in which a record of transactions, especially those made in a cryptocurrency, is maintained across computers that are linked in a peer-to-peer network.
a.It is a advanced database mechanism that allows transparent information sharing with in a business network.
b.It made by SANTOSHI NAKAMOTO in 2008.
63.CURRENCY-
a.Bitcoin-it is a innovative payment network and a new kind of money. Bitcoin is open-source; its design is public, nobody owns or controls Bitcoin and everyone can take part.
b.Ethereum-Ethereum is the community-run technology powering the cryptocurrency ether (ETH) and thousands of decentralized applications.Ethereum and its apps are transparent and open source.
c.ICO-An initial coin offering (ICO) is an event where a company sells a new cryptocurrency to raise money.
64.CADDY-Caddy is an extensible, cross-platform, open-source web server. Caddy distributions ship with a set of standard modules which include HTTP server, TLS automation, and PKI apps. It is best known for its automatic HTTPS features(SSL certificate).
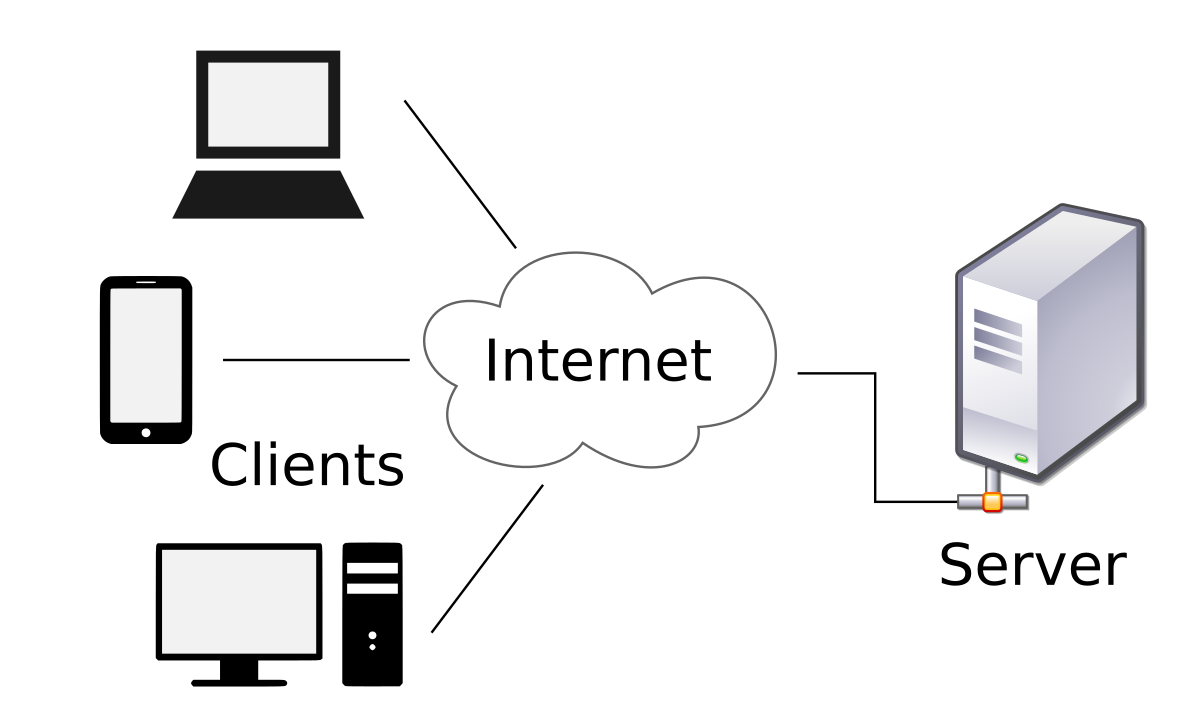
65.Client-Server-Client-server denotes a relationship between cooperating programs in an application, composed of clients initiating requests for services and servers providing that function or service.
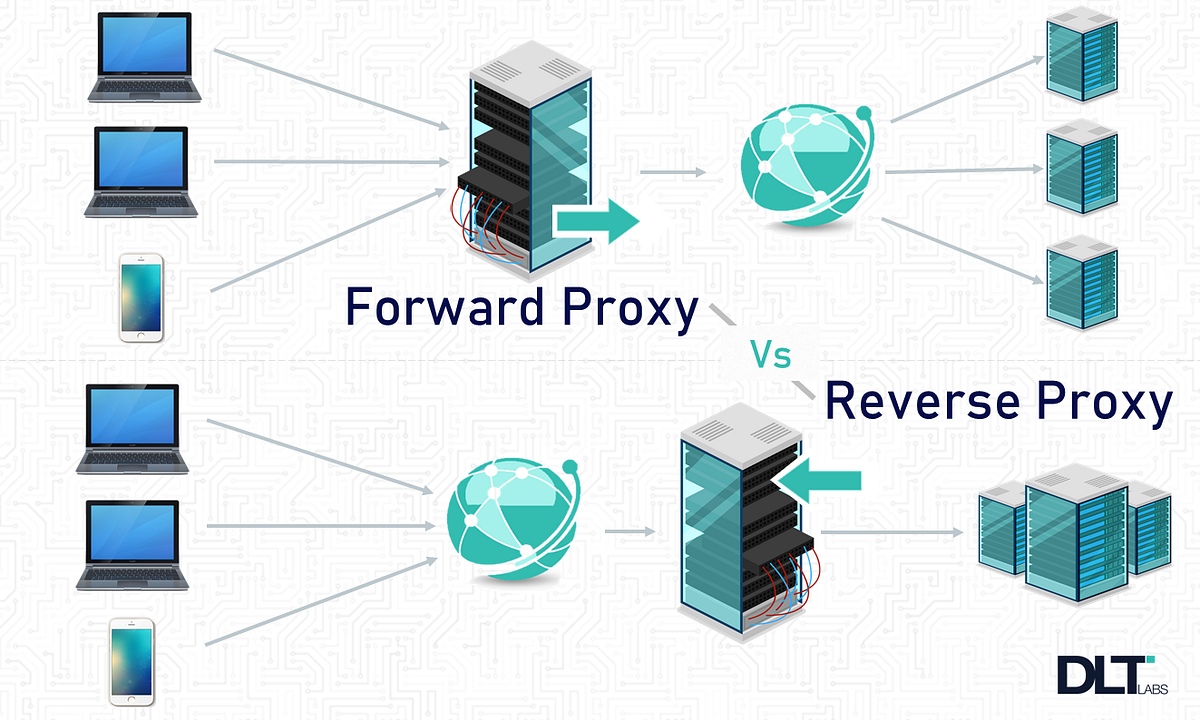
66.FORWARD PROXY-A forward proxy is an intermediary that sits between one or more user devices and the internet.a client request and sending it directly to a web server, a forward proxy server evaluates the request, takes any needed actions, and routes the request to the destination on the client's behalf.
67.REVERSE PROXY-A reverse proxy server is a type of proxy server that typically sits behind the firewall in a private network and directs client requests to the appropriate backend server.
68.PORT FORWARDING COMMAND- port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall.
69.ON-PREM[On-premises ]-"On-prem" refers to private data centers that companies house in their own facilities and maintain themselves.
70.CLUSTER- a cluster is a group of servers and other resources that act like a single system and enable high availability, load balancing and parallel processing.
71.kubernetes(K8S)-kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management.
72.TYPES OF COMPUTING-
a.DESKTOP-Desktop computing devices include workstations, personal computers, and network computing devices. A workstation or desktop personal computer does not have many resource restrictions when connected to a fixed network.
b.client-server-computing-In client server computing, the clients requests a resource and the server provides that resource. A server may serve multiple clients at the same time while a client is in contact with only one server.
c.cloud-computing-Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user.Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each of which is a data center.
d.edge-computing-Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data.
e.cluster/distributed-A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software. example:torrent and bitcoin.
f.decentralized-computing-Decentralized computing is the allocation of resources, both hardware and software, to each individual workstation, or office location. In contrast, centralized computing exists when the majority of functions are carried out, or obtained from a remote centralized location. Decentralized computing is a trend in modern-day business environments.
g.centralized-computing-Centralized computing is computing done at a central location, using terminals that are attached to a central computer. The computer itself may control all the peripherals directly (if they are physically connected to the central computer), or they may be attached via a terminal server.
73.DESIGN PATTERN-A design pattern typically shows relationship and interaction between classes or objects, without specifying final application classes or objects that are involved.
74.SYSTEM DESIGN-Systems design is therefore the process of defining and developing systems to satisfy specified requirements of the user.
75.FRONT END-A Front-End in which we develop websites and web applications.
--front end languages
1.HTML
2.CSS(Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a stylesheet language used to describe the presentation of a document written in HTML or XML )
3.JAVA SCRIPT
76.BACK END-The back end refers to parts of a computer application or a program's code that allow it to operate and that cannot be accessed by a user. --back end languages 1.python 2.go 3.JAVA --Spring Boot is an open-source, microservice-based Java web framework offered by Spring. 4.framework-server-side frameworks designed to make tasks easier for developers. example-DJANGO-Django is a high-level Python web framework that enables rapid development of secure and maintainable websites. And it is free and open source.
77.full stack-Full stack development refers to the end-to-end application software development, including the front end and back end.
dev means devtops and ops means operation.
CI/CD-continous integration/continous deployment. now ,this is called platform engineer .
79.CRYPTOGRAPHY-Cryptography is a method of protecting information and communications through the use of codes, so that only those for whom the information is intended can read and process.
80.TYPES OF CRYPTOGRAPHY-There are two types of cryptography
1.symmetric
2.asymmetric
81.VPC (VIRTUAL PRIVATE CLOUD)-A virtual private cloud (VPC) is a secure, isolated private cloud hosted within a public cloud.
82.POC-A proof of concept (POC) is a demonstration of a product in which work is focused on determining whether an idea can be turned into a reality.
83.ROUTE 53-Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service. Route 53 connects user requests to internet applications running on AWS or on-premises.
84.S3(bucket)-Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service offering industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance.
85.CLOUD WATCH-Amazon CloudWatch monitors your Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources and the applications you run on AWS in real time. The CloudWatch home page automatically displays metrics about every AWS service you use.With CloudWatch, you gain system-wide visibility into resource utilization, application performance, and operational health.
86.KVM-KVM (for Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a full virtualization solution for Linux on x86 hardware containing virtualization extensions (Intel VT or AMD-V). It consists of a loadable kernel module, kvm.ko, that provides the core virtualization infrastructure and a processor specific module, kvm-intel.ko or kvm-amd.ko.
87.XEN-Xen is a free and open-source type-1 hypervisor, providing services that allow multiple computer operating systems to execute on the same computer hardware concurrently.
88.proxmox-Proxmox Virtual Environment is an open source server virtualization management solution based on QEMU/KVM and LXC. You can manage virtual machines, containers, highly available clusters, storage and networks with an integrated, easy-to-use web interface or via CLI.
89.web assembly(WASM)-WebAssembly (abbreviated Wasm) is a binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine. Wasm is designed as a portable compilation target for programming languages, enabling deployment on the web for client and server applications.
90.RAID-RAID (redundant array of independent disks, originally redundant array of inexpensive disks is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit. Data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways called "RAID levels", depending on the level of redundancy and performance required.
91.CEPH-Ceph is an open source software-defined storage solution designed to address the block, file and object storage needs of modern enterprises.
92.DATA CENTRES-
RACKS-A rack also called an equipment rack, is a metal frame for holding and organizing networking devices. A networking component that is designed to be mounted in a rack is said to be rack-mountable. Rack-mountable devices include hubs, routers, Ethernet switches, patch panels, and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) devices.
SERVERS
SWITCHES
93.HYPERSCALERS-The term "hyperscale" refers to the ability of these companies to rapidly scale their infrastructure to accommodate the growing demands of their users.FOR EXAMPLE -YOTTA is a data centre open recently in noida which having mutiple servers and use to hyperscale the company
94.hyperconverse(HCI)-Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) is a software-defined, unified system that combines all the elements of a traditional data center: storage, computation, networking and management.
95.IBM-IBM (International Business Machines Corporation) is a multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, N.Y.
96.WEB-SCRAPING-Web scraping uses intelligence automation methods to get thousands or even millions of data sets in a smaller amount of time. Web scraping is an automatic method to obtain large amounts of data from websites. Most of this data is unstructured data in an HTML format which is then converted into structured data in a spreadsheet or a database so that it can be used in various applications.Many large websites, like Google, Twitter, Facebook, StackOverflow, etc. have API’s that allow you to access their data in a structured format.
97.POSTMAN APPLICATION-Postman: Postman is an API(application programming interface) development tool which helps to build, test and modify APIs.
98.REST API-Representational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style that defines a set of constraints to be used for creating web services. REST API is a way of accessing web services in a simple and flexible way without having any processing.
99.CRUD(CREATE READ UPDATE DELETE)-
100.GRPC(graphic Remote Procedure Call )-gRPC is a modern open source high performance Remote Procedure Call (RPC) framework that can run in any environment. It can efficiently connect services in and across data centers with pluggable support for load balancing, tracing, health checking and authentication. It is also applicable in last mile of distributed computing to connect devices, mobile applications and browsers to backend services.gRPC uses Protobuf, which is not human readable and Mainly used to scale API's.
101.GRAPH QL- GraphQL uses human-readable formats such as JSON or XML. GraphQL is a language for querying data and mainly used to scale API'S.
102.YAML-YAML stands for yet another markup language or YAML ain't markup language (a recursive acronym), which emphasizes that YAML is for data, not documents. YAML is a popular programming language because it is designed to be easy to read and understand.
103.JSON-JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format. It is easy for humans to read and write. It is easy for machines to parse and generate.
104.EBPF-Extended BerKeley Packet Filter (eBPF) addresses both these issues. eBPF is a kernel technology (fully available since Linux 4.4). It lets programs run without needing to add additional modules or modify the kernel source code.eBPF programs are used to access hardware and services from the Linux kernel area.
105.CNI-CNI (Container Network Interface), a Cloud Native Computing Foundation project, consists of a specification and libraries for writing plugins to configure network interfaces in Linux and Windows containers, along with a number of supported plugins.
Calico: Calico is a highly scalable CNI plugin that provides network policy enforcement and supports various networking modes, including BGP peering for routing.
Flannel: Flannel is a simple and lightweight CNI plugin that can be used for both overlay and host-gateway networking. It’s easy to set up and configure.
Cilium: Cilium is designed for modern, high-performance networking and security in Kubernetes. It uses eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) for fine-grained network policies.
VPP (Vector Packet Processing) CNI: VPP is an open-source networking stack that can be used as a CNI plugin to achieve high-performance networking.
RKT-RKT (pronounced as “rocket”) is a CLI for running app containers on a Linux platform. Its main purpose is to be secure, fast, and composable, and therefore it is designed as secure, composable, and standards-based.
106.BGP-BGP is responsible for looking at all of the available paths that data could travel and picking the best route, which usually means hopping between autonomous systems.
User-mode Linux (UML)– paravirtualized kernel
ovirt-oVirt is an open-source distributed virtualization solution, designed to manage your entire enterprise infrastructure. oVirt uses the trusted KVM hypervisor and is built upon several other community projects, including libvirt, Gluster, PatternFly, and Ansible.
kubevirt- Thus KubeVirt delivers three things to provide the new functionality:
#Additional types - so called Custom Resource Definition (CRD) - are added to the Kubernetes API
#Additional controllers for cluster wide logic associated with these new types
#Additional daemons for node specific logic associated with new types
108.CRD-A custom resource is an object that extends the Kubernetes API or allows you to introduce your own API into a project or a cluster. A custom resource definition (CRD) file defines your own object kinds and lets the API Server handle the entire lifecycle.
109.CNCF-The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) is an open source software foundation that promotes the adoption of cloud-native computing.
110.OVERLAY- overlaying means "the process of transferring a block of program code or other data into main memory, replacing what is already stored".
111.TUN-TUN, short for network TUNnel, is a virtual interface that implements a software-based abstraction of a network by emulating the behavior of physical devices like Ethernet or Wi-Fi interface cards.It operates on layer 3 of the OSI model, handling the transmission and reception of IP packets.
112.OVS-Open vSwitch, sometimes abbreviated as OVS, is an open-source implementation of a distributed virtual multilayer switch. The main purpose of Open vSwitch is to provide a switching stack for hardware virtualization environments, while supporting multiple protocols and standards used in computer networks.
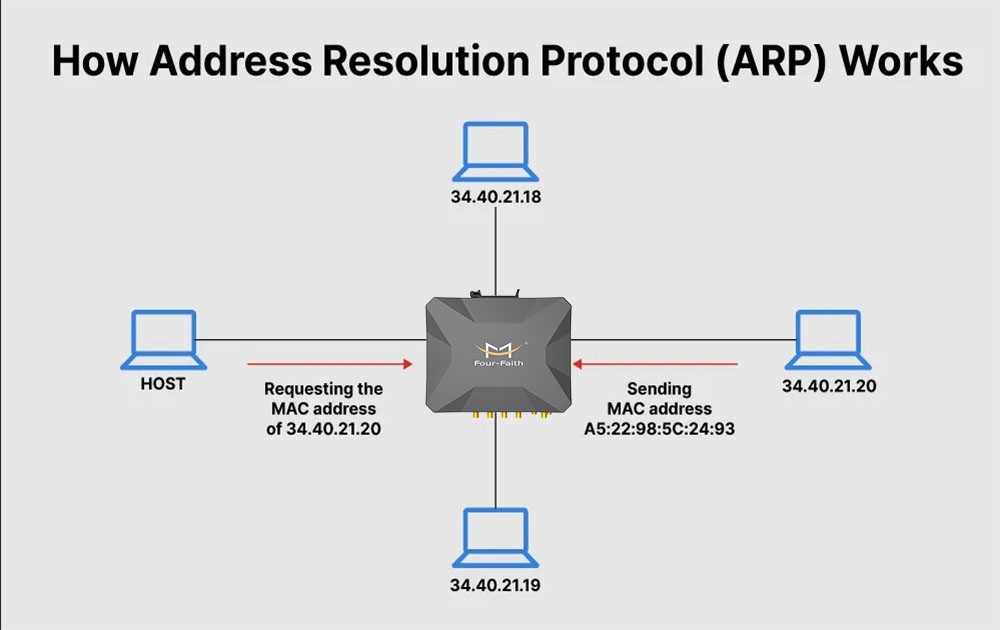
113.ARP-Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol or procedure that connects an ever-changing Internet Protocol (IP) address to a fixed physical machine address, also known as a media access control (MAC) address, in a local-area network (LAN).
114.REV ARP-The Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is an obsolete computer communication protocol used by a client computer to request its Internet Protocol (IPv4) address from a computer network, when all it has available is its link layer or hardware address, such as a MAC address.
115.ESM-Enterprise Service Management – often referred to as ESM, is the extension of IT Service Management (ITSM) principles to enable better service delivery for business teams like Human Resources (HR), legal, facilities, marketing, and finance.
116.ETCD-etcd is a strongly consistent, distributed key-value store that provides a reliable way to store data that needs to be accessed by a distributed system or cluster of machines. It gracefully handles leader elections during network partitions and can tolerate machine failure, even in the leader node.
117.RAFT-Raft is a consensus algorithm designed as an alternative to the Paxos family of algorithms. It was meant to be more understandable than Paxos by means of separation of logic, but it is also formally proven safe and offers some additional features.
118.MESOS- It is an open source cluster manager that handles workloads in a distributed environment through dynamic resource sharing and isolation. Mesos is suited for the deployment and management of applications in large-scale clustered environments.
119.TERRAFORM- Terraform is an infrastructure as code tool that lets you define both cloud and on-prem resources in human-readable configuration files that you can version, reuse, and share. You can then use a consistent workflow to provision and manage all of your infrastructure throughout its lifecycle. Terraform can manage low-level components like compute, storage, and networking resources, as well as high-level components like DNS entries and SaaS features.
120.GRAPHINE CS-For privacy and security
121.hcl-A hardware compatibility list (HCL) is a list of computer hardware (typically including many types of peripheral devices) that is compatible with a particular operating system or device management software.
122.TAP-A network tap is a system that monitors events on a local network. A tap is typically a dedicated hardware device, which provides a way to access the data flowing across a computer network.
123.cockroachDB-CockroachDB replicates your data for availability and guarantees consistency between replicas using the Raft consensus algorithm, a popular alternative to Paxos.
124.DHCP-DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network management protocol used to dynamically assign an IP address to any device, or node, on a network so it can communicate using IP.
125.Rancher-Rancher is used to provision and manage Kubernetes clusters.
126.green fields vs brownfields application-A greenfield project is a new project that starts from scratch. Whereas, a brownfield project has already gotten worked on by people.