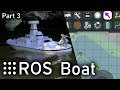
Tuna is an open-electronics and open-software GNSS platform for ROS, based on the Pi 4. It uses diff drive control for locomotion with diff_drive_simple, a standard percision GNSS receiver for absolute localization with navsat_simple, and an IMU for rotational data. If you see the overreaching theme there, I'm trying to keep everything as simple as possible.
In the current iteration it uses Vizanti as the mission planner and line_planner as its local planner. You can find more specific info below or in the related videos.
List of videos about construction and testing:
Base requirements:
Clone repos:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/MoffKalast/tuna.git
# Diff drive controller
git clone https://github.com/MoffKalast/diff_drive_simple.git
# Localization fusion
git clone https://github.com/MoffKalast/navsat_simple.git
# Goal planner
git clone https://github.com/MoffKalast/line_planner.git
# Optional, for RViz Viewing
git clone https://github.com/nobleo/rviz_satellite.git
# ign bridge setup, skip if already installed
export IGNITION_VERSION=fortress
git clone https://github.com/osrf/ros_ign.git -b noetic
cd ~/catkin_ws
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro=noetic -y
catkin_makeRun:
# Run the sim
roscd tuna_gazebo
ign gazebo water_world.sdf -r
# Run bridge and navigation nodes
roslaunch tuna_gazebo ign.launch
# Visualize
roslaunch tuna_viz rviz.launch
# Turn on currnent/wind simulation
rosrun tuna_gazebo wave_generator.py
Install:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
https://github.com/MoffKalast/vizanti.git
cd ..
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro=noetic -y
catkin_makeRun:
roslaunch vizanti server.launchThen view http://localhost:5000
Clone hw drivers:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/dpkoch/imu_calib.git
git clone https://github.com/MoffKalast/onewiretemp.git
git clone https://github.com/MoffKalast/safety_light.git
git clone https://github.com/MoffKalast/mpu9255.git
cd ~/catkin_ws
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro=noetic -y
catkin_makeTo run this on a Pi 4, start with a 20.04 Ubuntu Pi image, install everything as listed above, plus pigpio.
Fix services to set up correct ROS params and autorun at boot:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src/tuna/tuna_bringup/config_scripts
sudo cp roscore.service /etc/systemd/system/roscore.service
sudo cp magni-base /usr/sbin/magni-base
sudo cp roscore /usr/sbin/roscore
sudo cp env.sh /etc/ubiquity/env.sh
sudo cp ros_setup.bash /etc/ubiquity/ros_setup.bash
sudo cp ros_setup.sh /etc/ubiquity/ros_setup.shChanges to /boot/config.txt for i2c, uart, and LED power saving:
# disable rainbow splash screen for faster booting
disable_splash=1
# Set up UART and disable BT
dtoverlay=disable-bt
dtoverlay=uart0
# Set up I2C
dtoverlay=i2c-gpio,i2c_gpio_sda=2,i2c_gpio_scl=3,bus=1 core_freq=250
# Disable the PWR LED
dtparam=pwr_led_trigger=none
dtparam=pwr_led_activelow=off
# Disable the Activity LED
dtparam=act_led_trigger=none
dtparam=act_led_activelow=off
# Disable ethernet port LEDs
dtparam=eth_led0=4
dtparam=eth_led1=4For the safety_light to have the correct kernel interface access create /etc/udev/rules.d/99-gpio.rules with the following contents (if it doesn't already exist):
SUBSYSTEM=="bcm2835-gpiomem", KERNEL=="gpiomem", GROUP="gpio", MODE="0660"
SUBSYSTEM=="gpio", KERNEL=="gpiochip*", ACTION=="add", RUN+="/bin/sh -c 'chown root:gpio /sys/class/gpio/export /sys/class/gpio/unexport ; chmod 220 /sys/class/gpio/export /sys/class/gpio/unexport'"
SUBSYSTEM=="gpio", KERNEL=="gpio*", ACTION=="add", RUN+="/bin/chown root:gpio /sys%p/active_low /sys%p/edge /sys%p/direction /sys%p/value", RUN+="/bin/chmod 660 /sys%p/active_low /sys%p/edge /sys%p/direction /sys%p/value"This launch file will also launch automatically at boot via the magni-base service.
roslaunch tuna_bringup core.launch