A JupyterLab extension for version control using Git
To see the extension in action, open the example notebook included in the Binder demo.
- JupyterLab >= 3.0 (older version available for 2.x)
- Git (version
>=2.x)
- Open the Git extension from the Git tab on the left panel
- Set up authentication
To install perform the following steps, with pip:
pip install --upgrade jupyterlab jupyterlab-gitor with conda:
conda install -c conda-forge jupyterlab jupyterlab-gitFor JupyterLab < 3, you will need to run the following command after installing the package:
jupyter lab buildpip uninstall jupyterlab-gitor with conda:
conda remove jupyterlab-gitFor JupyterLab < 3, you will also need to run the following command after removing the Python package:
jupyter labextension uninstall @jupyterlab/gitThis extensions does not handle credentials or authentication details. In order to connect to a remote host, it is recommended to use SSH.
If you are seeing errors similar to [E yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss ServerApp] 500 POST /git/<clone|push|pull|status> on the console which is running the JupyterLab server, you probably need to set up a credentials store for your local Git repository. One of the possibility is to use SSH.
Here are the steps to follow (skip any that is already accomplished for your project):
- Create a SSH key
- Register the public part of it to your Git server:
- Optionally, if you have more than one key managed by your ssh agent: Create a config file for the ssh-agent
- Tell your local Git repository to connect to remote via ssh
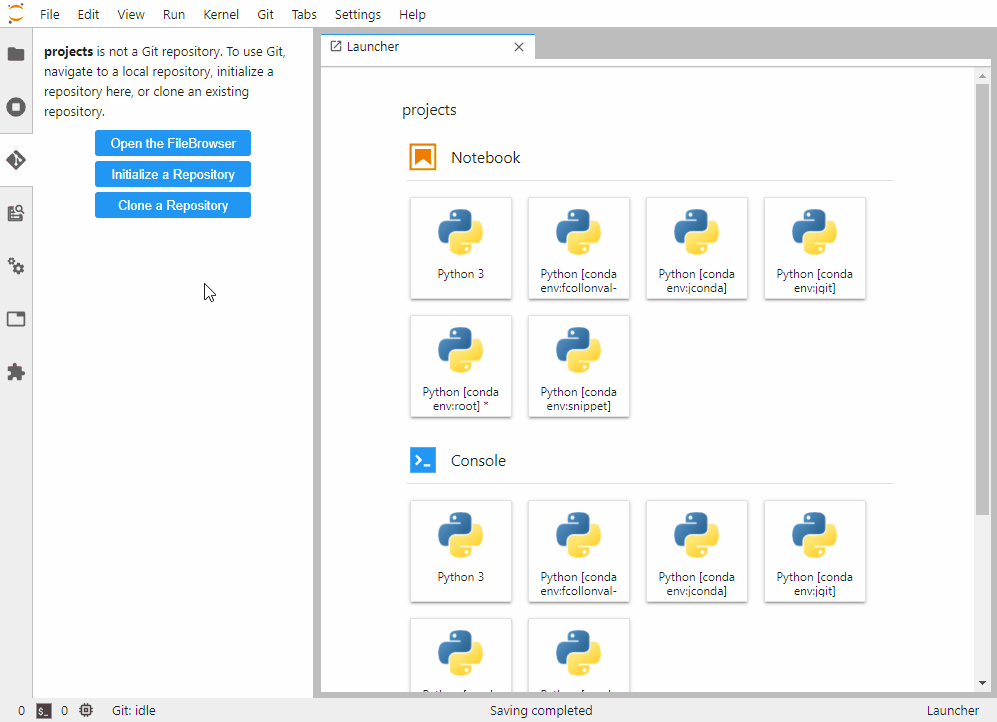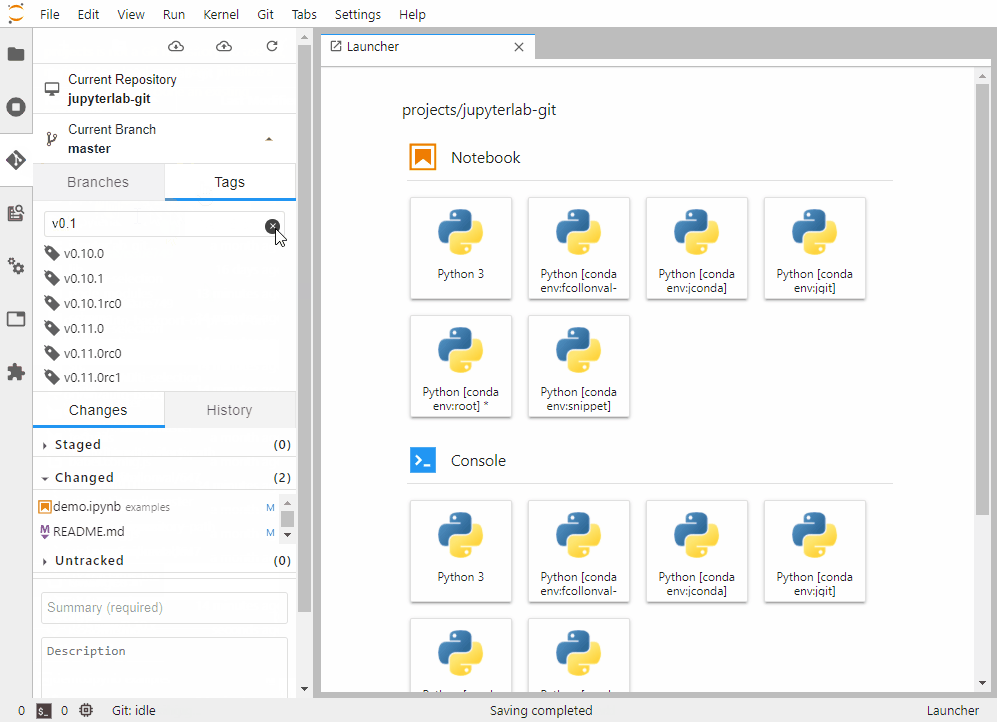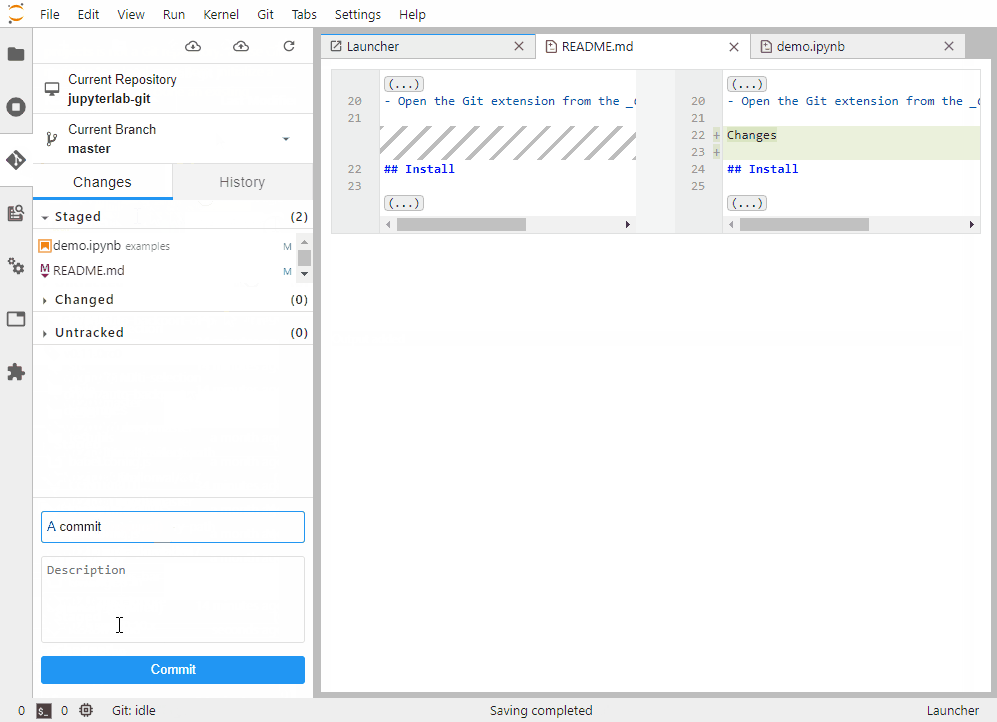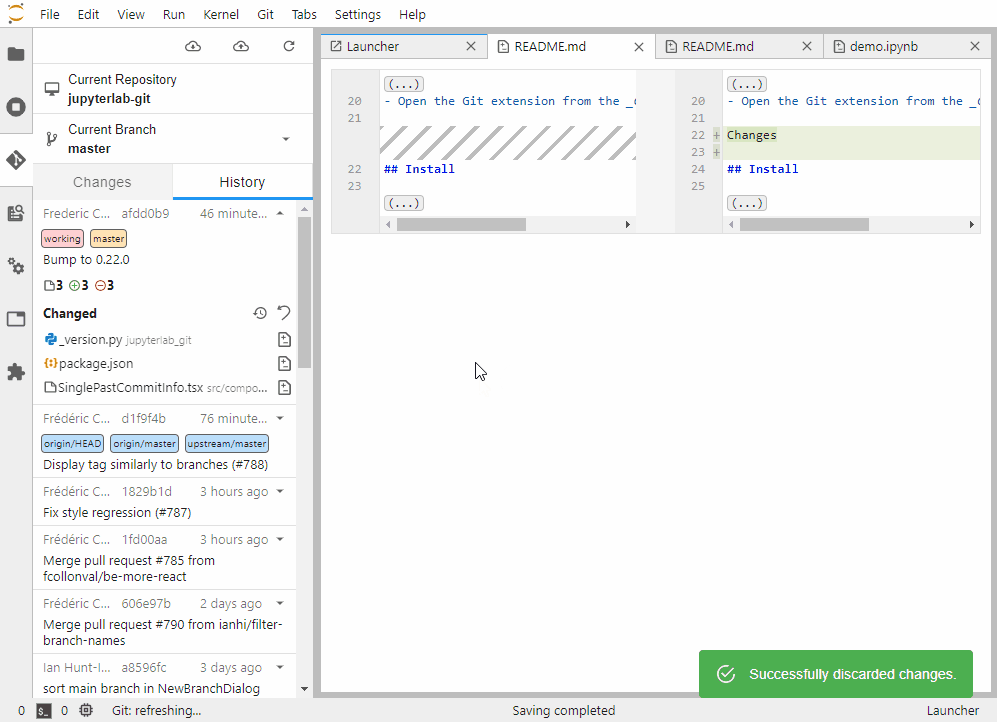
You should now be able to pull and push committed changes to and from your remote repository using the respective buttons on the top of the extension's panel.
Once installed, extension behavior can be modified via the following settings which can be set in JupyterLab's advanced settings editor:
- blockWhileCommandExecutes: suspend JupyterLab user interaction until Git commands (e.g.,
commit,pull,reset,revert) finish executing. Setting this totruehelps mitigate potential race conditions leading to data loss, conflicts, and a broken Git history. Unless running a slow network, UI suspension should not interfere with standard workflows. Setting this tofalseallows for actions to trigger multiple concurrent Git actions. - cancelPullMergeConflict: cancel pulling changes from a remote repository if there exists a merge conflict. If set to
true, when fetching and integrating changes from a remote repository, a conflicting merge is canceled and the working tree left untouched. - commitAndPush: Whether to trigger or not a push for each commit; default is
false. - disableBranchWithChanges: disable all branch operations, such as creating a new branch or switching to a different branch, when there are changed/staged files. When set to
true, this setting guards against overwriting and/or losing uncommitted changes. - displayStatus: display Git extension status updates in the JupyterLab status bar. If
true, the extension displays status updates in the JupyterLab status bar, such as when pulling and pushing changes, switching branches, and polling for changes. Depending on the level of extension activity, some users may find the status updates distracting. In which case, setting this tofalseshould reduce visual noise. - doubleClickDiff: double click a file in the Git extension panel to open a diff of the file instead of opening the file for editing.
- historyCount: number of commits shown in the history log, beginning with the most recent. Displaying a larger number of commits can lead to performance degradation, so use caution when modifying this setting.
- refreshIfHidden: whether to refresh even if the Git tab is hidden; default to
false(i.e. refresh is turned off if the Git tab is hidden). - refreshInterval: number of milliseconds between polling the file system for changes. In order to ensure that the UI correctly displays the current repository status, the extension must poll the file system for changes. Longer polling times increase the likelihood that the UI does not reflect the current status; however, longer polling times also incur less performance overhead.
- simpleStaging: enable a simplified concept of staging. When this setting is
true, all files with changes are automatically staged. When we develop in JupyterLab, we often only care about what files have changed (in the broadest sense) and don't need to distinguish between "tracked" and "untracked" files. Accordingly, this setting allows us to simplify the visual presentation of changes, which is especially useful for those less acquainted with Git.
- Post git init actions: It is possible to provide a list of commands to be executed in a folder after it is initialized as Git repository.
In ~/.jupyter/jupyter_notebook_config.py:
c.JupyterLabGit.actions = {"post_init": ["touch dummy_init.dat"]}Or equivalently in jupyter_notebook_config.json:
{
"JupyterLabGit": {
"actions": {
"post_init": ["touch dummy_init.dat"]
}
}
}Before consulting the following list, be sure the jupyterlab_git server extension and the @jupyterlab/git frontend extension have the same version by executing the following commands:
jupyter server extension list
jupyter labextension listIf they do not match or one is missing, please reinstall the package.
-
Issue: the Git panel does not recognize that you are in a Git repository.
Possible fixes:
-
Be sure to be in a Git repository in the filebrowser tab
-
Check the server log. If you see a warning with a 404 code similar to:
[W 00:27:41.800 LabApp] 404 GET /git/settings?version=0.20.0Explicitly enable the server extension by running:
jupyter server extension enable --py jupyterlab_git -
If you are using JupyterHub or some other technologies requiring an initialization script which includes the jupyterlab-git extension, be sure to install both the frontend and the server extension before launching JupyterLab.
-
-
Issue: the Git panel is not visible.
Possible fixes:
-
Check that the JupyterLab extension is installed:
jupyter labextension list
If you don't see
@jupyterlab/git v... enabled OKin the list, explicitly install the jupyter labextension by running:jupyter labextension install @jupyterlab/git
If you see
@jupyterlab/gitunderUninstalled core extensions:, your installation may have been corrupted. You can runjupyter lab clean --alland reinstall all your extensions.
-
If you would like to contribute to the project, please read our contributor documentation.
JupyterLab follows the official Jupyter Code of Conduct.
Note: You will need NodeJS to build the extension package.
The jlpm command is JupyterLab's pinned version of
yarn that is installed with JupyterLab. You may use
yarn or npm in lieu of jlpm below.
# Clone the repo to your local environment
git clone https://github.com/jupyterlab/jupyterlab-git.git
# Change directory to the jupyterlab-git directory
cd jupyterlab-git
# Install package in development mode
pip install -e .[dev]
pre-commit install
# Link your development version of the extension with JupyterLab
jupyter labextension develop . --overwrite
# Rebuild extension Typescript source after making changes
jlpm run buildYou can watch the source directory and run JupyterLab at the same time in different terminals to watch for changes in the extension's source and automatically rebuild the extension.
# Watch the source directory in one terminal, automatically rebuilding when needed
jlpm run watch
# Run JupyterLab in another terminal
jupyter labWith the watch command running, every saved change will immediately be built locally and available in your running JupyterLab. Refresh JupyterLab to load the change in your browser (you may need to wait several seconds for the extension to be rebuilt).
By default, the jlpm run build command generates the source maps for this extension to make it easier to debug using the browser dev tools. To also generate source maps for the JupyterLab core extensions, you can run the following command:
jupyter lab build --minimize=FalseTo execute the tests
pytest jupyterlab_git
jlpm run testThe Jupyter Git extension is part of Project Jupyter and is developed by an open community of contributors. To see who has been active recently, please look at the "Contributors" tab. Below we list the people and entities who contributed in different ways to the project (emoji key):
This project follows the all-contributors specification. Contributions of any kind are welcomed!
To add yourself, or someone else, to this list you can either use the bot (@all-contributors please add <username> for <contributions>) or the CLI (jlpm all-contributors add <username> <contributions>).
If you manually edit the .all-contributorsrc config file, run yarn run contributors:generate.