-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 233
Building Applications with Kundera and Spring
Spring framework is an open source enterprise application framework for java platform. It is a very popular framework to build web application on the top of j2ee platform.
Being an object mapper, Kundera can be used at DAO layer to persist and retrieve data from NoSQL as well as RDBMS datastores. Kundera also supports polyglot persistence to store data across NoSQL as well as RDBMS datastores using Spring.
In order to configure Spring application with Kundera you only need to create appContext.xml for spring. It is a XML file for spring configuration. All bean specific configurations can be specified here.
appContext.xml :
Create a bean called emf-p for Local Entity Manager Factory for persistence-unit “cassandra-pu”.
<bean id="emf-p"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="persistenceUnitName" value="pu-name" />
<property name="loadTimeWeaver">
<bean class="org.springframework.instrument.classloading.InstrumentationLoadTimeWeaver" />
</property>
</bean>
Configure location of your persistence.xml ( default location would be META-INF/persistence.xml).
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor">
</bean>
<bean id="pum"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.persistenceunit.DefaultPersistenceUnitManager">
<property name="persistenceXmlLocations">
<list>
<value>META-INF/persistence.xml</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
Creating/Injecting EntityManager/EntityManagerFactory :
For container managed Entity Manager, use a annotation called persistence context annotation. And provide persistence-unit name and type of persistence context to that annotation at field for creating entity manager.
@PersistenceContext (unitName="pu-name", type=PersistenceContextType.EXTENDED)
private EntityManager em;
For Application managed EntityManager use a annotation called called persistence unit annotation and provide persistence-unit name to that annotation at field level for creating entity manager factory. After that you can create entity manager from entity manager factory by calling createEntityManager method.
@PersistenceUnit (unitName="pu-name")
private EntityManagerFactory emf;
Create Entity Manager
private EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager ();
Follow the given steps to implement polyglot persistence using Spring with Kundera.
A sample project for same is available at https://github.com/impetus-opensource/Kundera/tree/trunk/examples
Configure applicationContext.xml:
<bean id="emf-p"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="persistenceUnitName" value="cassandra-pu,mongo-pu" />
<property name="loadTimeWeaver">
<bean class="org.springframework.instrument.classloading.InstrumentationLoadTimeWeaver" />
</property>
</bean>
<!-- emf-p1 and emf-p2 are required only in case of polyglot persistence
(i.e. using multiple cross data store persistence unit -->
<bean id="emf-p1"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="persistenceUnitName" value="cassandra-pu" />
<property name="loadTimeWeaver">
<bean class="org.springframework.instrument.classloading.InstrumentationLoadTimeWeaver" />
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="emf-p2"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="persistenceUnitName" value="mongo-pu" />
<property name="loadTimeWeaver">
<bean class="org.springframework.instrument.classloading.InstrumentationLoadTimeWeaver" />
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor" >
</bean>
<bean id="pum"
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.persistenceunit.DefaultPersistenceUnitManager">
<property name="persistenceXmlLocations">
<list>
<value>META-INF/persistence.xml</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
Persistence.xml : Create three persistence-unit one for cassandra-pu one for mongo-pu and last one for polyglot persistence i.e. cassandra-pu,mongo-pu.
<persistence-unit name="cassandra-pu">
<provider>com.impetus.kundera.KunderaPersistence</provider>
<class>com.impetus.kundera.datakeeper.entities.DocumentInfo</class>
<class>com.impetus.kundera.datakeeper.entities.Employee</class>
<class>com.impetus.kundera.datakeeper.entities.SubordinatesCounter</class>
<exclude-unlisted-classes>true</exclude-unlisted-classes>
<properties>
<property name="kundera.nodes" value="localhost" />
<property name="kundera.port" value="9160" />
<property name="kundera.keyspace" value="datakeeper" />
<property name="kundera.client" value="thrift" />
<property name="kundera.client.lookup.class"
value="com.impetus.client.cassandra.thrift.ThriftClientFactory" />
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
<persistence-unit name="mongo-pu">
<provider>com.impetus.kundera.KunderaPersistence</provider>
<class>com.impetus.kundera.datakeeper.entities.DocumentInfo</class>
<exclude-unlisted-classes>true</exclude-unlisted-classes>
<properties>
<property name="kundera.nodes" value="localhost" />
<property name="kundera.port" value="27017" />
<property name="kundera.keyspace" value="datakeeper" />
<property name="kundera.client.lookup.class"
value="com.impetus.mongodb.MongoDBClientFactory" />
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
<persistence-unit name="cassandra-pu,mongo-pu">
<provider>com.impetus.kundera.KunderaPersistence</provider>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
Note: In case of polyglot persistence you need to mention classes under persistence-unit class tag to specify that entities belong to a particular datastore.
Build the project using
mvn clean install
Copy war of project and deploy it on Tomcat.
Hit the following URL to start http://localhost:8080/datakeeper/xhtml/login/login.jsf
You should be able to see following screens if your project is deployed properly on tomcat.
-
Registration page :
Provide all Employee details to register.
-
Login page :
After success full registeration you will be able to login and following page will appear.
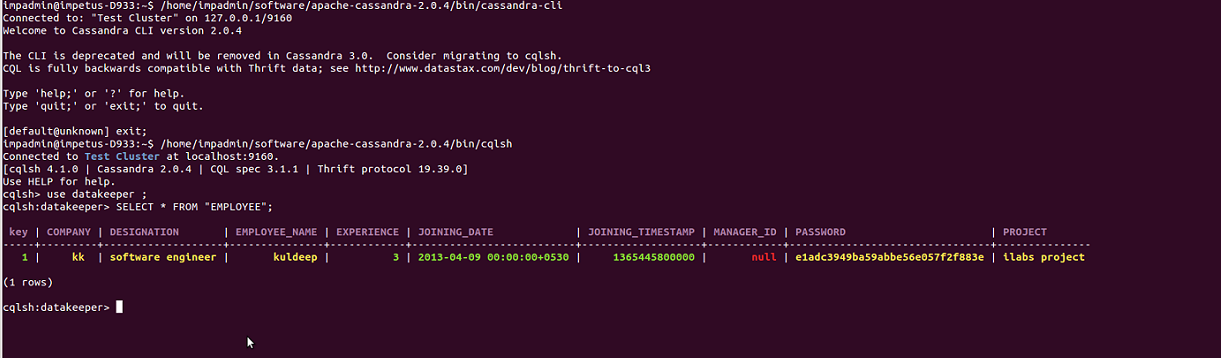
Now validate the Employee data which is stored in Cassandra via Cassandra's command line utility :
-
Datastores Supported
- Releases
-
Architecture
-
Concepts
-
Getting Started in 5 minutes
-
Features
- Object Mapper
- Polyglot Persistence
- Queries Support
- JPQL (JPA Query Language)
- Native Queries
- Batch insert update
- Schema Generation
- Primary Key Auto generation
- Transaction Management
- REST Based Access
- Geospatial Persistence and Queries
- Graph Database Support
-
Composite Keys
-
No hard annotation for schema
-
Support for Mapped superclass
-
Object to NoSQL Data Mapping
-
Cassandra's User Defined Types and Indexes on Collections
-
Support for aggregation
- Scalar Queries over Cassandra
- Connection pooling using Kundera Cassandra
- Configuration
-
Kundera with Couchdb
-
Kundera with Elasticsearch
-
Kundera with HBase
-
Kundera with Kudu
-
Kundera with RethinkDB
-
Kundera with MongoDB
-
Kundera with OracleNoSQL
-
Kundera with Redis
-
Kundera with Spark
-
Extend Kundera
- Sample Codes and Examples
-
Blogs and Articles
-
Tutorials
* Kundera with Openshift
* Kundera with Play Framework
* Kundera with GWT
* Kundera with JBoss
* Kundera with Spring
-
Performance
-
Troubleshooting
-
FAQ
- Production deployments
- Feedback