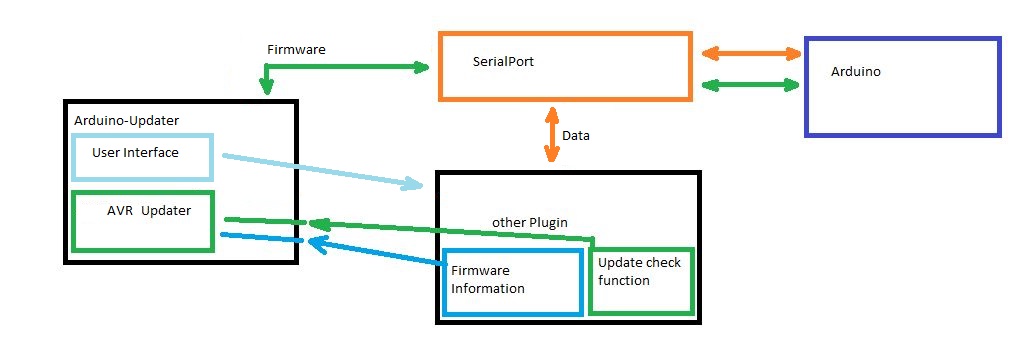
Plugin to update the Software for every "Arduino" connected to Pimatic.
=======================
As an User you must only add arduino-updater to your plugin list in pimatic. After that all Plugins which supports the arduino-updater can now update the software on their arduinos.
{
"plugin": "arduino-updater"
}The pimatic-arduino-updater implements a GUI into the mobile-frontend. In this page you can see all registered plugins, with their arduino configs. You can also force a manual update.
####You like control?
In the GUI you can allow automatically updates. These accesses are stored in the whitelist of arduino-updater.
{
"plugin": "arduino-updater",
"whitelist": [
"rflink",
"homeduino"
]
}Did you install arduino-updater all plugins, which support it, should ask now for an specific arduino board.
{
"plugin": "homeduino",
"driver": "serialport",
"driverOptions": {
"serialDevice": "/dev/ttyUSB0",
"baudrate": 115200,
"board": "nano328" <--- This entry is now neccessary
},
"receiverPin": 1,
"transmitterPin": 4
},The plguin should provide you a list with supportet boards. RFLink for example supports only Arduino Mega boards.
You want to modify your Arduino sketch and want to upload it to your arduino? In the arduino-updater config, you can override the hexfile path for your purposes.
{
"plugin": "arduino-updater",
"whitelist": [
"homeduino"
],
"alternativeHexfiles": {
"homeduino": "/home/pi/blink.hex"
},
"debug": true
}=======================
Your plugin must provide some functions and it must register it self in arduino-updater to got recognized.
Following the example for Pimatic-Homeduino
#This a nice way to get your plugin path
@pluginPath = @framework.pluginManager.pathToPlugin("pimatic-"+@config.plugin)
_registerArduUpdater:()=>
#Check for real Arduino config
if @config.driver is "serialport"
#Wait for all plugins get loaded
@framework.on "after init", =>
#Get arduino-manager plugin
arduUpdater = @framework.pluginManager.getPlugin("arduino-updater")
#Check if it is installed
if arduUpdater?
#Get all supported boards. These are the different Uploader
arduinos = arduUpdater.getSupportedBoards()
#Create string from Mapping keys for Users
boards = (key for key, val of @supportedArduBoards)
#Check if an board type is set
unless @config.driverOptions.board?
env.logger.warn("You have installed pimatic-arduino-updater but you haven´t "+
"specified a Arduino board for Homeduino. "+
"Supported boards are: #{boards.join(", ")}")
#Check if the configured board type is supportet.
else if @supportedArduBoards[@config.driverOptions.board] not in arduinos
env.logger.warn("You have specified a unsupported Arduino board. "+
"Supported boards are: #{boards.join(", ")}")
#register this plugin to arduino-updater
else
#This is your registration
pluginProperties = {
name: @config.plugin
port: @config.driverOptions.serialDevice
board: @config.driverOptions.board
uploader: @supportedArduBoards[@config.driverOptions.board]
file: @pluginPath+"/arduino/Homeduino_"+@config.driverOptions.board+".hex"
}
#returns true for success and false for an wrong pluginPropertie
@arduUpdaterReg = arduUpdater.registerPlugin(pluginProperties)
#returns the state of your whitelist entry.
@autoUpdate = arduUpdater.autoUpdateAllow(@config.plugin)Your plugin must also provide two functions called "disconnect" and "connect". The disconnect function must return a Promise which disconnects your serialport.
disconnect:()=>
return @nextAction( =>
# Give the board some more time before disconnect
return Promise.delay(2000).then( =>
return @board.disconnect()
)
)
connect:()=>
@_conectToBoard()####Hexfiles
Your plugin must provide also ALL possible hex files for all Arduinos. To simplifie this @leader21 has created an bash script, which compiles your arduino .ino sketch to all defined boards.
#!/bin/bash
################################################################################
################################################################################
#
# this script compiles arduino files to hex files and stores them
# for the pimatic-arduino plugin for automatic update procedure.
#
# created by leader21 for the pimatic home automation project
# version 0.1
#
# usage : sudo ./MakeAll
#
# the Makefile needs to be adapted to your needs.
# the script parses the Makefile and changes the BOARD_TAG for itself
#
# all hex files will be stored in the DESTINATION_PATH directory as well as in the builds
#
################################################################################
#Set the hexfile Prefix here. A good string would be "PLUGIN_Arduino".
#The compiled file looks like this "PLUGIN_Arduino_pro328.hex"
TARGET_FILE_PREFIX="Homeduino"
#Set your target directory here. Normally a directory in your Pimatic plugin.
DESTINATION_PATH="/home/USER/pimatic-dev/node_modules/pimatic-homeduino/arduino"
# declare for which boards the arduino file should be compiled
boards=(diecimila leonardo mega2560 mini328 mini nano328 nano pro328 pro5v328 pro5v pro uno)
# check if the upload directory exists, if not create it
echo "Your Arduino code will be compiled into $DESTINATION_PATH"
if ! [ -d $DESTINATION_PATH ]
then
mkdir $DESTINATION_PATH
echo "created destination directory"
else
echo "destination directory already exists"
fi
sleep 2
# for every board the below loop will be executed once, files will be stored in the upload directory
for board in ${boards[@]}
do
echo -e "\n$board will be compiled now"
sleep 2
sed -i "s/BOARD_TAG\s\+=\s\+\w\+/BOARD_TAG = $board/g" Makefile
make
cp build-$board/*.hex "$DESTINATION_PATH/""$TARGET_FILE_PREFIX""_${board}.hex"
echo "done with compiling of $board"
done
ls -l $DESTINATION_PATH
echo -e "\nthe hex files have been compiled and can be found in the $DESTINATION_PATH directory"
exit
To use this script you need to install arduino-mk. There are many examples to archieve this. Example for homeduino.
Install libs
sudo apt-get install arduino-core avr-libc avrdude binutils-avr gcc-avr libconfig-yaml-perl libftdi1 libyaml-perl screen python-serial
- clone homeduino
git clone --recursive https://github.com/pimatic/homeduino.git
Copy the MakeAll skript into the created directory and configure it. now run
./MakeAll
But we have now a mismatch between the compiled files and the arduino-uploader. The uploader supports these boards. "uno", "nano", "mega", "leonardo", "micro", "duemilanove168", "blend-micro" "tinyduino", "sf-pro-micro", "qduino", "pinoccio", "imuduino", "feather"
But compiled files are for "diecimila" "leonardo" "mega2560" "mini328" "mini" "nano328" "nano" "pro328" "pro5v328" "pro5v" "pro" "uno"
To match these boards with the uploader we use an mapping array, which must be stored in your plugin or can be get from arduino-updater.
#This is our uploader mapping. The key (left) value represents the arduino gcc hex file.
#The value (right) is the used uploader. You can see we used often the nano uploader.
@supportedArduBoards = {
"uno": "uno"
"mega": "mega"
"mega2560": "mega"
"leonardo": "leonardo"
"micro": "micro"
"nano328": "nano"
"nano": "nano"
"pro328": "nano"
"pro5v": "nano"
"pro5v328": "nano"
"pro": "nano"
"diecimila": "duemilanove168"
}You can now simple pass the user defined board tag to this mapping and you get the neccessary uploader type.
@supportedArduBoards[@config.driverOptions.board]You can activate the debug output for arduino-uploader in the plugin config.
{
"plugin": "arduino-updater",
"whitelist": [
"homeduino"
],
"alternativeHexfiles": {
"homeduino": "/home/pi/blink.hex"
},
"debug": true
}