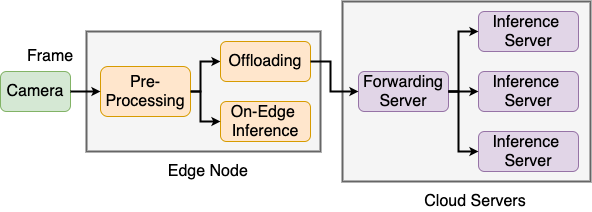
SmartEye is an open source framework for real-time video analytics by leveraging the edge-cloud collaboration. The system consists of 1) an on-edge processing layer which enables video preprocessing, model selection, on-edge inference, and task offloading; 2) a request forwarding layer which serves as a gateway of the cloud and forwards the offloaded tasks to backend workers; and 3) a backend inference layer that processes the offloaded tasks with specified DNN models.
- The Edge Node performs video frame reading, video preprocessing, local inference, offloading, and decision making, etc. The edge node reads video frames from the camera or video files and preprocesses the video frames. After preprocessing, the inference for a video frame can be performed on the edge node or offloaded to the cloud. The decision engine makes video preprocessing and offloading decisions based on the control policies.
- The Forwarding Server serves as the cloud's gateway to respond to the edge node's offloading requests. The edge node submits an HTTP request to the forwarding server by attaching the video frame. The forwarding server dispatches the inference requests among the backend servers based on the forwarding policy. The forwarding server monitors the backend servers and uses the status information to make dispatch decisions.
- The Inference Server are provisioned in the cloud to conduct video analytics inferences. Each inference server loads several DNN models for video analytics. The inference servers receive the offloaded tasks from the forwarding server and make inferences with the specified models.
System Requirements
Please click the above links for the installation of the dependent software.
It may require to install some lacked libraries, e.g., opencv, torchvision, torch, psutil, grpc, flask. There are three parts in this installation:
Part 1: install libraries in the edge node.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install libopencv-dev
pip3 install loguru
pip3 install psutil
pip3 install configparserPart 2: install libraries in the forwarding server.
pip3 install grpcio
pip3 install grpcio-tools googleapis-common-protos
pip3 install flask
pip3 install apscheduler
pip3 install loguruPart 3: install libraries in the backend inference server.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install libopencv-dev
pip3 install loguru
pip3 install psutil
pip3 install grpcio
pip3 install grpcio-tools googleapis-common-protos
You need to install the Git Large File Storage (LFS) to clone the large DNN models from this repository. For deb linux user, you can download and install with the following command.
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/github/git-lfs/script.python.sh | bash
sudo apt-get install git-lfs
git init
git lfs installAfter installing Git LFS, you can clone the souce code of this project from GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/MSNLAB/SmartEye.gitRevise the configuration file SmartEye/config/config.ini.
The edge node, forwarding server, and background inference servers read the configuration from config/config.ini. Make sure each item is set with appropriate value according to your system configuration.
Replace 'server_1_ip' with the real IP address of your server, and leave the IP port number unchanged. You can add lines in this format as many as your backend inference servers under the [grpc-url] section.
[grpc-url]
url0=server_1_ip:50051
url1=server_2_ip:50051
Replace the forwarding_server_ip with the real IP address of your forwarding server, and leave the IP port number and the other parts unchanged.
[flask-url]
video_frame_url=http://forwarding_server_ip:5000/image_handler
You can copy the configured source codes to the edge node, the forwarding server, and the backend inference servers respectively for deployment. You can use the scp command to do it.
scp -r SmartEye/ server_account@server_ip_address:target_pathTo start the service, there are three steps to go:
Step 1: start every backend inference server. If you have more than one inference server, start them one by one. The GPU used by the inference server can be specified in the command line.
cd ~/SmartEye/backend_server/
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=gpu_device_number python3 rpc_server.pyIf you are using servers without GPU, you can start the server with the following command line.
cd ~/SmartEye/backend_server/
nohup python3 rpc_server.py > error_msg &Step 2: start the forwarding server.
cd ~/SmartEye/frontend_server/
nohup python3 forwarding_server.py > server.log 2>&1 &Step 3: start the edge node.
cd ~/SmartEye
python3 edge_main.py -f your_video_path -i 50-f, --file: the path of a local video file
-i, --interval: type int, interval between reading two frames in millisecond (ms)
If the edge node reads video frames from an RTSP camera, you need to first configure config/config.ini.
[camera-info]
account=your_account
password=your_password
ip_address=camera_ip
channel=1Then you can use the following command for reading from the specified camera
cd ~/SmartEye
python3 edge_main --rtsp -i 50-r, --rtsp: use the RTSP camera
-i, --interval: type int, interval between reading two frames in ms
replace device_no with your real camera device no, e.g., 0
cd ~/SmartEye
python3 edge_main -f device_no -i 50-f, --file: the device number of a local camera
-i, --interval: type int, interval between reading two frames in millisecond (ms)
You can visually check the results for object detection under the folder of info_system/handled_result.
You can choose one of the following three policies by changing the value of control_policy under the edge-setting section in config/config.ini.
There are three policies you can use to process your video:
- always_local_fastest_model
- always_cloud_lowest_delay
- threshold_offload_policy
always_local_fastest_model: the inference is only conducted on the edge with the fastest model without preprocessing.
always_cloud_lowest_delay: the inference is conducted only in the cloud with the most accurate model, and video frames are downsized before offloading.
threshold_offload_policy: if the number of local pending tasks is less than a threshold (i.e., 2), the inference for the next video frame will be conducted on the edge node with the fastest model; otherwise, the next video frame will be first downsized and then offloaded to the cloud for inference with the most accurate model.
If you want to customize the control policy of the edge node, you can proceed with the following steps:
- define a policy functon in decision_engine.py, and implement the policies for video frame preprocessing, model selection, and offloading.
- add the function name into self.policy_set of the init()function of class DecisionEngine.
- changing the value of control_policy into the name of your policy function under the edge-setting section in config/config.ini.
THIS SOFTWARE IS RELEASED UNDER THE MIT LICENSE (MIT) Copyright (c), 2021, NUST SCE
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
If you find any problem with this software, please feel free to contact us, your feedback is appreciated.
Email: [email protected]; [email protected]