Python script for monitoring www.cvedetails.com vulnerabilities database
$ git clone https://github.com/Amet13/vulncontrol
$ cd vulncontrol/
First go here, find your software and add links to products.txt.
Script parameters:
-tTelegram token and ID (no usage by default)-dDate in formatYYYY-MM-DD(today by default, it can be incorrectly works with custom data, because cvedetails has bad API)-mMin CVSS (by default 0)
Then you can run script in two ways.
First way without Telegram support:
$ ./vulncontrol.py
There are no available vulnerabilities at 2017-02-28
$ ./vulncontrol.py -d 2017-02-18 -m 5
CVE-2017-6074 9.3 http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2017-6074/
CVE-2017-6001 7.6 http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2017-6001/
CVE-2017-5986 7.1 http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2017-5986/
Telegram alert did not sent
Second way with Telegram support:
- go to @BotFather and create
/newbot, for exampleVulncontrolBot - then you have token like
111111111:ABCDE... - after go to @MyTelegramID_bot and
/startit - then you have your telegram ID like
123456789
Now you can run script with your token and ID:
$ ./vulncontrol.py -t 111111111:ABCDE 123456789
There are no available vulnerabilities at 2017-02-28
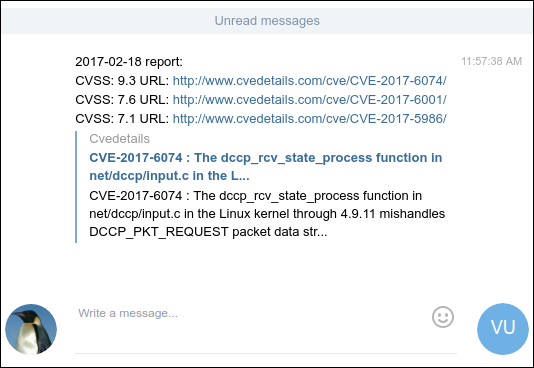
$ ./vulncontrol.py -t 111111111:ABCDE 123456789 -d 2017-02-18 -m 5
CVE-2017-6074 9.3 http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2017-6074/
CVE-2017-6001 7.6 http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2017-6001/
CVE-2017-5986 7.1 http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2017-5986/
Telegram alert sent
Check your Telegram messages:
You can add script to you monitoring system (Nagios/Icinga2, Zabbix, etc) or cron.
Example for cron:
$ crontab -e
* */12 * * * /path/to/vulncontrol.py -t 111111111:ABCDE 123456789 -m 5
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | There are no available vulnerabilities |
| 1 | Vulnerabilities available, Telegram alert did not sent |
| 2 | Vulnerabilities available, Telegram alert sent |
| 3 | Vulnerabilities available, Telegram alert did not sent, check your token and ID |
You can customize result with more keys.
Available keys:
cve_idcvss_scorecwe_idexploit_countpublish_datesummaryupdate_dateurl
Example of JSON-output:
{
"cve_id": "CVE-2017-5551",
"cvss_score": "3.6",
"cwe_id": "264",
"exploit_count": "0",
"publish_date": "2017-02-06",
"summary": "The simple_set_acl function in fs/posix_acl.c in the Linux kernel before 4.9.6 preserves the setgid bit during a setxattr call involving a tmpfs filesystem, which allows local users to gain group privileges by leveraging the existence of a setgid program with restrictions on execute permissions. NOTE: this vulnerability exists because of an incomplete fix for CVE-2016-7097.",
"update_date": "2017-02-09",
"url": "http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2017-5551/"
}
curl "https://www.cvedetails.com/json-feed.php?key1=value1&key2=value2..."
Custom parameters:
| Key | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| year | 2017 | Year |
| month | 1-12 | Month |
| vendor_id | 33 | Vendor ID |
| product_id | 47 | Product ID |
| orderby | 1-3 | Sort type (1 - Publish Date, 2 - Last Update Date, 3 - CVE ID) |
| cvssscoremin | 0-10 | Min CVSS |
| cvssscoremax | 0-10 | Max CVSS |
| numrows | 0-30 | Number of rows |
Boolean parameters (0 by default, 1 - yes):
| Key | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| hasexp | 0 | Has exploits |
| opec | 0 | Code execution |
| opov | 0 | Overflows |
| opcsrf | 0 | Cross Site Request Forgery |
| opfileinc | 0 | File inclusion |
| opgpriv | 0 | Gain privilege |
| opsqli | 0 | Sql injection |
| opxss | 0 | Cross site scripting |
| opdirt | 0 | Directory traversal |
| opmemc | 0 | Memory corruption |
| ophttprs | 0 | Http response splitting |
| opbyp | 0 | Bypass something |
| opginf | 0 | Gain information |
| opdos | 0 | Denial of service |