You are given an undirected weighted connected graph containing n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and an integer array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi with weight wi.
Some edges have a weight of -1 (wi = -1), while others have a positive weight (wi > 0).
Your task is to modify all edges with a weight of -1 by assigning them positive integer values in the range [1, 2 * 109] so that the shortest distance between the nodes source and destination becomes equal to an integer target. If there are multiple modifications that make the shortest distance between source and destination equal to target, any of them will be considered correct.
Return an array containing all edges (even unmodified ones) in any order if it is possible to make the shortest distance from source to destination equal to target, or an empty array if it's impossible.
Note: You are not allowed to modify the weights of edges with initial positive weights.
Example 1:
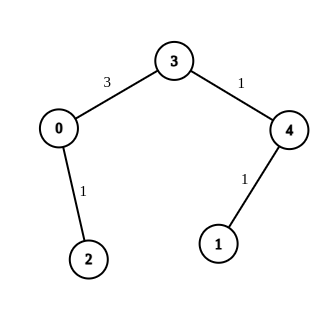
Input: n = 5, edges = [[4,1,-1],[2,0,-1],[0,3,-1],[4,3,-1]], source = 0, destination = 1, target = 5 Output: [[4,1,1],[2,0,1],[0,3,3],[4,3,1]] Explanation: The graph above shows a possible modification to the edges, making the distance from 0 to 1 equal to 5.
Example 2:
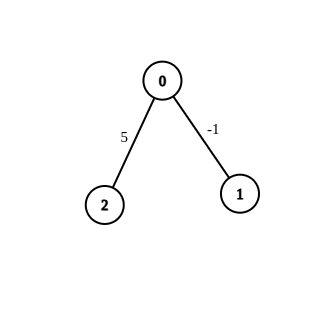
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,-1],[0,2,5]], source = 0, destination = 2, target = 6 Output: [] Explanation: The graph above contains the initial edges. It is not possible to make the distance from 0 to 2 equal to 6 by modifying the edge with weight -1. So, an empty array is returned.
Example 3:
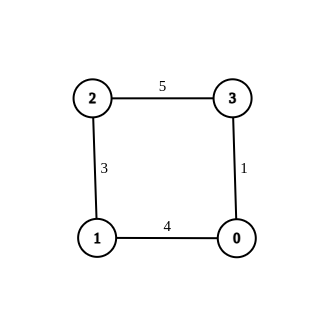
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,0,4],[1,2,3],[2,3,5],[0,3,-1]], source = 0, destination = 2, target = 6 Output: [[1,0,4],[1,2,3],[2,3,5],[0,3,1]] Explanation: The graph above shows a modified graph having the shortest distance from 0 to 2 as 6.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2edges[i].length == 30 <= ai, bi < nwi = -1or1 <= wi <= 107ai != bi0 <= source, destination < nsource != destination1 <= target <= 109- The graph is connected, and there are no self-loops or repeated edges
class Solution:
def modifiedGraphEdges(
self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int, target: int
) -> List[List[int]]:
def dijkstra(edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g = [[inf] * n for _ in range(n)]
for a, b, w in edges:
if w == -1:
continue
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = w
dist = [inf] * n
dist[source] = 0
vis = [False] * n
for _ in range(n):
k = -1
for j in range(n):
if not vis[j] and (k == -1 or dist[k] > dist[j]):
k = j
vis[k] = True
for j in range(n):
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[k] + g[k][j])
return dist[destination]
inf = 2 * 10**9
d = dijkstra(edges)
if d < target:
return []
ok = d == target
for e in edges:
if e[2] > 0:
continue
if ok:
e[2] = inf
continue
e[2] = 1
d = dijkstra(edges)
if d <= target:
ok = True
e[2] += target - d
return edges if ok else []class Solution {
private final int inf = 2000000000;
public int[][] modifiedGraphEdges(
int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination, int target) {
long d = dijkstra(edges, n, source, destination);
if (d < target) {
return new int[0][];
}
boolean ok = d == target;
for (var e : edges) {
if (e[2] > 0) {
continue;
}
if (ok) {
e[2] = inf;
continue;
}
e[2] = 1;
d = dijkstra(edges, n, source, destination);
if (d <= target) {
ok = true;
e[2] += target - d;
}
}
return ok ? edges : new int[0][];
}
private long dijkstra(int[][] edges, int n, int src, int dest) {
int[][] g = new int[n][n];
long[] dist = new long[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, inf);
dist[src] = 0;
for (var f : g) {
Arrays.fill(f, inf);
}
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1], w = e[2];
if (w == -1) {
continue;
}
g[a][b] = w;
g[b][a] = w;
}
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int k = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (k == -1 || dist[k] > dist[j])) {
k = j;
}
}
vis[k] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[k] + g[k][j]);
}
}
return dist[dest];
}
}using ll = long long;
const int inf = 2e9;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> modifiedGraphEdges(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int source, int destination, int target) {
ll d = dijkstra(edges, n, source, destination);
if (d < target) {
return {};
}
bool ok = d == target;
for (auto& e : edges) {
if (e[2] > 0) {
continue;
}
if (ok) {
e[2] = inf;
continue;
}
e[2] = 1;
d = dijkstra(edges, n, source, destination);
if (d <= target) {
ok = true;
e[2] += target - d;
}
}
return ok ? edges : vector<vector<int>>{};
}
ll dijkstra(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int n, int src, int dest) {
ll g[n][n];
ll dist[n];
bool vis[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
fill(g[i], g[i] + n, inf);
dist[i] = inf;
vis[i] = false;
}
dist[src] = 0;
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1], w = e[2];
if (w == -1) {
continue;
}
g[a][b] = w;
g[b][a] = w;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int k = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (k == -1 || dist[j] < dist[k])) {
k = j;
}
}
vis[k] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[k] + g[k][j]);
}
}
return dist[dest];
}
};func modifiedGraphEdges(n int, edges [][]int, source int, destination int, target int) [][]int {
const inf int = 2e9
dijkstra := func(edges [][]int) int {
g := make([][]int, n)
dist := make([]int, n)
vis := make([]bool, n)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range g[i] {
g[i][j] = inf
}
dist[i] = inf
}
dist[source] = 0
for _, e := range edges {
a, b, w := e[0], e[1], e[2]
if w == -1 {
continue
}
g[a][b], g[b][a] = w, w
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
k := -1
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if !vis[j] && (k == -1 || dist[j] < dist[k]) {
k = j
}
}
vis[k] = true
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[k]+g[k][j])
}
}
return dist[destination]
}
d := dijkstra(edges)
if d < target {
return [][]int{}
}
ok := d == target
for _, e := range edges {
if e[2] > 0 {
continue
}
if ok {
e[2] = inf
continue
}
e[2] = 1
d := dijkstra(edges)
if d <= target {
ok = true
e[2] += target - d
}
}
if ok {
return edges
}
return [][]int{}
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}function modifiedGraphEdges(
n: number,
edges: number[][],
source: number,
destination: number,
target: number,
): number[][] {
const inf = 2e9;
const dijkstra = (edges: number[][]): number => {
const g: number[][] = Array(n)
.fill(0)
.map(() => Array(n).fill(inf));
const dist: number[] = Array(n).fill(inf);
const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
for (const [a, b, w] of edges) {
if (w === -1) {
continue;
}
g[a][b] = w;
g[b][a] = w;
}
dist[source] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
let k = -1;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (k === -1 || dist[j] < dist[k])) {
k = j;
}
}
vis[k] = true;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[k] + g[k][j]);
}
}
return dist[destination];
};
let d = dijkstra(edges);
if (d < target) {
return [];
}
let ok = d === target;
for (const e of edges) {
if (e[2] > 0) {
continue;
}
if (ok) {
e[2] = inf;
continue;
}
e[2] = 1;
d = dijkstra(edges);
if (d <= target) {
ok = true;
e[2] += target - d;
}
}
return ok ? edges : [];
}