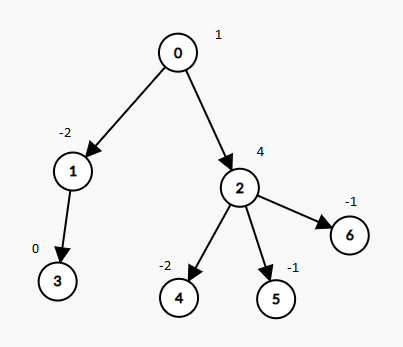
A tree rooted at node 0 is given as follows:
- The number of nodes is
nodes; - The value of the
ithnode isvalue[i]; - The parent of the
ithnode isparent[i].
Remove every subtree whose sum of values of nodes is zero.
Return the number of the remaining nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
Input: nodes = 7, parent = [-1,0,0,1,2,2,2], value = [1,-2,4,0,-2,-1,-1] Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nodes = 7, parent = [-1,0,0,1,2,2,2], value = [1,-2,4,0,-2,-1,-2] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= nodes <= 104parent.length == nodes0 <= parent[i] <= nodes - 1parent[0] == -1which indicates that0is the root.value.length == nodes-105 <= value[i] <= 105- The given input is guaranteed to represent a valid tree.
class Solution:
def deleteTreeNodes(self, nodes: int, parent: List[int], value: List[int]) -> int:
def dfs(i):
s, m = value[i], 1
for j in g[i]:
t, n = dfs(j)
s += t
m += n
if s == 0:
m = 0
return (s, m)
g = defaultdict(list)
for i in range(1, nodes):
g[parent[i]].append(i)
return dfs(0)[1]class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int[] value;
public int deleteTreeNodes(int nodes, int[] parent, int[] value) {
g = new List[nodes];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 1; i < nodes; ++i) {
g[parent[i]].add(i);
}
this.value = value;
return dfs(0)[1];
}
private int[] dfs(int i) {
int[] res = new int[] {value[i], 1};
for (int j : g[i]) {
int[] t = dfs(j);
res[0] += t[0];
res[1] += t[1];
}
if (res[0] == 0) {
res[1] = 0;
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int deleteTreeNodes(int nodes, vector<int>& parent, vector<int>& value) {
vector<vector<int>> g(nodes);
for (int i = 1; i < nodes; ++i) {
g[parent[i]].emplace_back(i);
}
function<pair<int, int>(int)> dfs = [&](int i) -> pair<int, int> {
int s = value[i], m = 1;
for (int j : g[i]) {
auto [t, n] = dfs(j);
s += t;
m += n;
}
if (s == 0) {
m = 0;
}
return pair<int, int>{s, m};
};
return dfs(0).second;
}
};func deleteTreeNodes(nodes int, parent []int, value []int) int {
g := make([][]int, nodes)
for i := 1; i < nodes; i++ {
g[parent[i]] = append(g[parent[i]], i)
}
type pair struct{ s, n int }
var dfs func(int) pair
dfs = func(i int) pair {
s, m := value[i], 1
for _, j := range g[i] {
t := dfs(j)
s += t.s
m += t.n
}
if s == 0 {
m = 0
}
return pair{s, m}
}
return dfs(0).n
}