On a 0-indexed 8 x 8 chessboard, there can be multiple black queens ad one white king.
You are given a 2D integer array queens where queens[i] = [xQueeni, yQueeni] represents the position of the ith black queen on the chessboard. You are also given an integer array king of length 2 where king = [xKing, yKing] represents the position of the white king.
Return the coordinates of the black queens that can directly attack the king. You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
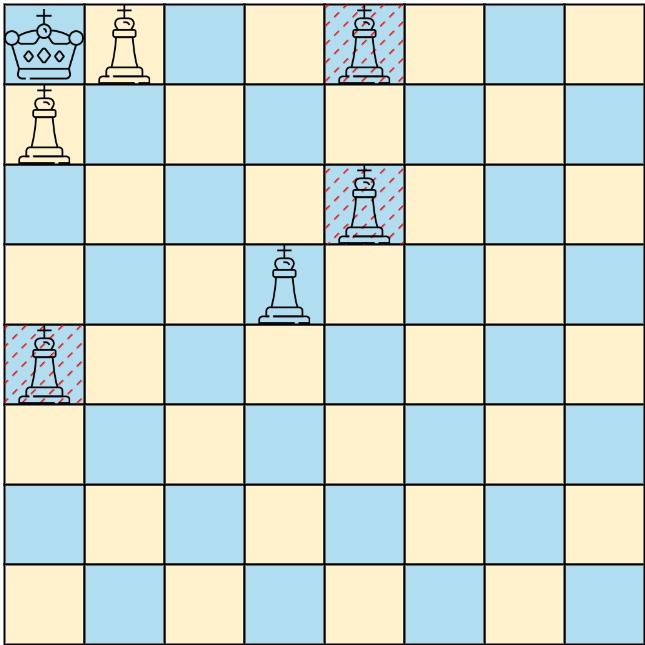
Input: queens = [[0,1],[1,0],[4,0],[0,4],[3,3],[2,4]], king = [0,0] Output: [[0,1],[1,0],[3,3]] Explanation: The diagram above shows the three queens that can directly attack the king and the three queens that cannot attack the king (i.e., marked with red dashes).
Example 2:
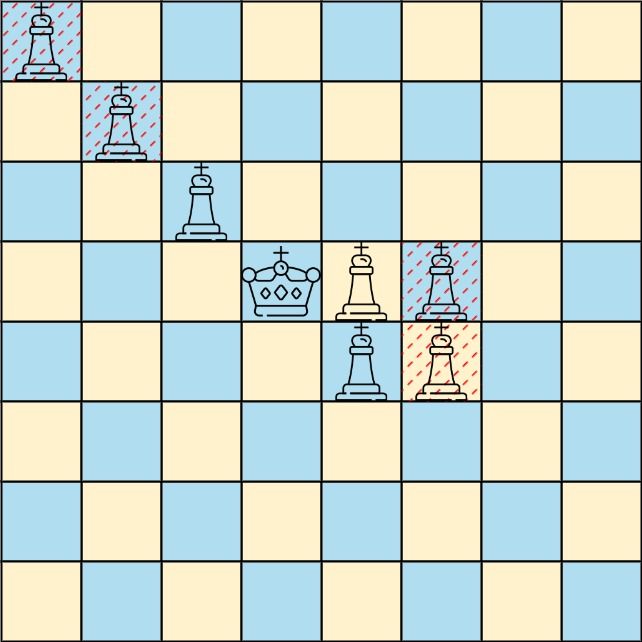
Input: queens = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[3,5],[4,4],[4,5]], king = [3,3] Output: [[2,2],[3,4],[4,4]] Explanation: The diagram above shows the three queens that can directly attack the king and the three queens that cannot attack the king (i.e., marked with red dashes).
Constraints:
1 <= queens.length < 64queens[i].length == king.length == 20 <= xQueeni, yQueeni, xKing, yKing < 8- All the given positions are unique.
class Solution:
def queensAttacktheKing(
self, queens: List[List[int]], king: List[int]
) -> List[List[int]]:
n = 8
s = {(i, j) for i, j in queens}
ans = []
for a, b in [
[-1, 0],
[1, 0],
[0, -1],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[-1, -1],
]:
x, y = king
while 0 <= x + a < n and 0 <= y + b < n:
x, y = x + a, y + b
if (x, y) in s:
ans.append([x, y])
break
return ansclass Solution {
private static final int N = 8;
private int[][] dirs
= new int[][] {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {1, 1}, {1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {-1, -1}};
public List<List<Integer>> queensAttacktheKing(int[][] queens, int[] king) {
Set<Integer> s = get(queens);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int x = king[0], y = king[1];
int a = dir[0], b = dir[1];
while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < N && y + b >= 0 && y + b < N) {
x += a;
y += b;
if (s.contains(x * N + y)) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(x, y));
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private Set<Integer> get(int[][] queens) {
Set<Integer> ans = new HashSet<>();
for (int[] queen : queens) {
ans.add(queen[0] * N + queen[1]);
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> queensAttacktheKing(vector<vector<int>>& queens, vector<int>& king) {
unordered_set<int> s;
int n = 8;
for (auto& queen : queens) s.insert(queen[0] * n + queen[1]);
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {1, 1}, {1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {-1, -1}};
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (auto& dir : dirs) {
int x = king[0], y = king[1];
int a = dir[0], b = dir[1];
while (x + a >= 0 && x + a < n && y + b >= 0 && y + b < n) {
x += a;
y += b;
if (s.count(x * n + y)) {
ans.push_back({x, y});
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func queensAttacktheKing(queens [][]int, king []int) [][]int {
s := make(map[int]bool)
n := 8
for _, queen := range queens {
s[queen[0]*n+queen[1]] = true
}
dirs := [8][2]int{{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {1, 1}, {1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {-1, -1}}
var ans [][]int
for _, dir := range dirs {
x, y := king[0], king[1]
a, b := dir[0], dir[1]
for x+a >= 0 && x+a < n && y+b >= 0 && y+b < n {
x, y = x+a, y+b
if s[x*n+y] {
ans = append(ans, []int{x, y})
break
}
}
}
return ans
}