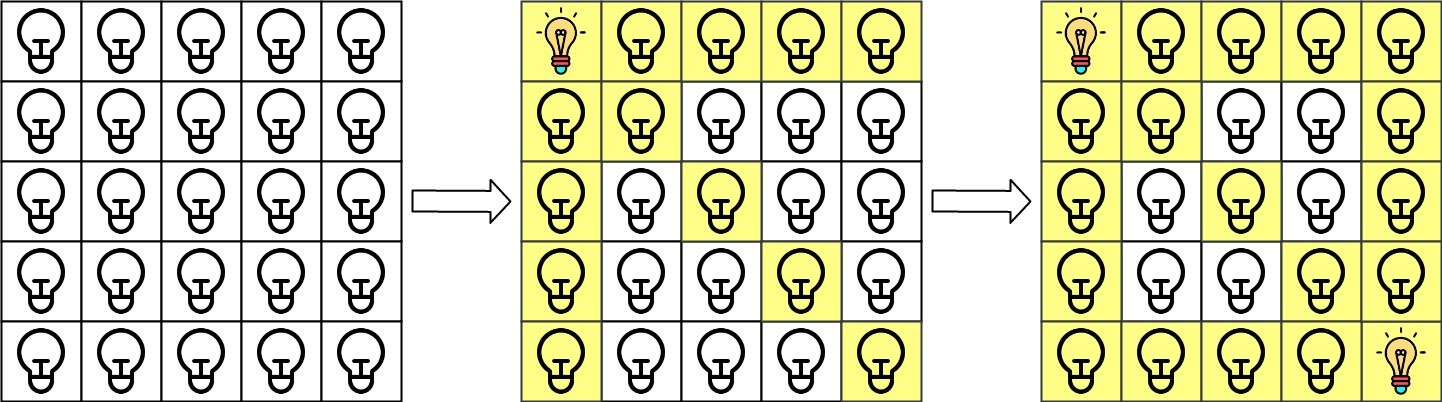
There is a 2D grid of size n x n where each cell of this grid has a lamp that is initially turned off.
You are given a 2D array of lamp positions lamps, where lamps[i] = [rowi, coli] indicates that the lamp at grid[rowi][coli] is turned on. Even if the same lamp is listed more than once, it is turned on.
When a lamp is turned on, it illuminates its cell and all other cells in the same row, column, or diagonal.
You are also given another 2D array queries, where queries[j] = [rowj, colj]. For the jth query, determine whether grid[rowj][colj] is illuminated or not. After answering the jth query, turn off the lamp at grid[rowj][colj] and its 8 adjacent lamps if they exist. A lamp is adjacent if its cell shares either a side or corner with grid[rowj][colj].
Return an array of integers ans, where ans[j] should be 1 if the cell in the jth query was illuminated, or 0 if the lamp was not.
Example 1:
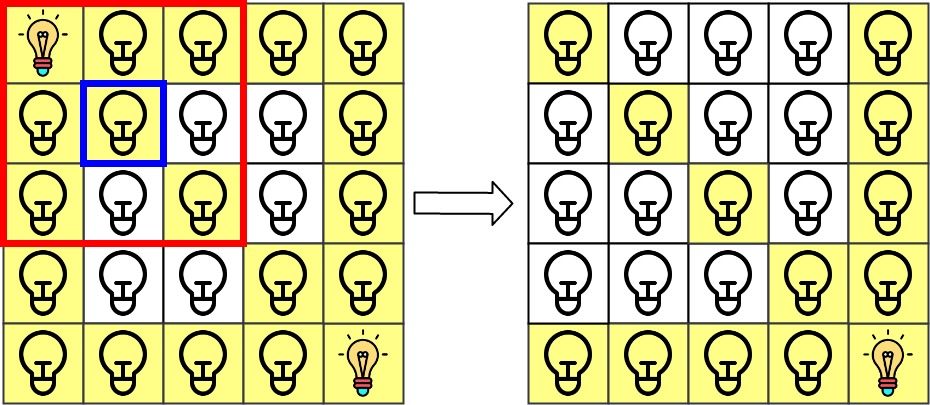
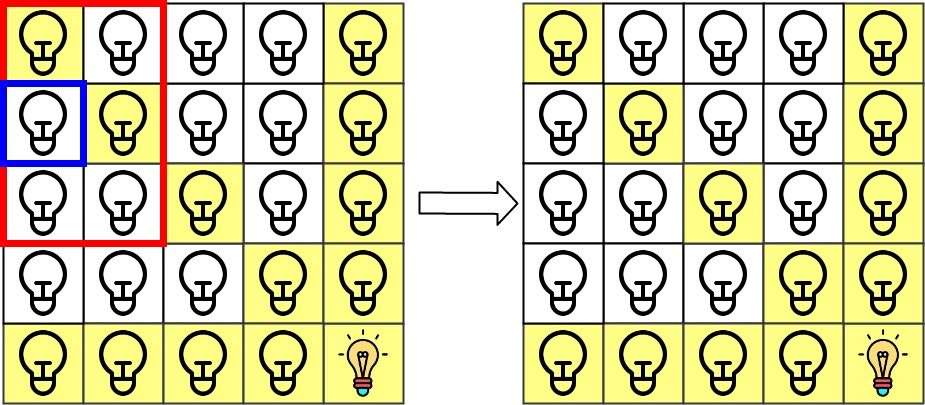
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[4,4]], queries = [[1,1],[1,0]] Output: [1,0] Explanation: We have the initial grid with all lamps turned off. In the above picture we see the grid after turning on the lamp at grid[0][0] then turning on the lamp at grid[4][4]. The 0th query asks if the lamp at grid[1][1] is illuminated or not (the blue square). It is illuminated, so set ans[0] = 1. Then, we turn off all lamps in the red square.The 1st query asks if the lamp at grid[1][0] is illuminated or not (the blue square). It is not illuminated, so set ans[1] = 0. Then, we turn off all lamps in the red rectangle.
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[4,4]], queries = [[1,1],[1,1]] Output: [1,1]
Example 3:
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[0,4]], queries = [[0,4],[0,1],[1,4]] Output: [1,1,0]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1090 <= lamps.length <= 200000 <= queries.length <= 20000lamps[i].length == 20 <= rowi, coli < nqueries[j].length == 20 <= rowj, colj < n
class Solution:
def gridIllumination(
self, n: int, lamps: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]
) -> List[int]:
s = {(i, j) for i, j in lamps}
row, col, diag1, diag2 = Counter(), Counter(), Counter(), Counter()
for i, j in s:
row[i] += 1
col[j] += 1
diag1[i - j] += 1
diag2[i + j] += 1
ans = [0] * len(queries)
for k, (i, j) in enumerate(queries):
if row[i] or col[j] or diag1[i - j] or diag2[i + j]:
ans[k] = 1
for x in range(i - 1, i + 2):
for y in range(j - 1, j + 2):
if (x, y) in s:
s.remove((x, y))
row[x] -= 1
col[y] -= 1
diag1[x - y] -= 1
diag2[x + y] -= 1
return ansclass Solution {
private int n;
public int[] gridIllumination(int n, int[][] lamps, int[][] queries) {
this.n = n;
Set<Long> s = new HashSet<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> row = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> col = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> diag1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> diag2 = new HashMap<>();
for (var lamp : lamps) {
int i = lamp[0], j = lamp[1];
if (s.add(f(i, j))) {
merge(row, i, 1);
merge(col, j, 1);
merge(diag1, i - j, 1);
merge(diag2, i + j, 1);
}
}
int m = queries.length;
int[] ans = new int[m];
for (int k = 0; k < m; ++k) {
int i = queries[k][0], j = queries[k][1];
if (exist(row, i) || exist(col, j) || exist(diag1, i - j) || exist(diag2, i + j)) {
ans[k] = 1;
}
for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) {
for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) {
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= n || !s.contains(f(x, y))) {
continue;
}
s.remove(f(x, y));
merge(row, x, -1);
merge(col, y, -1);
merge(diag1, x - y, -1);
merge(diag2, x + y, -1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private void merge(Map<Integer, Integer> cnt, int x, int d) {
if (cnt.merge(x, d, Integer::sum) == 0) {
cnt.remove(x);
}
}
private boolean exist(Map<Integer, Integer> cnt, int x) {
return cnt.getOrDefault(x, 0) > 0;
}
private long f(long i, long j) {
return i * n + j;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> gridIllumination(int n, vector<vector<int>>& lamps, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
auto f = [&](int i, int j) -> long long {
return (long long) i * n + j;
};
unordered_set<long long> s;
unordered_map<int, int> row, col, diag1, diag2;
for (auto& lamp : lamps) {
int i = lamp[0], j = lamp[1];
if (!s.count(f(i, j))) {
s.insert(f(i, j));
row[i]++;
col[j]++;
diag1[i - j]++;
diag2[i + j]++;
}
}
int m = queries.size();
vector<int> ans(m);
for (int k = 0; k < m; ++k) {
int i = queries[k][0], j = queries[k][1];
if (row[i] > 0 || col[j] > 0 || diag1[i - j] > 0 || diag2[i + j] > 0) {
ans[k] = 1;
}
for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) {
for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) {
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= n || !s.count(f(x, y))) {
continue;
}
s.erase(f(x, y));
row[x]--;
col[y]--;
diag1[x - y]--;
diag2[x + y]--;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func gridIllumination(n int, lamps [][]int, queries [][]int) []int {
row, col, diag1, diag2 := map[int]int{}, map[int]int{}, map[int]int{}, map[int]int{}
type pair struct{ x, y int }
s := map[pair]bool{}
for _, lamp := range lamps {
i, j := lamp[0], lamp[1]
p := pair{i, j}
if !s[p] {
s[p] = true
row[i]++
col[j]++
diag1[i-j]++
diag2[i+j]++
}
}
m := len(queries)
ans := make([]int, m)
for k, q := range queries {
i, j := q[0], q[1]
if row[i] > 0 || col[j] > 0 || diag1[i-j] > 0 || diag2[i+j] > 0 {
ans[k] = 1
}
for x := i - 1; x <= i+1; x++ {
for y := j - 1; y <= j+1; y++ {
p := pair{x, y}
if s[p] {
s[p] = false
row[x]--
col[y]--
diag1[x-y]--
diag2[x+y]--
}
}
}
}
return ans
}function gridIllumination(
n: number,
lamps: number[][],
queries: number[][],
): number[] {
const row = new Map<number, number>();
const col = new Map<number, number>();
const diag1 = new Map<number, number>();
const diag2 = new Map<number, number>();
const s = new Set<number>();
for (const [i, j] of lamps) {
if (s.has(i * n + j)) {
continue;
}
s.add(i * n + j);
row.set(i, (row.get(i) || 0) + 1);
col.set(j, (col.get(j) || 0) + 1);
diag1.set(i - j, (diag1.get(i - j) || 0) + 1);
diag2.set(i + j, (diag2.get(i + j) || 0) + 1);
}
const ans: number[] = [];
for (const [i, j] of queries) {
if (
row.get(i)! > 0 ||
col.get(j)! > 0 ||
diag1.get(i - j)! > 0 ||
diag2.get(i + j)! > 0
) {
ans.push(1);
} else {
ans.push(0);
}
for (let x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) {
for (let y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) {
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= n || !s.has(x * n + y)) {
continue;
}
s.delete(x * n + y);
row.set(x, row.get(x)! - 1);
col.set(y, col.get(y)! - 1);
diag1.set(x - y, diag1.get(x - y)! - 1);
diag2.set(x + y, diag2.get(x + y)! - 1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}