You are given an m x n integer array grid where grid[i][j] could be:
1representing the starting square. There is exactly one starting square.2representing the ending square. There is exactly one ending square.0representing empty squares we can walk over.-1representing obstacles that we cannot walk over.
Return the number of 4-directional walks from the starting square to the ending square, that walk over every non-obstacle square exactly once.
Example 1:
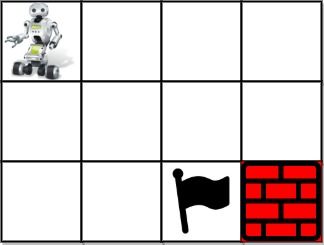
Input: grid = [[1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,2,-1]] Output: 2 Explanation: We have the following two paths: 1. (0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2) 2. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(2,2)
Example 2:
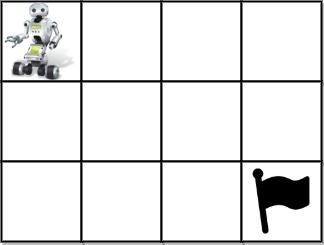
Input: grid = [[1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,2]] Output: 4 Explanation: We have the following four paths: 1. (0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(2,3) 2. (0,0),(0,1),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(1,2),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(2,3) 3. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(1,2),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(2,3) 4. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(2,2),(2,3)
Example 3:
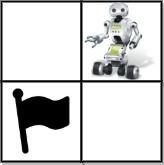
Input: grid = [[0,1],[2,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: There is no path that walks over every empty square exactly once. Note that the starting and ending square can be anywhere in the grid.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 201 <= m * n <= 20-1 <= grid[i][j] <= 2- There is exactly one starting cell and one ending cell.
class Solution:
def uniquePathsIII(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(i, j, k):
if grid[i][j] == 2:
return int(k == cnt + 1)
ans = 0
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and (x, y) not in vis and grid[x][y] != -1:
vis.add((x, y))
ans += dfs(x, y, k + 1)
vis.remove((x, y))
return ans
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
start = next((i, j) for i in range(m) for j in range(n) if grid[i][j] == 1)
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
cnt = sum(grid[i][j] == 0 for i in range(m) for j in range(n))
vis = {start}
return dfs(*start, 0)class Solution {
private int m;
private int n;
private int cnt;
private int[][] grid;
private boolean[][] vis;
public int uniquePathsIII(int[][] grid) {
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
this.grid = grid;
int x = 0, y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) {
++cnt;
} else if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
vis = new boolean[m][n];
vis[x][y] = true;
return dfs(x, y, 0);
}
private int dfs(int i, int j, int k) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
return k == cnt + 1 ? 1 : 0;
}
int ans = 0;
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int h = 0; h < 4; ++h) {
int x = i + dirs[h], y = j + dirs[h + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && grid[x][y] != -1) {
vis[x][y] = true;
ans += dfs(x, y, k + 1);
vis[x][y] = false;
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int uniquePathsIII(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
int cnt = 0;
for (auto& row : grid) {
for (auto& x : row) {
cnt += x == 0;
}
}
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
bool vis[m][n];
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
function<int(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int j, int k) -> int {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
return k == cnt + 1 ? 1 : 0;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int h = 0; h < 4; ++h) {
int x = i + dirs[h], y = j + dirs[h + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && grid[x][y] != -1) {
vis[x][y] = true;
ans += dfs(x, y, k + 1);
vis[x][y] = false;
}
}
return ans;
};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
vis[i][j] = true;
return dfs(i, j, 0);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};func uniquePathsIII(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
cnt := 0
vis := make([][]bool, m)
x, y := 0, 0
for i, row := range grid {
vis[i] = make([]bool, n)
for j, v := range row {
if v == 0 {
cnt++
} else if v == 1 {
x, y = i, j
}
}
}
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
var dfs func(i, j, k int) int
dfs = func(i, j, k int) int {
if grid[i][j] == 2 {
if k == cnt+1 {
return 1
}
return 0
}
ans := 0
for h := 0; h < 4; h++ {
x, y := i+dirs[h], j+dirs[h+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && grid[x][y] != -1 {
vis[x][y] = true
ans += dfs(x, y, k+1)
vis[x][y] = false
}
}
return ans
}
vis[x][y] = true
return dfs(x, y, 0)
}