-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
/
Copy pathrust-collections.html
734 lines (474 loc) · 16.4 KB
/
rust-collections.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
630
631
632
633
634
635
636
637
638
639
640
641
642
643
644
645
646
647
648
649
650
651
652
653
654
655
656
657
658
659
660
661
662
663
664
665
666
667
668
669
670
671
672
673
674
675
676
677
678
679
680
681
682
683
684
685
686
687
688
689
690
691
692
693
694
695
696
697
698
699
700
701
702
703
704
705
706
707
708
709
710
711
712
713
714
715
716
717
718
719
720
721
722
723
724
725
726
727
728
729
730
731
732
733
734
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Rust Collections</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
<style type="text/css" media="screen">
img {
max-width: 100%;
max-height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<textarea id="source">
class: middle, center
# Rust Collections
### 簡單好用的集合模組
<img
style="border-radius: 50px"
src="https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/67644641ead7ae60a795a14b7e102973?s=100"
alt="Weihang Lo">
<a href="https://github.com/weihanglo">@weihanglo</a>
---
## 何謂 Collections
#### From Oxford Dictionary
| kəˈlɛkʃ(ə)n |
_noun_
A group of accumulated **items** of a **particular kind**.
- ❌ heterogeneous
- ✅ homogeneous
#### From Rust Documentation
... efficient **implementations** of the most common general purpose programming data structures ...
- ❌ Abstract Data Types
- ✅ Concrete Data Structures
---
class: middle, center
## From Weihang Lo
> 開箱即用的通用資料結構。
---
## Rust Collections 特別之處
1. 繞過區域變數必須在編譯期確認記憶體大小的限制。
2. 一種智慧指標,將資料儲存在 heap 上。
3. 可使用在 _no\_std_ 環境(但是需要有 heap allocator)
---
## 變數記憶體大小檢查
```rust
fn main() {
let a: [i32];
}
```
```sh
Compiling playground v0.0.1 (file:///playground)
error[E0277]: the trait bound `[i32]: std::marker::Sized` is not satisfied
--> src/main.rs:3:9
|
3 | let a: [i32];
| ^ `[i32]` does not have a constant size known at compile-time
|
= help: the trait `std::marker::Sized` is not implemented for `[i32]`
= note: all local variables must have a statically known size
```
**變數在編譯期必須有常數的記憶體大小。**
> 有常數記憶體大小代表該型別有實作 [`std::marker:Sized`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/marker/trait.Sized.html)
---
## 智慧指標
- 特殊的指標類別,可動態配置記憶體(Dynamic allocation)。
- 資料會配置在 heap,而指標本身配置在 stack。
- 類似 C 的 `malloc` 等記憶體配置函數,但不需要對應的 `free`。
- 又稱 fat pointer,因為儲存指向資料的指標外,通常會儲存額外資訊,例如陣列長度,空間需求稍大。
---
## Rust Collections 有什麼
- Vector
- VecDeque
- LinkedList
- HashMap
- BTreeMap
- HashSet
- BTreeSet
- BinaryHeap
完整描述請參考 [std::collections](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/collections/)
---
## Vector
在相鄰的記憶體空間上儲存資料的動態陣列型別
- 只能儲存相同的型別
- 這個連續記憶體空間配置在 heap 上
- 類似 C++ `std::vector`
---
## 記憶體配置
<p style="text-align: center">
<img style="max-height: 450px" src="rust-collections/vec-mem-layout.png">
</p>
.center[Raph Levien, Google. CC BY]
---
## 建立 Vector 實例
`Vec::new` 建構式
```rust
let v = Vec::new() // []
```
`vec!` macro
```rust
let v1 = vec![1, 2, 3]; // [1, 2, 3]
let v2 = vec![1; 5]; // [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
```
`into_vec`:轉換同時轉移 ownership(without clone)
```rust
let s: Box<[i32]> = Box::new([10, 40, 30]);
let x = s.into_vec();
```
`to_vec`:以 clone 方式建構新的 Vector
```rust
let s = [10, 40, 30];
let x = s.to_vec(); // `s` `x` 可以獨立被修改
```
---
## Bonus: 轉型慣例命名
**into_xx**:多用於轉移 ownership 的操作。
**as_xx**:多用於轉變型別,但不影響 ownership 也不 clone 的操作。
**to_xx**:多用於 clone 的操作。
---
## Get
indexing `v[]`
- Vector 有實作 `Index`/`IndexMut` traits
- out of bound 時會 panic
```rust
let mut rna = vec!['A', 'T', 'C', 'G'];
rna[1] = 'U'; // ['A', 'U', 'C', 'G']
```
Safer indexing with `Vec::get` and `Vec::get_mut`
- `get`: immutable borrowed of subslice
- `get_mut`: immutable borrowed of subslice
```rust
let mut rna = vec!['A', 'T', 'C', 'G'];
rna.get_mut(1).map(|x| *x = 'U'); // ['A', 'U', 'C', 'G']
rna.get_mut(4).map(|x| *x = 'Z'); // Out of bound. No-op.
```
---
## Slicing
`v[]` 與 `v.get`/`v.get_mut` 也可傳入 Range operator,切出 sub slice。
```Rust
let mut v = vec![0, 1, 2, 3, 4];
{
let v1 = &v[3..];
println!("{:?}", v1); // [3, 4]
}
{
let v2 = v.get_mut(1..3);
if let Some(v2) = v2 {
v2.get_mut(1).map(|x| *x *= 2);
println!("{:?}", v2) // [1, 4]
}
}
println!("{:?}", v); // [0, 1, 4, 3, 4]
{
let v_slice = &mut v[..]; // mutable borrowed of the Whole vector
v_slice[1] *= 10;
println!("{:?}", v_slice); // [0, 10, 4, 3, 4]
}
println!("{:?}", v); // [0, 10, 4, 3, 4]
```
---
## Modify
```rust
let mut v = Vec::new(); // []
v.push(6); // [6]
v.push(8); // [6, 8]
v.push(9); // [6, 8, 9]
v.pop(); // 9; [6, 8]
v.pop(); // 8; [6]
v.append(&mut vec![5, 4]); // [6, 5, 4]
v.insert(1, 2); // [6, 2, 5 ,4]
```
---
## Search
Vector 本身也是一種 slice,所以繼承許多 slice 的 method。例如 `binary_search`、`contains`、`starts_with` 等等。
```rust
// binary_search from rust doc
let s = [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55];
assert_eq!(s.binary_search(&13), Ok(9));
assert_eq!(s.binary_search(&4), Err(7));
assert_eq!(s.binary_search(&100), Err(13));
let r = s.binary_search(&1);
assert!(match r { Ok(1...4) => true, _ => false, });
```
---
## Iterate
Rust 的 for loop 一種 iterator 語法糖。若一個型別非 Iterator,但是有實作 [`IntoIterator`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/iter/trait.IntoIterator.html) trait,則會呼叫 `YourType::into_iter` 來產生迭代器。
```rust
// Original
let v = vec![1, 2, 3];
for i in v {}
println!("{:?}", v);
// error[E0382]: use of moved value: `v`
// --> src/main.rs:4:18
// |
// 3 | for i in v {}
// | - value moved here
// 4 | println!("{:?}", v);
// | ^ value used here after move
// |
// = note: move occurs because `v` has type `std::vec::Vec<i32>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
```
.right[什麼鬼,我的 Vec 被 consume 掉了?]
---
### 如何避免 for-loop ownership comsuption
1. 使用 `Vec::iter` `Vec::iter_mut`。
2. 使用 borrow(`&` or `&mut`),讓 Vec 自動 deref 成 slice
```rust
let mut v = vec![1, 2, 3];
for i in &v {}
for i in &mut v {}
for i in v.iter() {}
for i in v.iter_mut() {}
println!("{:?}", v); // [1, 2, 3]
```
---
## Reallocation
動態陣列在特定的時間點,重新配置陣列,以符合資料所需記憶體大小,這個行為我們稱之「**Reallocation**」。

---
## Reallocation 的時機
`Vec<T>` 預設會在下列兩個狀況下發生 reallocation:
- 當執行 push 或新增元素的操作時,Vec 的 `len == capacity`。
- 手動執行 `Vec::shrink_to_fit`,清理沒用到的記憶體空間。
除此之外,當執行 `Vec::pop` 等移除部分元素的 method,`Vec<T>` 永遠不會自動 realloction 來清理未用的記憶體空間。據說這是最佳化化來著(C++ 也這麼幹)。
---
## Performance
**get**: O(1)
**push**: O(1) amortized
**pop**: O(1)
**insert(i)**: O(n - i) amortized
**remove(i)**: O(n - i)
---
## 如何在同個 Vec 儲存不同型別資料
使用 `enum`。
```rust
enum SpreadsheetCell {
Int(i32),
Float(f64),
Text(String),
}
let row = vec![
SpreadsheetCell::Int(3),
SpreadsheetCell::Text(String::from("blue")),
SpreadsheetCell::Float(10.12),
];
```
> 注意,Rust enum 佔用的記憶體空間會以最大的 variant 為準。切莫將大小差異過大的 variant 放在同個 Vec。
---
## 什麼時候該用 `Vec<T>`
✅ 你需要蒐集一缸子元素進行處理或傳遞,且不關心它們到底是什麼。
✅ 你需要一個有序的序列,且只會在序列尾端新增元素。
✅ 你需要一個 stack。
✅ 你需要一個可變的 array。
✅ 你需要一個配置在 heap。
❌ 你需要一個 queue(請使用 [VecDeque](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/collections/struct.VecDeque.html))。
---
class: middle, center
# HashMap
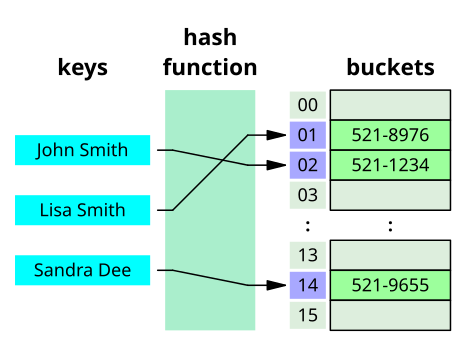
.center[[Jorge Stolfi](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Jorge_Stolfi) CC BY-SA 3.0]
---
## 說文解字
### 什麼是 hash?
Map data of **arbitrary size** to data of **fixed size**.
### 什麼是 Map?
A collection of **key-value pairs** that each key is **unique** to the collection.
### 什麼是 hash map?
透過雜湊函數,將任意資料轉換成固定長度鍵值,並將此鍵值與一筆資料綁定成「鍵值——資料」配對。這些配對的集合稱為 hash map(或 hash table、associative array、dictionary 等)。
---
## Rust 的 HashMap 怎麼實作的
**HashMap** = **Linear probing** + **Robin Hood hashing**
預設雜湊演算法為 [SipHash 2-4](https://131002.net/siphash/)
---
## Linear probing
一種解決雜湊碰撞(hash collision)的策略,屬於 Open Addressing 類。在 Linear probing 策略下,每一個 hash map 的格子(cell)只會儲存一對 key-value pair。若
雜湊函數產生碰撞,則往下一個有空間的格子插入新的 key-value pair。
**Pros**:比 [Separate chaining](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash_table#Separate_chaining) 節省記憶體空間;儲存在同陣列較 cache-friendly。
**Cons**:格子會用完,需要 reallocation 和 rehash;很倚賴雜湊函數的品質。
<img style="height: 300px" src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/90/HASHTB12.svg/690px-HASHTB12.svg.png">
---
## Create
`HashMap::new` 建構式
```rust
let map = HashMap::new();
```
從 tuple 蒐集
```rust
let alpha = vec![String::from("A"), String::from("B")];
let num = vec![1, 2];
let map: HashMap<_, _> = alpha.iter().zip(num.iter()).collect();
// {"B": 2, "A": 1}
```
---
## Get and Update
- 直接 Indexing:`map[&key]`
- 安全的 get:`map.get(&key)` 與 `map.get_mut(&key)`
```rust
let mut map = HashMap::new();
map.insert(String::from("a"), 1);
assert_eq!(map.get(&"a"), Some(&1));
assert_eq!(map.get(&"b"), None);
assert_eq!(map[&"a"], 1);
// assert_eq!(map[&"b"], 2);
// panicked at 'no entry found for key'
if let Some(value) = map.get_mut("a") {
*value += 1;
}
println!("{:?}", map); // {"a": 2}
```
---
class: middle, center
# 這種 update 方法太冗了!
---
## Entry API
[Entry](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/collections/hash_map/enum.Entry.html) 提供 chaining 的 API,告訴你該 key 是否已有值,並可以對結果操作
- `or_insert` 插入(預設)值,或
- `and_modify` 改變其值。
```rust
// 簡化版
enum Entry {
Vacant(VacantEntry<K, V>),
Occupied(OccupiedEntry<K, V>),
}
```
```rust
let mut map = HashMap::new();
map.entry("a").or_insert(1);
assert_eq!(map["a"], 1);
map.entry("a").and_modify(|v| *v *= 5);
assert_eq!(map["a"], 5);
```
---
## Performance
**get**: expected O(1)
**insert(i)**: expected O(1) amortized
**remove(i)**: expectd O(1)
---
## 什麼時候該用 HashMap
✅ 你想要讓任意 key 與 value 有關聯。
✅ 你想要有個 cache 機制。
✅ 你就是想要一個 map,沒有其他特殊需求。
✅ 你想要處理 JSON 的時候(誠心推薦 [serde.rs](https://serde.rs/))。
❌ 你的 map 內的 value 毫無意義。(請使用 [HashSet](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/collections/struct.HashSet.html))
> Set 其實就是 HashMap 的 value 是 zero size type「`()`」
---
class: middle, center
# String

---
## 字串
Rust 的字串非常複雜,相關型別至少有七種,其中的轉換更是駭人聽聞。
| Type | Ownersip | Encoding | Scenario |
| -------- | :------- | :--------------------- | :--------- |
| String | owned | UTF8 | 基礎型別 |
| str | borrowed | UTF8 | 基礎型別 |
| char | - | Unicode scalar value | 基礎型別 |
| OsString | owned | varies | 與 OS 溝通 |
| OsStr | borrowed | varies | 與 OS 溝通 |
| CString | owned | - (with Nul teminator) | 與 C 溝通 |
| CStr | borrowed | - (with Nul teminator) | 與 C 溝通 |
---
## 建立不可變的字串 `&str`
最簡單的 string literal 的型別是 `&str`。實際上是一個 **immutable slice**,因此 slice 的 method 大部分都可直接使用。
> 字串字面量皆使用雙引號 `""`。
```rust
let s = "hello, world";
let (first, last) = s.split_at(6);
assert_eq!("hello,", first);
assert_eq!(" world", last);
```
---
## 可變動的字串 `String`
`String` 則是可以成長,變動的字串。
```rust
let s = String::new();
s.push_str("hello");
s.push_str(", world");
println!("{:?}", s); // hello, world
```
---
class: middle, center
# 那 Rust 有字元型別?
---
## UTF8 by default
Rust 的世界中,預設的字串是 UTF8 encoding。也就是說,Rust 的 `char` 型別代表的是 [Unicode scalar value](https://www.unicode.org/glossary/#unicode_scalar_value),佔用 4 bytes,而非 C char 的 1 bytes。
因此,Rust 的 `String` 可以被視為 `Vec<u8>` 的 byte array。
```rust
let v = vec!['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'];
// 一個元素 4 bytes * 5 = 20 bytes
assert_eq!(20, v.len() * std::mem::size_of::<char>());
let s = String::from("hello");
// 一個 hello string 和五個 char 大小不同! 怪哉!!!
assert_eq!(5, s.len() * std::mem::size_of::<u8>());
```
> 字元字面量使用 `''` 單引號。
---
## String 長度和你想像的不一樣
```rust
use std::mem::size_of_val;
let s = "中文";
println!("{:?}", s.len()); // 6
println!("{:?}", &s[0..3]); // 中
println!("{:?}", size_of_val(&s[..3])); // 3 bytes
let s = "abc";
println!("{:?}", s.len()); // 3
println!("{:?}", &s[0..3]); // abc
println!("{:?}", size_of_val(&s[..3])); // 3 bytes
println!("{:?}", size_of_val(&s[0])); // 1 bytes ('a' in UTF8)
// The werid part
println!("{:?}", size_of_val(&'a')); // 4 bytes (Unicode scalar value)
```
---
## UTF8 bytes 對照表

.center[Wikipedia CC SA 3.0]
我們可以得知:
`char` 總是佔 **4 bytes**;而`String` 或 `str` 中的字元則是依 UTF-8 定義,以該字元的 code point range 決定大小。
因此,直接對 `String` 或 `&str` indexing 很容易切在非 Character boundary 的地方,儘量避免此一操作。
---
## 型別轉換
### `&str` to `String`
```rust
let s = "hello".to_string();
println!("{:?}", s); // hello
let s = String::from("hello");
println!("{:?}", s); // hello
let s: String = "hello".into();
println!("{:?}", s); // hello
let s = "hello".to_owned();
println!("{:?}", s); // hello
```
---
## 將字串作為參數傳遞
我們試著寫一個接受字串的函數。
```rust
fn print_str(s: String) {
println!("{:?}", s);
}
let my_string = String::from("hello");
let my_str = "hello"; // &str
print_str(my_string); // hello
print_str(my_str); // panic!!!
// = note: expected type `std::string::String`
// found type `&'static str`
```
---
## 將字串作為參數傳遞
最簡單的做法就是一律用 `&str` 作為參數。
```rust
fn print_str(s: &str) {
println!("{:?}", s);
}
let my_string = String::from("hello");
let my_str = "hello"; // &str
print_str(&my_string); // hello
print_str(my_str); // hello
```
---
## 其他好玩的社群 collections
[smallvec](https://github.com/servo/rust-smallvec):儲存在 stack 上的 vec(servo 開發,用在 CSS 與 font glyph)
[slab](https://github.com/carllerche/slab):提供一致性型別集合 pre-allocated storge,類似 HashMap 的高效資料結構([mio](https://github.com/carllerche/mio) 的作者開發)
---
class: middle, center
# Any advice?
We are from [Hahow 好學校](https://hahow.in/). Ask us anything!
</textarea>
<script src="https://remarkjs.com/downloads/remark-latest.min.js" type="text/javascript">
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var slideshow = remark.create();
</script>
</body>
</html>