The NYX system uses docker as service manager. In order to behave properly, all the containers defined in the system must run.
In order to interact with docker, the user must have root privileges. An easy way to list the running containers is to use the following command:
docker ps -a
This command should return a list of containers as shown below:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS
5a83d0733d03 snuids/nyx_restapi:v3.9.0 "gunicorn -b 0.0.0.0…" 4 weeks ago Up 4 weeks
09e4ed1bd791 snuids/nyx_reportscheduler:v0.0.4 "python nyx_reportsc…" 4 weeks ago Up 4 weeks
234a5102a3a4 snuids/nodered:v0.20.3-v10 "npm start -- --user…" 4 weeks ago Up 4 weeks 1880/tcp
da05596d3777 docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:6.5.4 "/usr/local/bin/dock…" 4 weeks ago Up 4 weeks 9200/tcp, 9300/tcp
533a68d2d69f snuids/par_import_coswin:v0.0.8 "python par_import_c…" 5 weeks ago Up 5 weeks
3994a7a1c75f snuids/nyx_lambda:v1.5.2 "python nyx_lambda.py" 2 months ago Up 3 days
830b7572bdbe snuids/nyx_lambda:v1.5.2 "python nyx_lambda.py" 2 months ago Up 5 weeks
ec4be44c06aa snuids/nyx_ui:v3.24.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 2 months ago Up 2 months
47cd4afd2596 snuids/nyx_monitordocker:v1.0.5 "python nyx_monitord…" 2 months ago Up 5 weeks
In order to list the containers that are not in the Up status, use the following command:
docker ps -a | grep -v Up
This command should return an empty list.
If the list retrieved by the previous command is not empty, it means that some containers must be restarted / started.
The easiest way of starting / restarting containers is to use the docker-compose up -d command. It must be executed in the docker-compose folder of the NYX root installation folder.
It is possible to find this folder via the following commands:
cd / ===> go to root directory
find . -name "docker-compose.yml" ===> search recursively the file docker-compose.yml
[root@ip-10-10-251-142 ~]# cd /
[root@ip-10-10-251-142 /]# find . -name "docker-compose.yml"
find: './proc/699/task/996/fd/424': No such file or directory
./home/nyx/docker-compose/docker-compose.yml
./home/nyx/backup/tempzip/docker-compose/docker-compose.yml
In this installation two files were retrieved. The good one is of course the first one, because it is not in the backup folder.
You can move your shell to the appropriate directory using the command:
cd /home/nyx/docker-compose/ =====> Depends on the previous result
Issue then the following command to restart the stopped containers.
docker-compose up -d
[root@ip-10-10-251-142 /]# cd ./home/nyx/docker-compose/
[root@ip-10-10-251-142 docker-compose]# docker-compose up -d
redis is up-to-date
par_import_kizeo is up-to-date
openvpn is up-to-date
nyx_restapi is up-to-date
anacondab is up-to-date
nyx_reportscheduler is up-to-date
cerebro is up-to-date
esnode1 is up-to-date
postgres is up-to-date
...
You can reissue the docker-compose up -d command until the list of containers says that they are all up-to-date.
If everything is fine, the web site should pop up using the following url:
https://YOUR_DOMAIN/
If a web site appears and the icon on the first page keep on spinning, this probably means that the REST API is not started properly. It is possible to check the REST API itself using the following address:
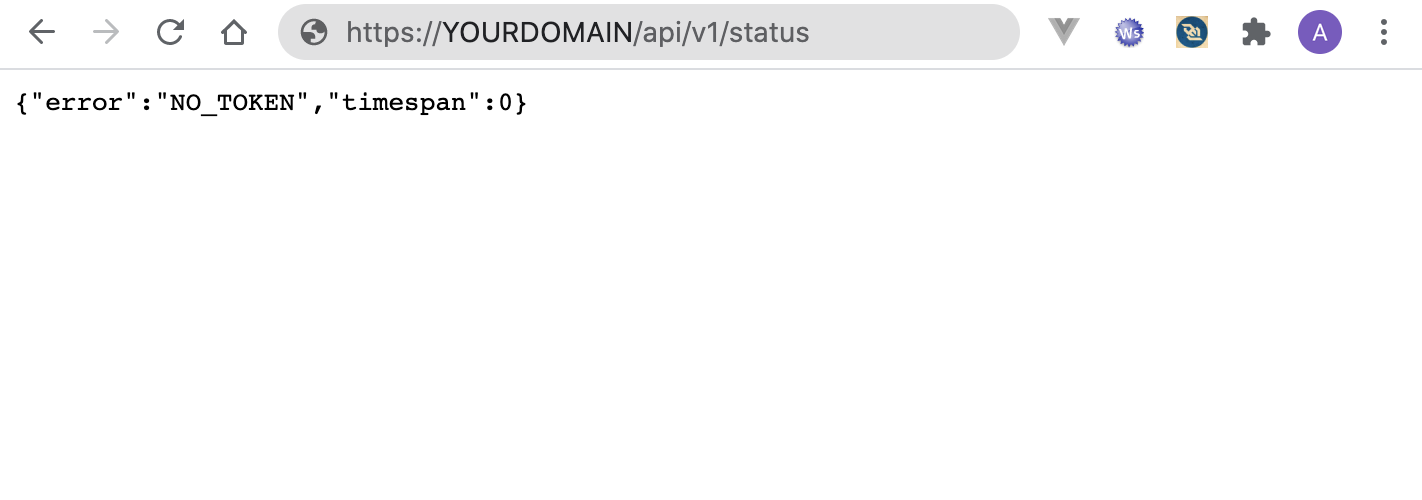
https://YOUR_DOMAIN/api/v1/status
This should return the following web page:
If an error such as a 404 or 503 appears, this could be a race condition between containers startup sequence. In a perfect scenario the nginx (web site) container should be started when all the others are up and running.
If the previous problem occurs simply use the following command in the a shell:
docker restart nginx
Once the container restarted, retry to open the two previous urls in order to check that everything is started properly
The following command will display the last 100 lines of log of a specific container. For example, for nginx, you can type:
docker logs --tail 100 nginx
This is useful to understand why a specific container is not starting.
Elastic search will not behave properly if the fill percentage of the disk is greater than 75 %.
It is possible to check the linux partition fill using the following command:
df -h
In order to determine recursively the size of a specific folder, you can use the following command:
du -sh .
Note that the linux NCDU package can make the research of big files easier.(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ncdu)