It's a is a JavaScript function that runs as soon as it is defined. It's a design pattern which contains two major parts. The first is the anonymous function with lexical scope which prevents accessing variables within the IIFE as well as polluting the global scope. The second part is creating the immediately executing function expression (), through which the JavaScript engine will directly interpret the function.
(function () {
var aName = "Barry";
})();
// Variable name is not accessible from the outside scope
aName // throws "Uncaught ReferenceError: aName is not defined"
var result = (function () {
var name = "Barry";
return name;
})();
// Immediately creates the output:
result; // "Barry"
Functions that operate on other functions, either by taking them as arguments or by returning them, are called higher-order functions.
function greaterThan(n) {
return function(m) { return m > n; };
}
var greaterThan10 = greaterThan(10);
console.log(greaterThan10(11));
// true
var range = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var consoleLogger = function(number){
console.log(number)
}
range.forEach(consoleLogger) // 0 1 2 3 4 5
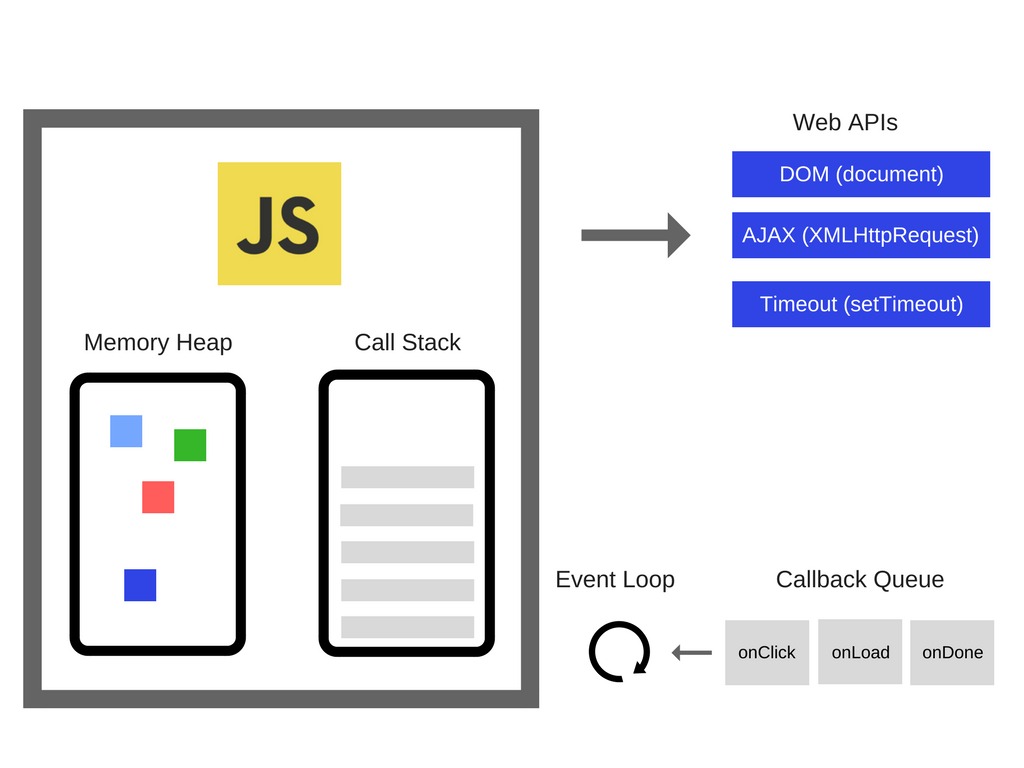
A stack is an array-like data structure but with some limitations — you can only add items to the back and only remove the last item. JavaScript has a single call stack in which it keeps track of what function we’re currently executing and what function is to be executed after that.
Every time you call a setTimeout function or you do some async operation — it is added to the Event Table.Once that event occurs (timeout, click, mouse move) it moves the event to Callback Queue.
The Event Queue is a data structure similar to the stack — again you add items to the back but can only remove them from the front. It receives the function calls from the Event Table, but it needs to somehow send them to the Call Stack? This is where the Event Loop comes in.
The event loop is the loop that processes tasks in the queue such that the callback functions get pushed onto the stack.
setTimeout(() => console.log('first'), 0)
console.log('second') // second first