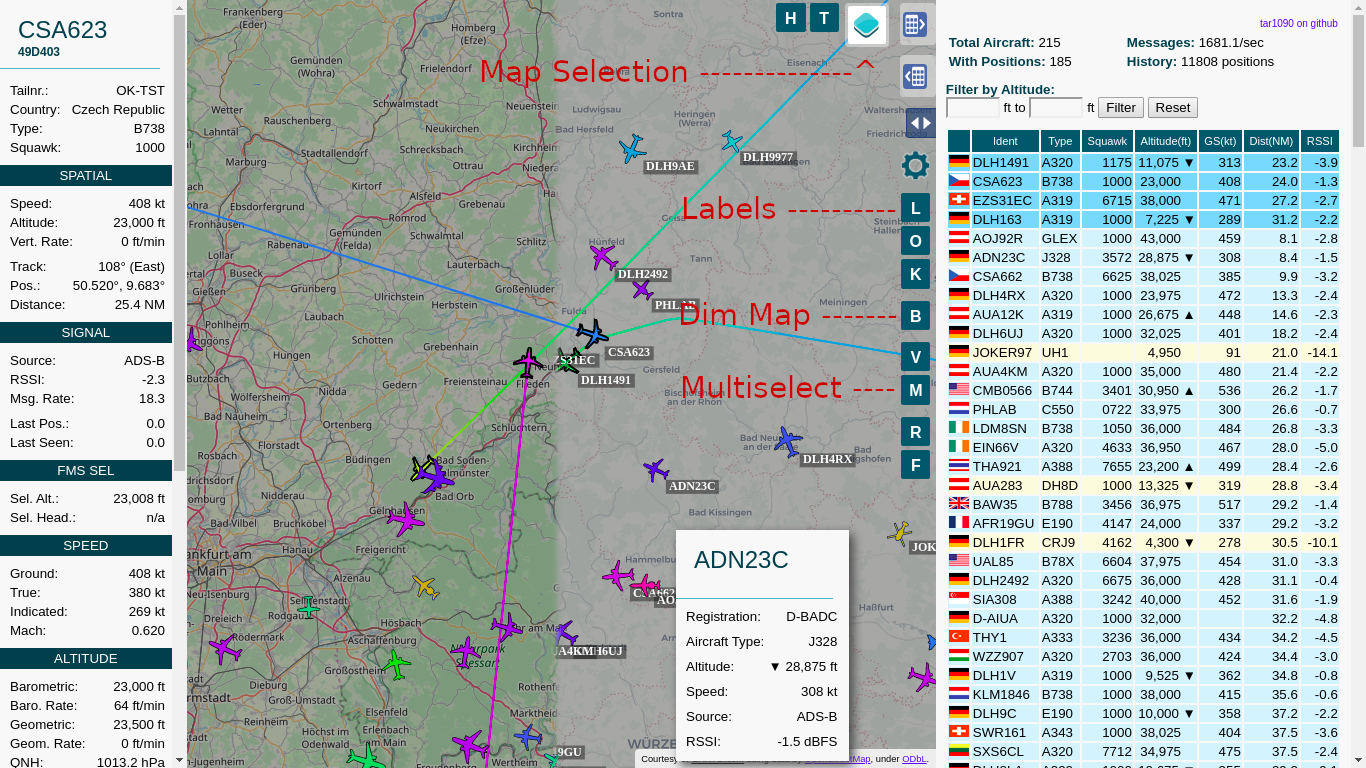
Provides an improved webinterface for use with ADS-B decoders readsb / dump1090-fa
- Improved adjustable history
- Show All Tracks much faster than original with many planes
- Multiple Maps available
- Map can be dimmed/darkened
- Multiple aircraft can be selected
- Labels with the callsign can be switched on and off
See the bottom of this page or the LICENSE for details. While striving not to disrupt an existing Raspbian / Debian / Ubuntu installation, this can't be guaranteed. This install script assumes Raspbian / Debian / Ubunutu and will not work on systems without apt.
tar1090 is not a readsb / dump1090-fa replacement, it merely adds an additional webinterface for an existing readsb or dump1090-fa installation. dump1090-mutability installations should work as well, aircraft details will be limited though.
sudo bash -c "$(wget -nv -O - https://github.com/rkarikari/tar1090/raw/master/install.sh)"
Click the following URL and replace the IP address with address of your Raspberry Pi:
If you are curious about your coverage, try this URL:
http://192.168.x.yy/tar1090/?pTracks
Check further down for keyboard shortcuts.
sudo bash -c "$(wget -nv -O - https://github.com/rkarikari/tar1090/raw/master/install.sh)"
Configuration should be preserved.
Edit the configuration file to change the interval in seconds and number of history files saved:
sudo nano /etc/default/tar1090
Ctrl-x to exit, y (yes) and enter to save.
Apply the configuration:
sudo systemctl restart tar1090
The duration of the history in seconds can be calculated as interval times history_size.
Remove the // at the start of a line, otherwise the setting will not be used.
sudo nano /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
Ctrl-x to exit, y (yes) and enter to save. Then Ctrl-F5 to refresh the web interface in the browser.
If you somehow broke the interface or want the default config back:
sudo rm /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
Then run the install script again.
This is set in the decoder, so readsb or dump1090-fa, if you used one of my scripts to install their readme will have further instructions on how to set the location.
The commit log on the github page is the only form of change log. If you can't find the commit log or don't understand what it means, you have 3 options:
- Assume there is no update and use the currently installed version.
- Run the update script as provided above and let it surprise you!
- Complain about the lack of a change log and be mocked.
While i make this interface available for others to install and hope you like it, i maintain this interface mainly for users who are curious and can figure it out themselves. Documentation and explanation is time consuming to do and as such i choose to limit it to the essential.
If you think you have found a bug, open an issue here on github. Please check all the buttons and read all the tooltips before you do. Try deleting the browser cache for the tar1090 page.
# ENABLE:
sudo sed -i -e 's?.*flightawareLinks.*?flightawareLinks = true;?' /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
# ENABLE if the above doesn't work (updated from previous version)
echo 'flightawareLinks = true;' | sudo tee -a /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
# DISABLE:
sudo sed -i -e 's?.*flightawareLinks.*?flightawareLinks = false;?' /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
Then F5 to refresh the web interface in the browser.
If your instance is not at /tar1090 you'll need to edit the config.js in the approppriate html folder, see "Multiple instances".
# ENABLE:
sudo sed -i -e 's?.*shareBaseUrl.*?shareBaseUrl = "https://globe.adsbexchange.com/";?' /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
# ENABLE if the above doesn't work (updated from previous version)
echo 'shareBaseUrl = "https://globe.adsbexchange.com/";' | sudo tee -a /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
# DISABLE:
sudo sed -i -e 's?.*shareBaseUrl.*?shareBaseUrl = false;?' /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
If your instance is not at /tar1090 you'll need to edit the config.js in the approppriate html folder, see "Multiple instances".
See the instructions for "Configuration part 1". This is the relevant part in the configuration file:
# Change to yes to enable UAT/978 display in tar1090
ENABLE_978=no
# If running dump978-fa on another computer, modify the IP-address as appropriate.
URL_978="http://127.0.0.1/skyaware978"
Open and save as described above in the Configuration section. Follow the instructions in the file.
tar1090 running on the same pi as the skyaware978/dump978-fa:
echo /run/skyaware978 tar1090 | sudo tee /etc/default/tar1090_instances
After that run the install script and it should work. 978 should be disabled in the config file for this configuration. UAT traffic will be displayed as ADS-B, this can't be avoided.
wget -nv -O /tmp/install.sh https://github.com/rkarikari/tar1090/raw/master/install.sh
sudo bash /tmp/install.sh /run/combine1090
sudo bash -c "$(wget -nv -O - https://github.com/rkarikari/tar1090/raw/master/uninstall.sh)"
js regex format, some basics (much more extensive issue available online on javascript regex syntax):
- a single
.is the wildcard for exactly one character - multiple patterns can be combined with or:
|
B737 family: B73. (B73 and any character in the fourth position)
A320 family: A32.
B737-900 and B737 Max 9: B739|B39M
737 family including max: B73.|B3.M
B737 / A320 families: B73.|B3.M|A32.|A2.N
Only A320 and B737 models: A32|B73
Exclude a certain type: ^(?!A320)
Exclude multiple patterns: ^(?!(A32.|B73.))
Helicopters: H..
Landplanes with 2 jet engines: L2J
Landplanes with any number of piston engines: L.P
Helicopters any number of turbin engines : H.T
All turboprop powered things, including turbine helicopters: ..T
Everything with 4 engines: .4.
Everything with 2 3 and 4 engines: .2.|.3.|.4.
- Q and E zoom out and in.
- A and D move West and East.
- W and S move North and South.
- C or Esc clears the selection.
- M toggles multiselect.
- T selects all aircraft
- B toggle map brightness
See README-query.md
The script can install multiple instances, this is accomplished by first editing /etc/default/tar1090_instances:
On each line there must be one instance. First on the line the source directory where the aircraft.json is located. Second on the line the name where you want to access the according website. (http://pi/tar1090 or http://pi/combo or http://pi/978 in this example)
If you want the instance at http://pi/, use webroot as a name.
The main instance needs to be included in this file.
Example file:
/run/dump1090-fa tar1090
/run/combine1090 combo
/run/skyaware978 978
/run/dump1090-fa webroot
After saving that file, just run the install script and it will install/update all instances.
Configuration for each instance will be separate, in the example the config files would be:
/etc/default/tar1090
/etc/default/tar1090-combo
/etc/default/tar1090-978
/etc/default/tar1090-webroot
The config.js will also have another path, to edit each config:
sudo nano /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/config.js
sudo nano /usr/local/share/tar1090/html-combo/config.js
sudo nano /usr/local/share/tar1090/html-978/config.js
sudo nano /usr/local/share/tar1090/html-webroot/config.js
HTML folders will be:
/usr/local/share/tar1090/html
/usr/local/share/tar1090/html-combo
/usr/local/share/tar1090/html-978
/usr/local/share/tar1090/html-webroot
The run folder and systemd service will be called tar1090-combo and tar1090-978 in this example file. The main instance is the exception to that rule, having systemd service and run directory called just tar1090.
For example removing the instance with the name combo and 978:
First remove the corresponding line from /etc/default/tar1090_instances and
save the file so when you update it doesn't get installed again.
Then run the following command adapted to your instance name, you'll need to include the tar1090- which is automatically added for the service names:
sudo bash /usr/local/share/tar1090/uninstall.sh tar1090-combo
sudo bash /usr/local/share/tar1090/uninstall.sh tar1090-978
If the instance was installed with the old method without the tar1090_instances file, you'll have to try without the tar1090- before the combo, like this:
sudo bash /usr/local/share/tar1090/uninstall.sh combo
sudo bash /usr/local/share/tar1090/uninstall.sh 978
tar1090 is now available at :8504 by default when using lighttpd. (port 8504)
To display tar1090 at /, add an instance as described above that has the name webroot. It will be available at /
If nginx is installed, the install script should give you a configuration file you can include. The configuration needs to go into the appropriate server { } section. In the usual configuration that means to add this line:
include /usr/local/share/tar1090/nginx-tar1090.conf;
in the server { } section of either /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default or /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf depending on your system configuration.
Don't forget to restart the nginx service.
To judge the actual range (/?pTracks, see next chapter), one needs to first know what kind of range is even possible for the receiver location. 1090 MHz reception requires a direct line of sight through air to what you want to receive, thus depends on obstacles and the curvature of the earth. To get that theoretical range for a location, follow the guide in this chapter.
- Visit http://www.heywhatsthat.com/
- Click "New Panorama"
- Set the location for your antenna precisely
- Enter a title / submit the request and wait for it to finish
- Scroll down to the map, look at the buttons in the top right of the map
- Use the "up in the air" button on the map, reduce map magnification
- You can change the altitudes (ft) below the map to view different outlines for your location
- Those outlines tell you how far you can receive aircraft at the associated altitudes
- The panorama does not take into account obstacles closer to the antenna than approximately 100 ft, trees are also not considered but can block reception
- For use on the tar1090 map the altitude will be set by changing the download URL
- Near the top of the page, an URL for the panorama is mentioned.
- Replace the XXXXXX in the following command with the ID contained in your panorama URL, then run the command on your pi:
sudo /usr/local/share/tar1090/getupintheair.sh XXXXX
-
You should now have a range outline for the theoretical range for aircraft at 40000 ft on your tar1090 map
-
It might be interesting to compare to http://192.168.x.yy/tar1090/?pTracks which will by default will display the last 8 hours of traces.
-
More options for loading multiple outlines and for a different instance
# load two outlines, 10000 ft and 40000 ft
sudo /usr/local/share/tar1090/getupintheair.sh XXXXX 3048,12192
# load a 10000 ft outline for the tar1090 instance located at /978
sudo /usr/local/share/tar1090/getupintheair.sh XXXXX 3048 978
# load a 40000 ft outline for the tar1090 instance located at /adsbx
sudo /usr/local/share/tar1090/getupintheair.sh XXXXX 12192 adsbx
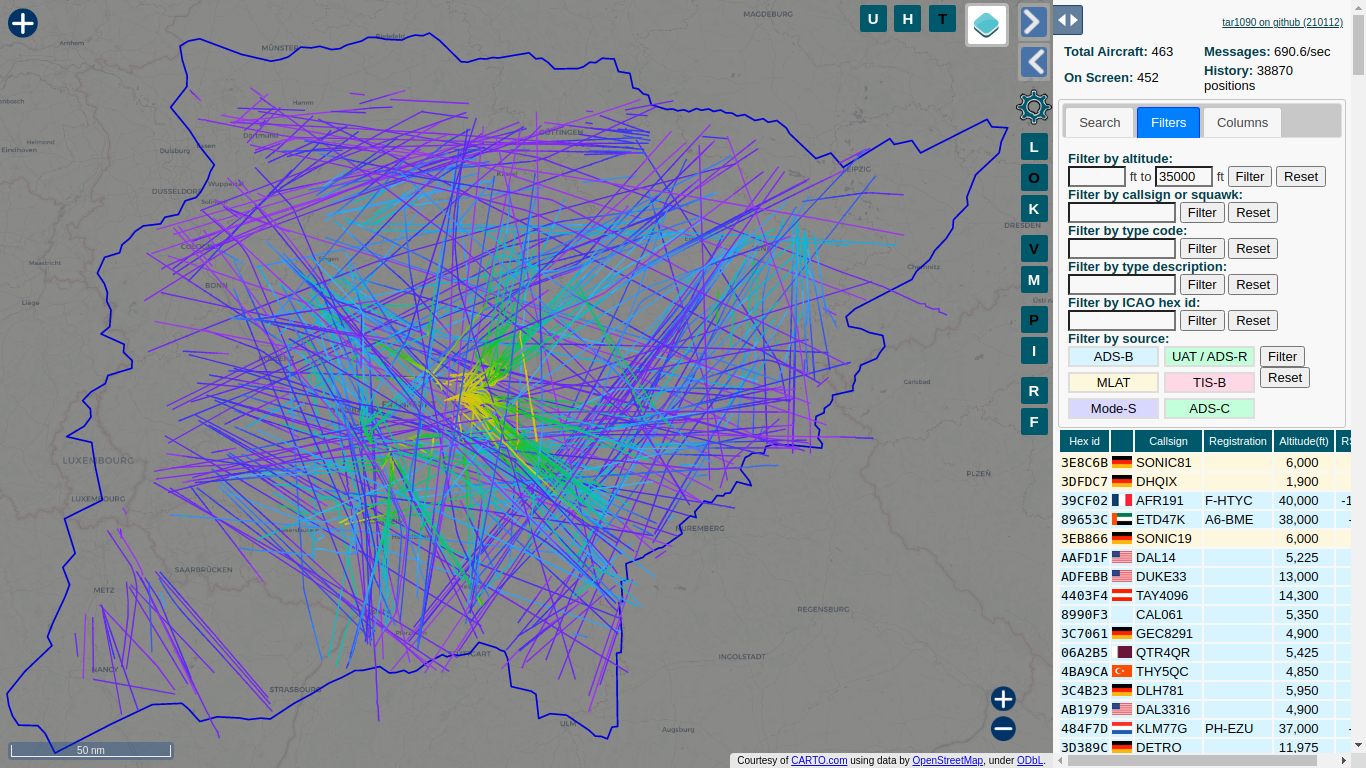
- Add /?pTracks to the usual /tar1090 URL, should look like this: http://192.168.x.yy/tar1090/?pTracks
- Shows the last 8 hours of traces you have seen, gives a nice visual representation of your coverage / range
- Can be filtered by altitude with the altitude filter
- Configure a longer duration than 8 hours via the configuration
- Restrict the duration shown to 2 hours: /tar1090/?pTracks=2
- Draw less points which reduces display time (higher interval, lower compute time, default 15): /tar1090/?pTracks=8&pTracksInterval=60
History function as used by several online aggregators using tar1090 (destroy sd-card is a bit of a joke but obviously it will use disk space and create quite a few files, they will be kept indefinitely so if the folder grows too big you'll have to delete old files yourself)
The data is generated by my version of readsb so you'll have to run that: https://github.com/wiedehopf/readsb https://github.com/wiedehopf/adsb-scripts/wiki/Automatic-installation-for-readsb
The following command line options need to be added to for example the decoder options in /etc/default/readsb
--write-globe-history /var/globe_history --heatmap 30
Aggregators will generally use --write-json-globe-index as well but that's not necessary if you don't have more than 500 concurrent planes.
/var/globe_history needs to be a directory writeable by the user readsb.
sudo mkdir /var/globe_history and sudo chown readsb /var/globe_history are useful for that.
You should also download
wget -O /usr/local/share/tar1090/aircraft.csv.gz https://github.com/wiedehopf/tar1090-db/raw/csv/aircraft.csv.gz
and add this command line option (for exaple via /etc/default/readsb):
--db-file /usr/local/share/tar1090/aircraft.csv.gz
You will also need to point tar1090 to /run/readsb in case you are using another dump1090/readsb. See the "multiple instances" readme section.
If you don't want readsb to read data from the SDR, you'll also need to change the receiver options line to something like this:
RECEIVER_OPTIONS="--net-only --net-connector 192.168.2.7,30005,beast_in"
If you have another dump1090/readsb running on the same machine, you'll also need to change all the ports to avoid conflicts.
This will obviously write data to the hard drive, be aware of that. The data format is subject to change, don't expect this to be stable. Be aware of that when upgrading either tar1090 or readsb to a new commit.
For these features i only maintain the nginx configuration, not the lighttpd configuration.
Thus you'll need to use nginx with the config file provided by the tar1090 install script
or change the lighttpd configuration yourself.
On the default nginx install you'll usually find the server section in this config file:
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
If you can't figure out how to make it work with the above information, please don't ask. I don't support this feature for the general user base. This information is only for people who could figure it out from the source code anyhow, so that they don't have to spend as much time figuring it out.
If you're using --write-json-globe-index with tar1090, you might be interested in tar1090 using the readsb API to get data, it's less requests and usually more efficient, for details see the file nginx-readsb-api.conf (this needs adding to your existing nginx tar1090 configuration, this is only for people who really know their stuff anyway)
If this seems too complicated for you or you don't want a 2nd instance, changing / adding PTRACKS=24 to the /etc/default/tar1090 configuration should also extend the history (for /?pTracks only).
sudo nano /etc/default/tar1090_instances
put in these two lines if you're using readsb
/run/readsb tar1090
/run/readsb persist
put in these two lines if you're using dump1090-fa
/run/dump1090-fa tar1090
/run/dump1090-fa persist
if you then run the tar1090 install script afterwards you'll have an extra instance you can configure the history retention for.
sudo bash -c "$(wget -nv -O - https://github.com/wiedehopf/tar1090/raw/master/install.sh)"
sudo nano /etc/default/tar1090-persist
change to these values for 24h of history:
# Interval at which the track history is saved
INTERVAL=20
# How many points in time are stored in the track history
HISTORY_SIZE=4300
then
sudo systemctl restart tar1090-persist
and the persist instance will start saving more data.
You can then visit /persist/?pTracks instead of /tar1090 to get the complete 24h history displayed.
Press T to toggle the traces on and off, this is recommended for zooming and panning as with the traces showing this can be slow.
(you can also look at /tar1090/?pTracks if you want to look only at the more recent tracks, interval / history can be configured in /etc/tar1090 for that instance)
For adding the range outline to the /persist instance after having used the method described earlier, copy over the json:
sudo cp /usr/local/share/tar1090/html/upintheair.json /usr/local/share/tar1090/html-persist
For a day or so i had a bug in the install script turning symbolic links in /etc/lighttpd/conf-enabled into copies of the files they were pointing to.
This can cause some other issues with my install script which fiddles with the lighttpd config files to make mod_setenv work.
Anyhow if just rerunning the install script does not fix your history loading issue, you can try this:
cd /etc/lighttpd/conf-enabled
for i in *; do if [ -f "../conf-available/$i" ]; then sudo ln -s -f "../conf-available/$i" $i; fi; done
After that rerun the install script. If you still have history loading issues, get back to me via the github issues or the various forums i frequent.
/var/globe_history needs to be a directory writeable by the user readsb.
sudo mkdir /var/globe_history and sudo chown readsb /var/globe_history are useful for that.
Add readsb options:
--heatmap-dir /var/globe_history --heatmap 30
/tar1090/?heatmap=200000
Maximum number of dots to draw is the number after heatmap. Optional arguments that can be added to the URL:
- duration in hours that shall be displayed: &heatDuration=48 (default: 24)
- set the end of the duration 48 hours into the past: &heatEnd=48 (default:0)
- radius of the dots: &heatRadius=2
- opacity of the dots: &heatAlpha=2
- only redraw the dots when pressing R on the keyboard: &heatManualRedraw
alternative display style: &realHeat
- blurryness: &heatBlur=2
- weight of each dot for the heatmap: &heatWeight=4
One of this forks main uses is to be the frontend of a global map. For that purpose it's used in conjunction with readsb.
Websites using this software:
- https://adsb.lol/
- https://globe.adsbexchange.com/
- https://globe.airplanes.live/
- https://globe.adsb.fi/
Notable Projects that use ADS-B data:
- https://gpsjam.org/
- https://adsb.exposed/
- https://tech.marksblogg.com/global-flight-tracking-adsb.html
https://github.com/wiedehopf/adsb-wiki/wiki/offline-map-tiles-tar1090
https://github.com/wiedehopf/zstddec-tar1090
When hosting a website with tar1090 via CF, CF needs to respect the various cache headers otherwise there will be caching issues. Change Browser Cache TTL from the default of 4h to "Respect Existing Headers": Caching -> Configuration -> Browser Cache TTL -> Respect Existing Headers
- BECAUSE THE PROGRAM IS LICENSED FREE OF CHARGE, THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.