Welcome to the AWS Cloud Computing Repository! This repository serves as a hub for information, guides, and resources related to cloud computing with a focus on Amazon Web Services (AWS). Whether you're a beginner looking to explore cloud technologies or an experienced AWS user seeking advanced insights, this repository aims to provide valuable content and foster a collaborative learning environment.
Cloud computing is like renting a computer, storage, or software over the internet instead of owning and maintaining your own physical hardware. Instead of running programs or storing data on your local computer, you can do it online through servers hosted by a third party.
- Cost-Efficiency: With cloud computing, you pay for what you use, avoiding the need to invest in expensive hardware upfront.
- Scalability: It allows you to easily scale up or down based on your needs without the hassle of buying and installing new equipment.
- Accessibility: You can access your data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, making collaboration and remote work more efficient.
- Massive Economies of scale: Because of aggregate usage from all customers, AWS can achieve higher economies of scale and pass savings on to customers.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines and storage.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, and run the software.

- Public Cloud ☁️:
- Explanation: Imagine renting a virtual space on the internet. Many people, like you and others, share this space for various needs.
- Real-world Example: Using Gmail or Google Drive, where you access and store your emails and documents on Google's servers that are shared with millions of users.
- Private Cloud 🏠:
- Explanation: This is like having your own exclusive club. Everything is just for your use. It's more private and customizable.
- Real-world Example: A company might have its own servers that only its employees can use for storing and accessing files.
- Hybrid Cloud 🔄:
- Explanation: Think of it as having a mix of both public and private spaces. Some things are shared with everyone, and some are just for your exclusive use.
- Real-world Example: A business might use a public cloud for customer-facing apps and a private cloud for confidential business files.
- Community Cloud 🏘️:
- Explanation: It's like a shared neighborhood where certain houses (organizations) share common spaces. These houses have similar needs and work together.
- Real-world Example: Different healthcare providers sharing a cloud platform for patient data exchange while ensuring privacy and compliance.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers a wide range of cloud services, including computing power, storage, and databases.
- Microsoft Azure: Provides a variety of services, from computing to analytics and storage, integrated with Microsoft products.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Offers cloud computing, storage, and machine learning services, backed by Google's infrastructure.
In summary, cloud computing is a flexible, cost-effective solution that allows individuals and businesses to access and use computing resources over the internet. It offers various services and deployment models to suit different needs, and major providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP make these resources easily accessible to a global audience.
Below, I'll provide some services and categories of AWS, but it's important to note that these are not the only ones available. AWS offers a wide range of services across various categories to cater to different business needs. The services mentioned here are just a subset of the comprehensive suite of solutions provided by AWS. Let's explore some of them below.
Web services are software systems designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network. In the context of AWS, they refer to cloud-based services accessible over the internet, providing computing power, storage, and other functionalities on-demand.
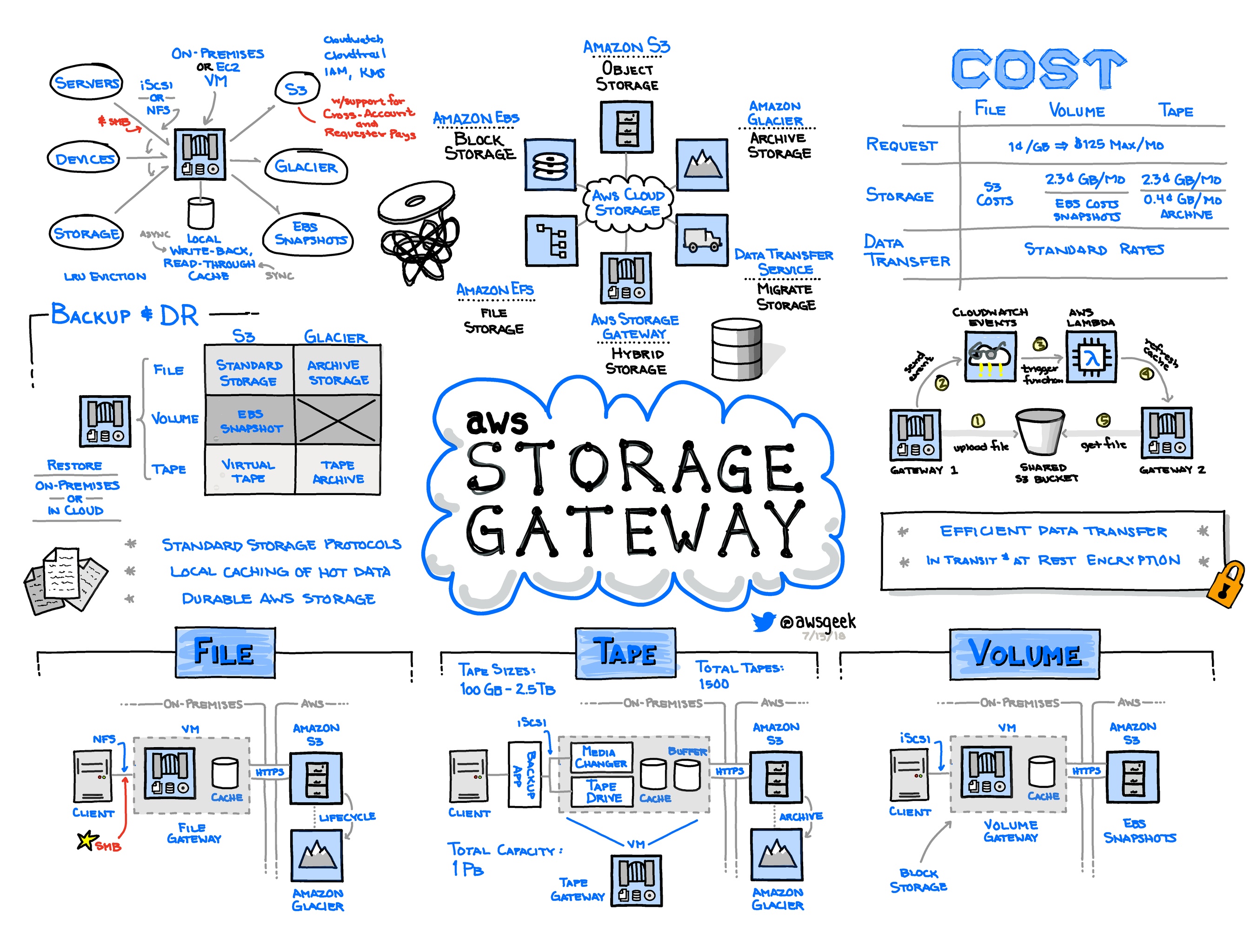
- Storage Services 🗄️:

- Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service): Scalable object storage designed to store and retrieve any amount of data.
- Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store): Persistent block storage volumes for use with Amazon EC2 instances.
- Amazon EFS (Elastic File System): Fully managed file storage for use with EC2 instances.
- Amazon Glacier: Low-cost storage for data archival and long-term backup.
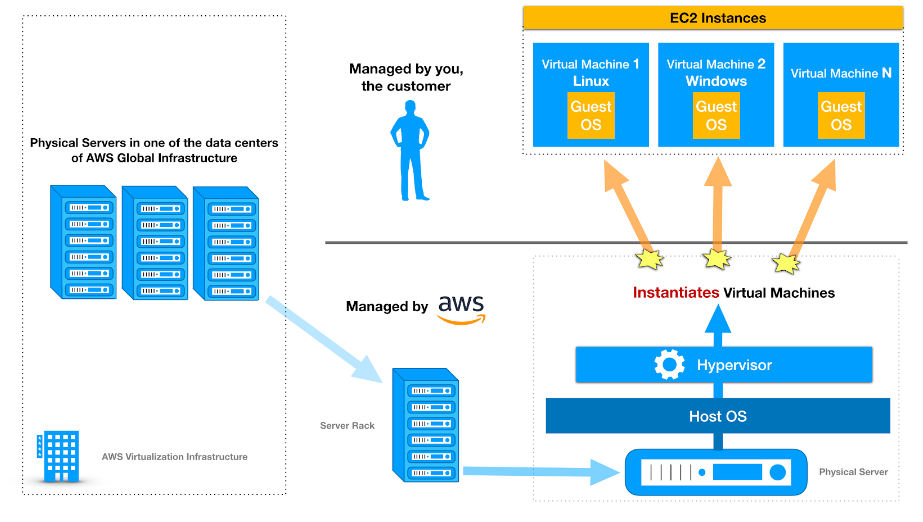
- Compute Services 💻:

- Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): Scalable virtual servers in the cloud.
- AWS Lambda: Serverless computing service for running code in response to events.
- Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service): Highly scalable container management service.
- Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service): Managed Kubernetes service for container orchestration.
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling: Enables you to automatically add or remove EC2 instances according to conditions that you define.
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR): A fully-managed Docker container registry that makes it easy for developers to store, manage, and deploy Docker container images.
- AWS Elastic Beanstalkis: A service for deploying and scaling web applications and services on familiar servers such as Apache and Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS).
- AWS Fargate: Serverless compute engine for containers.
- Database Services🛢️ :

- Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Managed relational database service.
- Amazon Aurora: High-performance relational database compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL.
- Amazon Redshift: Fully managed data warehouse service.
- Amazon DynamoDB: A key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale, with built-in security, backup and restore, and in-memory caching.
- Networking Services: 🌐

- Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Isolated cloud resources and customizable networking environment.
- Elastic Load Balancing: Automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, IP addresses, and Lambda functions.
- Amazon CloudFront: Global content delivery network (CDN) service.
- AWS Transit Gateway: Centrally manage and scale connectivity across VPCs and on-premises networks.
- Amazon Route 53: Scalable DNS (Domain Name System) web service.
- AWS Direct Connect: Dedicated network connection from on-premises to AWS.
- AWS VPN (Virtual Private Network): Securely connect on-premises networks to AWS.
- Security Services: 🔒

- AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management): Securely control access to AWS services and resources.
- AWS Organizations: Allows you to restrict what services and actions are allowed in your accounts.
- Amazon Cognito: Lets you add user sign-up, sign-in, and access control to your web and mobile apps.
- AWS Artifact: Provides on-demand access to AWS security and compliance reports and select online agreements.
- AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS): Enables you to create and manage keys. You can use AWS KMS to control the use of encryption across a wide range of AWS services and in your applications.
- AWS Shield: Managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service that safeguards applications running on AWS.
- Cost Management Services: 💰

- AWS Cost and Usage Report: Contains the most comprehensive set of AWS cost and usage data available, including additional metadata about AWS services, pricing, and reservations
- AWS Budgets: Set custom cost and usage budgets.
- AWS Cost Explorer: Visualize, understand, and manage AWS costs and usage.
- Management and Governance Services: 🛠️

- AWS Management Console: Provides a web-based user interface for accessing your AWS account.
- AWS Config: Assess, audit, and evaluate the configuration of AWS resources.
- AWS CloudWatch: Monitor and log AWS resources and applications.
- AWS Auto Scaling: Provides features that allow you to scale multiple resources to meet demand.
- AWS Command Line Interface: Provides a unified tool to manage AWS services.
- AWS Trusted Advisor: Optimize AWS resources for performance, security, and cost-effectiveness.
- AWS Well-Architected Tool: Review and improve your workloads based on AWS best practices.
- AWS CloudTrail: Tracks user activity and API usage
Think of IAM as the security gatekeeper for your AWS account. It controls who (users, groups, applications) can do what (actions) and to what (resources).
Imagine a pie cut in half.
- AWS's half: They manage the underlying infrastructure (hardware, software, facilities) and its security.
- Your half: You're responsible for securing your resources (data, applications, configurations) within the AWS account.
- Shared responsibility:
- AWS takes care of the "cloud infrastructure," you manage your "stuff within the cloud."
- IAM helps you assign access securely:
- Create users, groups, and roles.
- Define what each can do (permissions) and which resources they can access.
- Securing your account:
- Use strong passwords, rotate them regularly.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for extra security.
- Monitor your account activity and investigate suspicious behavior.
You and AWS are partners in securing your cloud environment. By understanding and managing your share of the responsibility, you can keep your data and applications safe.
Amazon offers several storage services that businesses and individuals can use to store their data securely and access it whenever they need to. Here are the main ones:
- Think of it as a big digital warehouse where you can store any type of data, like documents, images, or videos.
- For example, if you have a website, you can store all your images and files on S3, so they're safe and easy to access.
- It's like having a hard drive in the cloud. You can store data that you need to access quickly, like operating systems or database files.
- Imagine you're running a website with a database. You can use EBS to store the database files securely and ensure quick access whenever someone visits your site.
- This is like having a shared network drive in the cloud. Multiple users or systems can access the same files simultaneously.
- For example, if you're working on a project with your team, you can store all project files in EFS, and everyone can access and work on them together from different locations.
- It's a storage service for data that you don't need to access frequently but still want to keep for long-term storage.
- Think of it as a vault for your digital files. For instance, you might use Glacier to store old backups or archives of your company's documents that you need to keep for legal reasons.
Amazon storage services are like different types of storage units you can rent in the cloud. Depending on your needs, you can choose the one that best fits what you want to store and how you want to access it.
Amazon provides various compute services that allow you to run your applications and processes in the cloud efficiently. Here are the main ones:
- This is like renting virtual computers in the cloud. You can configure these instances with the exact amount of CPU, memory, and storage you need.
- For example, if you have a website, you can use EC2 to host it. You choose the instance type that suits your website's requirements, like how much traffic it gets and how much processing power it needs.
Containers are like lightweight, portable packages that contain everything your application needs to run. ECS and EKS help you manage and orchestrate these containers at scale.
- ECS is a fully managed container orchestration service that allows you to easily run, stop, and manage Docker containers on a cluster.
- With ECS, you can define your application as a collection of tasks and services, which are then scheduled and run on a cluster of EC2 instances or AWS Fargate.
- It provides features like automatic scaling, load balancing, and service discovery, making it easier to deploy and manage containerized applications at scale.
- For example, if you have a microservices architecture for your application, you can use ECS to deploy and manage each microservice as a separate container, ensuring efficient resource utilization and easy scalability.
- EKS is a fully managed Kubernetes service that allows you to run Kubernetes clusters on AWS without the complexity of managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- With EKS, you can take advantage of Kubernetes' rich ecosystem of tools and resources, including support for advanced features like custom networking, storage, and security policies.
- It simplifies the process of running Kubernetes clusters by handling tasks such as cluster provisioning, upgrading, and patching, allowing you to focus on developing and deploying your applications.
- For example, if you have a large, complex application with multiple components that need to be deployed and managed across different environments, you can use EKS to orchestrate and scale these components efficiently, ensuring high availability and reliability.
- Lambda allows you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. You just upload your code, and Lambda takes care of running it whenever it's triggered.
- For instance, let's say you have a mobile app that needs to resize images when users upload them. Instead of setting up servers to handle this, you can use Lambda to automatically resize the images as soon as they're uploaded.
- This service makes it easy to deploy and manage your applications in the cloud without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- Think of it as a platform that handles all the heavy lifting of deploying, scaling, and monitoring your application. You just upload your code, and Elastic Beanstalk takes care of the rest.
Amazon's compute services offer different ways to run your applications in the cloud, whether you need virtual machines, containers, serverless computing, or a managed platform for your apps. Each service caters to different needs and preferences, giving you flexibility and scalability for your projects.
It's crucial to ensure that your applications are not only available but also responsive to changing demands. That's where Auto Scaling and Monitoring come into play.
Auto Scaling 🎚️ allows you to automatically adjust the number of resources, such as compute instances, based on the workload. This means you can seamlessly handle fluctuations in traffic without manual intervention, ensuring your applications remain responsive and cost-efficient.
Monitoring 📺 is the process of keeping an eye on the health, performance, and security of your AWS resources and applications. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, you can gain valuable insights into how your systems are performing and detect any issues before they impact your users.
- Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses, to ensure optimal resource utilization and high availability.
- Think of it as a traffic cop for your applications. It monitors the health of your instances and redirects traffic away from unhealthy instances, ensuring that your application remains available and responsive.
- For example, if you have a web application hosted on multiple EC2 instances, ELB can evenly distribute incoming web requests to these instances, preventing any single instance from becoming overwhelmed with traffic.
- CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service that provides real-time insights into the performance and health of your AWS resources and applications.
- It collects and tracks metrics, monitors logs and events, and sets alarms to notify you of any changes or issues in your environment.
- Imagine CloudWatch as a dashboard for your AWS services. It gives you visibility into how your resources are performing, allowing you to troubleshoot problems, optimize resource usage, and ensure the reliability of your applications.
- EC2 Auto Scaling automatically adjusts the number of EC2 instances in your fleet based on demand, ensuring that you have the right amount of capacity to handle your workload at all times.
- It allows you to define scaling policies based on metrics like CPU utilization or request count, so your application can scale in or out dynamically in response to changes in traffic.
- Picture it as an elastic rubber band for your EC2 instances. When traffic increases, EC2 Auto Scaling adds more instances to handle the load, and when traffic decreases, it removes excess instances to save costs.
Elastic Load Balancing, Amazon CloudWatch, and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling work together to ensure that your applications are highly available, scalable, and performant in the AWS cloud. ELB distributes incoming traffic, CloudWatch monitors your resources and applications, and EC2 Auto Scaling automatically adjusts your capacity to match demand, providing a seamless and efficient experience for your users.
Amazon offers a range of database services that cater to various needs, from traditional relational databases to NoSQL and data warehousing solutions. These services provide scalable, reliable, and managed database solutions for different types of applications and workloads.
- RDS is a fully managed relational database service that supports popular database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and MariaDB.
- It simplifies database administration tasks such as provisioning, patching, backup, and scaling, allowing you to focus on developing your applications.
- For example, if you're building a web application that requires a relational database, you can use RDS to easily deploy and manage a MySQL or PostgreSQL database instance without worrying about server management.
- DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that offers low-latency, high-performance, and scalable storage for applications that require flexible data models.
- It provides features like automatic scaling, built-in security, and seamless integration with other AWS services, making it ideal for modern web and mobile applications.
- For instance, if you're developing a real-time analytics platform that needs to handle large volumes of data with low latency, you can use DynamoDB to store and query the data efficiently.
- Redshift is a fully managed data warehousing service that allows you to analyze large datasets using SQL queries.
- It's optimized for data warehousing workloads, with features like columnar storage, parallel query execution, and advanced compression techniques for high performance and cost-effectiveness.
- For example, if you're running an e-commerce platform and need to analyze sales data to make business decisions, you can use Redshift to store and query terabytes of data quickly and cost-effectively.
- Aurora is a fully managed relational database engine that is compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL, offering the performance and availability of commercial databases at a fraction of the cost.
- It's designed for applications that require high throughput, low latency, and scalability, with features like automatic failover, continuous backup, and read scalability.
- For instance, if you're running a mission-critical application that requires high availability and scalability, you can use Aurora to achieve performance levels comparable to commercial databases like Oracle or SQL Server at a lower cost.
Amazon's database services provide flexible and scalable solutions for various types of applications and workloads, enabling you to focus on building and scaling your applications without worrying about database management tasks. Whether you need a traditional relational database, a NoSQL database, or a data warehousing solution, Amazon has a service to meet your needs.
Amazon provides a comprehensive set of networking services to help you build a robust, scalable, and secure network infrastructure. These services enable you to connect your cloud resources, manage network traffic, and ensure the security and reliability of your applications.
- VPC allows you to create a logically isolated network in the AWS cloud.
- You have full control over your virtual networking environment, including IP address ranges, subnets, and routing tables.
- For example, you can use VPC to create a private network for your web application, separating public-facing servers from internal databases.
- CloudFront is a content delivery network (CDN) that delivers data, videos, and applications globally with low latency.
- It caches your content at edge locations worldwide, improving load times for users.
- For example, use CloudFront to quickly deliver your website’s static assets, like images and videos, to users around the globe.
- Direct Connect establishes a dedicated network connection from your premises to AWS.
- It provides a more consistent network experience compared to internet-based connections.
- For example, use Direct Connect for secure, high-speed data transfer between your on-premises data center and AWS.
- Route 53 is a scalable DNS web service for domain name registration and routing.
- It translates domain names into IP addresses and routes end users to your applications.
- For example, use Route 53 to route traffic to different AWS regions based on user location for better performance.
- Transit Gateway connects VPCs and on-premises networks through a central hub.
- It simplifies your network architecture by managing multiple connections through a single gateway.
- For example, use Transit Gateway to connect multiple VPCs in different regions for easier management and lower latency.
- Global Accelerator improves the availability and performance of your applications for global users.
- It provides static IP addresses and routes traffic to the nearest healthy endpoint.
- For example, use Global Accelerator to ensure your application is fast and reliable for users worldwide, regardless of their location.
AWS Networking Services like VPC, CloudFront, Direct Connect, Route 53, Transit Gateway, and Global Accelerator help you build a robust, scalable, and efficient network for your applications, ensuring optimal performance and security.
Amazon provides a suite of tools to help you monitor, manage, and optimize your spending on AWS. These services give you insights into your costs and usage, allowing you to control expenses and improve efficiency.
- Cost Explorer is a graphical interface that helps you visualize and analyze your AWS costs and usage.
- You can create custom reports to track spending patterns and identify cost drivers.
- For example, use Cost Explorer to see which services are driving up your monthly bill and adjust your usage accordingly.
- AWS Budgets allows you to set custom cost and usage budgets and receive alerts when you exceed or are forecasted to exceed your thresholds.
- You can track your spending against your budget and get notifications via email or SMS.
- For example, set a budget of $500 per month for your development environment, and AWS Budgets will alert you if you are close to this limit.
- The Cost and Usage Report provides detailed data about your AWS costs and usage.
- You can download comprehensive reports for in-depth analysis or integrate them with tools like Amazon Athena or Redshift.
- For example, use the CUR to analyze spending trends over the past year and identify opportunities for savings.
- Trusted Advisor provides real-time guidance to help you reduce costs, improve performance, and enhance security.
- It offers recommendations across five categories: cost optimization, performance, security, fault tolerance, and service limits.
- For example, Trusted Advisor might suggest terminating underutilized EC2 instances to save money.
- Cost Anomaly Detection uses machine learning to monitor your AWS usage and detect unusual spending patterns.
- It alerts you when an anomaly is detected, helping you quickly address unexpected costs.
- For example, receive notifications if your AWS bill spikes due to an unexpected increase in resource usage.
In summary, AWS Cost Management Services like Cost Explorer, Budgets, Cost and Usage Report, Trusted Advisor, and Cost Anomaly Detection help you gain insights into your spending, set and enforce budgets, and optimize costs, ensuring you get the most value from your AWS investments.
Amazon provides a suite of tools to help you manage and govern your AWS resources effectively. These services enable you to automate tasks, ensure compliance, monitor performance, and maintain control over your infrastructure.
AWS CloudFormation 🗂️
- CloudFormation allows you to define your cloud resources using templates.
- It automates the provisioning and configuration of your AWS resources, making it easier to manage infrastructure as code.
- For example, use CloudFormation to deploy a web application stack, including EC2 instances, RDS databases, and S3 buckets, with a single template.
AWS CloudTrail 🕵️♂️
- CloudTrail records all API calls and user activity within your AWS account.
- It provides a history of AWS API calls, including who made the request, the services used, and the actions taken.
- For example, use CloudTrail to monitor changes to your infrastructure and ensure compliance with security policies.
AWS Config 📜
- AWS Config tracks changes to your AWS resources and evaluates configurations against desired settings.
- It provides detailed resource configuration history and compliance auditing capabilities.
- For example, use AWS Config to ensure that all EC2 instances are configured with specific security settings.
AWS Systems Manager 🛠️
- Systems Manager provides a unified interface to view and control your AWS resources.
- It helps automate operational tasks, like patch management, configuration management, and software inventory.
- For example, use Systems Manager to automate the patching of your EC2 instances, ensuring they are up-to-date with the latest security updates.
AWS CloudWatch 📈
- CloudWatch monitors your AWS resources and applications in real-time.
- It collects and tracks metrics, sets alarms, and automatically reacts to changes in your AWS resources.
- For example, use CloudWatch to monitor the CPU usage of your EC2 instances and trigger an auto-scaling event if usage exceeds a certain threshold.
AWS Service Catalog 📋
- Service Catalog allows you to create and manage catalogs of approved IT services.
- It helps organizations manage and distribute approved software and service configurations.
- For example, use Service Catalog to provide your development teams with pre-approved AMIs, databases, and other resources they need to build applications.
AWS Organizations 🏢
- Organizations allow you to manage multiple AWS accounts centrally.
- It helps you apply policies, manage billing, and automate account creation across your organization.
- For example, use AWS Organizations to set policies that restrict certain actions across all accounts in your organization, ensuring compliance with company standards.
In summary, AWS Management and Governance Services like CloudFormation, CloudTrail, AWS Config, Systems Manager, CloudWatch, Service Catalog, and Organizations help you manage, automate, monitor, and govern your AWS resources efficiently, ensuring compliance, optimizing performance, and maintaining control over your infrastructure.
Amazon provides a range of specialized services to support cutting-edge technologies and emerging fields. These services help you explore new frontiers in blockchain, quantum computing, satellite communications, augmented and virtual reality, and machine learning.
- Managed Blockchain makes it easy to create and manage scalable blockchain networks using popular frameworks like Hyperledger Fabric and Ethereum.
- It simplifies the setup and management of blockchain networks, allowing you to focus on developing smart contracts and applications.
- For example, use Managed Blockchain to create a secure, scalable blockchain network for tracking supply chain data.
- Braket is a fully managed service that allows you to explore and experiment with quantum computing.
- It provides access to quantum hardware from multiple providers and simulators to develop and test quantum algorithms.
- For example, use Braket to experiment with quantum algorithms that could potentially solve complex optimization problems faster than classical algorithms.
- Ground Station is a fully managed service for controlling satellite communications, processing satellite data, and scaling satellite operations.
- It provides global ground station infrastructure, enabling you to connect with your satellites easily.
- For example, use Ground Station to download satellite imagery and process it in real-time using AWS analytics services.
- Sumerian is a service for creating and running augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and 3D applications.
- It provides a web-based editor and built-in templates to simplify the development of immersive experiences.
- For example, use Sumerian to create an interactive 3D training module for your employees that can be accessed via VR headsets or web browsers.
- SageMaker is a fully managed service for building, training, and deploying machine learning models.
- It provides a suite of tools and workflows to simplify each step of the machine learning process, from data labeling to model monitoring.
- For example, use SageMaker to develop a predictive maintenance model that can analyze sensor data and predict equipment failures.
- Polly is a service that turns text into lifelike speech using advanced deep learning technologies.
- It offers various voices and supports multiple languages, making it easy to add speech capabilities to your applications.
- For example, use Polly to create an interactive voice response system for your customer support line.
- Rekognition is a service that adds image and video analysis to your applications.
- It can detect objects, people, text, scenes, and activities in images and videos, and provides facial analysis and recognition.
- For example, use Rekognition to build a secure access system that uses facial recognition to verify employees' identities.
AWS provides a diverse range of specialized services like Managed Blockchain, Braket, Ground Station, Sumerian, SageMaker, Polly, and Rekognition. These services help you explore and implement advanced technologies in blockchain, quantum computing, satellite communications, AR/VR, and machine learning, enabling you to innovate and stay ahead in various fields.
Cloud computing has revolutionized how we build, deploy, and manage applications. It offers unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, enabling businesses of all sizes to innovate faster and deliver more value to their customers. By leveraging cloud services, organizations can focus on their core competencies while relying on cloud providers for the underlying infrastructure and services.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is at the forefront of this transformation, providing a comprehensive suite of cloud services that cater to a wide range of needs. From compute and storage to databases, networking, and beyond, AWS offers the tools and services necessary to build robust, scalable, and secure applications.
While this repository covers many of the most popular and widely used AWS services—such as Amazon EC2, S3, RDS, Lambda, and more—it’s important to note that AWS boasts an extensive catalog of services that we haven’t touched upon. Each service is designed to address specific use cases, ensuring that AWS can support virtually any cloud-based application or workload.
Thank you for visiting my AWS Cloud Computing Repository. I hope this collection of information has been helpful in understanding the vast landscape of AWS services and how they can be utilized to meet your cloud computing needs. Whether you’re a beginner just starting out or an experienced professional looking to deepen your knowledge, I hope you found valuable insights and practical information within these pages.
Feel free to explore further, experiment with AWS services, and leverage the power of cloud computing to drive your projects to new heights.
Happy cloud computing! ❤️