Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of all left leaves.
A leaf is a node with no children. A left leaf is a leaf that is the left child of another node.
Example 1:
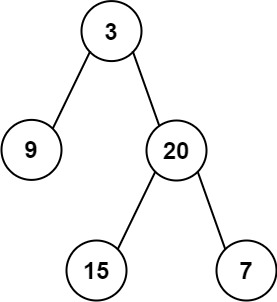
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 24
Explanation: There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
Solution
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.S = 0
if not root:
return 0
def dfs(root, x):
if not root.left and not root.right:
if x == 'left':
self.S += root.val
if root.left:
dfs(root.left, 'left')
if root.right:
dfs(root.right, 'right')
dfs(root, '')
return self.S