作者:Leo,编程导航 编号 12644
大家好,我是Leo哥🫣🫣🫣,今天继续带来一篇关于SpringBoot实现多数据源的实战案例。好了,话不多说让我们开始吧😎😎😎。
在实际开发中,我们往往面临一个应用需要访问多个数据库的情况。例如下面两种场景。
-
业务复杂: 数据分布在不同的数据库,数据库拆了,应用没拆,一个公司有多个子项目,各用各的数据库。
-
读写分离: 为了解决数据库的读性能瓶颈(读比写性能更高,写锁会影响读阻塞,从而影响读的性能)
很多数据库拥有主从架构,也就是说,一台 主数据库服务器,是对外提供增删改查业务的生产服务器;
另一台从数据库服务器,主要进行读的操作。
读写分离:解决高并发下读写受影响。数据更新在主库上进行,主库将数据变更信息同步给从库。在查询时,在从库上进行,从而分担主库的压力。
我们可以在代码层面解决这种动态数据源切换的问题,而不需要使用 mycat、shardingJDBC 等其他中间件。本文将主要以自定义注解 + 继承 AbstractRoutingDataSource 实现读写分离。
在 SpringBoot 项目中实现读写分离通常需要以下几步:
- 配置数据源:你需要为读操作和写操作分别配置一个数据源。
- 创建数据源路由逻辑:这通常通过扩展 Spring 的
AbstractRoutingDataSource来实现。它允许你根据一定的逻辑来决定使用哪个数据源(读或写)。 - 配置事务管理器:这使得你能够在使用不同数据源时保持事务的一致性。
- 服务层或DAO层设计:确保在执行读操作时使用读数据源,在执行写操作时使用写数据源。
- 自定义切面,在切面中解析 @DataSource 注解。当一个方法或者类上面,有 @DataSource 注解的时候,将 @DataSource 注解所标记的数据源列出来存入到 ThreadLocal 中。
注意:这里使用ThreadLocal的原因是为了保证我们的线程安全。
接下来我们就按照以上步骤进行编码实现。
首先我们创建一个新的模块命名为:springboot-dynamic-source
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis plus-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>server:
port: 8007
spring:
application:
name: dynamic-source
jackson:
date-format: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
time-zone: GMT+8
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
ds:
# 主库数据源
master:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/test01?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: root
password: root
# 从库数据源
slave:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/test02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: root
password: root
# 初始连接数
initialSize: 5
# 最小连接池数量
minIdle: 10
# 最大连接池数量
maxActive: 20
# 配置获取连接等待超时的时间
maxWait: 60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
# 配置一个连接在池中最大生存的时间,单位是毫秒
maxEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 900000
# 配置检测连接是否有效
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
webStatFilter:
enabled: true
statViewServlet:
enabled: true
# 设置白名单,不填则允许所有访问
allow:
url-pattern: /druid/*
# 控制台管理用户名和密码
login-username: admin
login-password: 123456
filter:
stat:
enabled: true
# 慢SQL记录
log-slow-sql: true
slow-sql-millis: 1000
merge-sql: true
wall:
config:
multi-statement-allow: true
logging:
level:
org.javatop: debug
pattern:
dateformat: HH:mm:ss:SSS
file:
path: "logs/${spring.application.name}"ds 中是我们的所有数据源。master 是默认的数据源,不可修改,其他的数据源可以修改并添加多个。
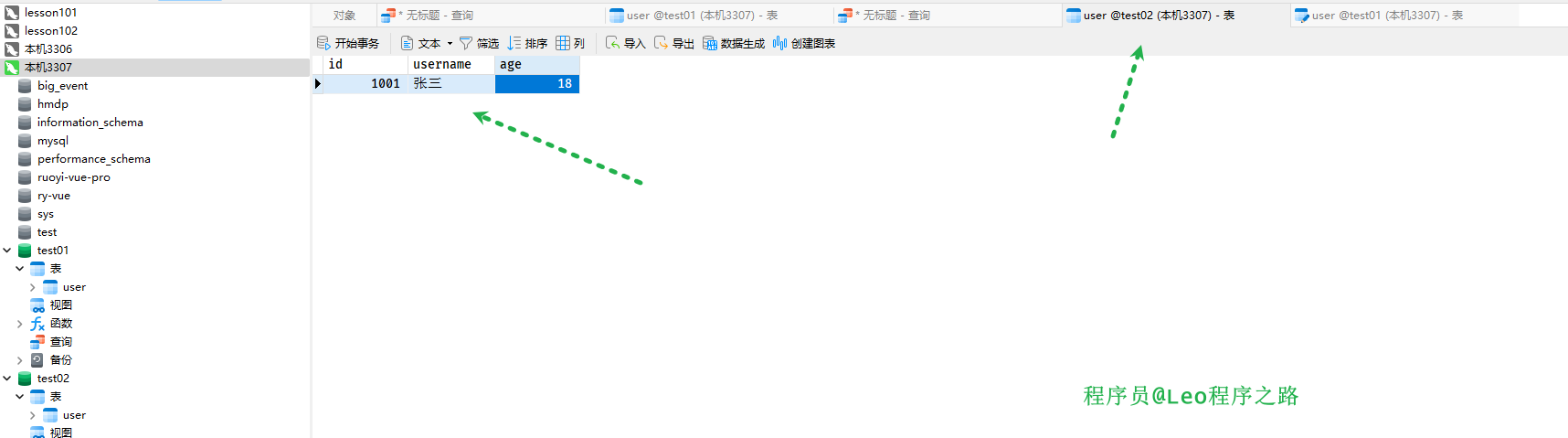
我这里需要提前准备两个数据库,一个是主数据库master,一个是从数据库slave。
我们会后面会通过一个自定义注解去实现动态切换数据库。
这里给出我们创建的一个user表的SQL语句。
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=101 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;我们可以通过@ConfigurationProperties 注解加载定义的配置文件。spring.datasource 对应的注解都会匹配到。
package org.javatop.dynamic.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:10
* @description :
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public class DruidProperties {
private String type;
private String driverClassName;
private Map<String, Map<String,String>> ds;
private Integer initialSize;
private Integer minIdle;
private Integer maxActive;
private Integer maxWait;
/**
*一会在外部构建好一个 DruidDataSource 对象,包含三个核心属性 url、username、password
* 在这个方法中设置公共属性
* @param druidDataSource
* @return
*/
public DataSource dataSource(DruidDataSource druidDataSource){
druidDataSource.setInitialSize(initialSize);
druidDataSource.setMinIdle(minIdle);
druidDataSource.setMaxActive(maxActive);
druidDataSource.setMaxWait(maxWait);
return druidDataSource;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getDriverClassName() {
return driverClassName;
}
public void setDriverClassName(String driverClassName) {
this.driverClassName = driverClassName;
}
public Map<String, Map<String, String>> getDs() {
return ds;
}
public void setDs(Map<String, Map<String, String>> ds) {
this.ds = ds;
}
public Integer getInitialSize() {
return initialSize;
}
public void setInitialSize(Integer initialSize) {
this.initialSize = initialSize;
}
public Integer getMinIdle() {
return minIdle;
}
public void setMinIdle(Integer minIdle) {
this.minIdle = minIdle;
}
public Integer getMaxActive() {
return maxActive;
}
public void setMaxActive(Integer maxActive) {
this.maxActive = maxActive;
}
public Integer getMaxWait() {
return maxWait;
}
public void setMaxWait(Integer maxWait) {
this.maxWait = maxWait;
}
}然后我们开始通过进行加载DruidProperties来加载数据源。
@EnableConfigurationProperties :这个注解的意思是使 ConfigurationProperties 注解生效。
package org.javatop.dynamic.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:12
* @description : 加载数据源
*/
@Component
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DruidProperties.class)
public class LoadDataSource {
@Autowired
DruidProperties druidProperties;
public Map<String, DataSource> loadAllDataSource() {
Map<String, DataSource> map =new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Map<String, String>> ds = druidProperties.getDs();
try {
Set<String> keySet = ds.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
map.put(key, druidProperties.dataSource((DruidDataSource) DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(ds.get(key))));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return map;
}
}loadAllDataSource() 方法可以通过读取application.yml配置文件中所有数据源对象。(我们这里有一个master主数据库,和一个slave从数据库)
druidProperties.dataSource(DruidDataSource druidDataSource) 这个方法为每个数据源配置其他额外的属性(最大连接池等信息)。
DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(ds.get(key):创建一个数据源,赋予三个核心的属性。(username、url、password)
最终,所有的数据源都会存入map中。
我们这里定义一个简单的ThreadLocal工具类
package org.javatop.dynamic.utils;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:13
* @description : ThreadLocal工具类
*/
public class DynamicDataSourceUtil {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> CONTEXT_HOLDER =new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setDataSourceType(String dsType){
CONTEXT_HOLDER.set(dsType);
}
public static String getDataSourceType(){
return CONTEXT_HOLDER.get();
}
public static void clear(){
CONTEXT_HOLDER.remove();
}
}首先需要通过一个枚举类来设定一下我们的默认数据源,也是是master主数据库。
package org.javatop.dynamic.constant;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:13
* @description :
*/
public interface DataSourceType {
String default_ds_name ="master";
}然后自定义一个注解,后面也就是通过这个注解来动态的配置切换我们的数据源,这里就也叫Datasource吧。
package org.javatop.dynamic.annotation;
import org.javatop.dynamic.constant.DataSourceType;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:14
* @description : 这个注解将来可以加在某一个 service 类上或者方法上,通过 value 属性来指定类或者方法应该使用哪个数据源
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface DataSource{
/**
* 如果一个方法上加了 @DataSource 注解,但是却没有指定数据源的名称,那么默认使用 Master 数据源
* @return
*/
String value() default DataSourceType.default_ds_name;
}package org.javatop.dynamic.annotation;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.javatop.dynamic.utils.DynamicDataSourceUtil;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:15
* @description : AOP解析自定义注解
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class DataSourceAspect {
/**
* @annotation(org.javatop.dynamic.annotation.DataSource) 表示方法上有 @DataSource 注解 就将方法拦截下来。
* @within :如果类上面有 @DataSource 注解,就将类中的方法拦截下来。
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.javatop.dynamic.annotation.DataSource) || " +
"@within(org.javatop.dynamic.annotation.DataSource)")
public void pc(){
}
@Around("pc()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point){
//获取方法上面的注解
DataSource dataSource =getDataSource(point);
if(dataSource!=null){
// 注解中数据源的名称
String value = dataSource.value();
DynamicDataSourceUtil.setDataSourceType(value);
}
try {
return point.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DynamicDataSourceUtil.clear();
}
return null;
}
private DataSource getDataSource(ProceedingJoinPoint point) {
/**
* 先去查找方法上的注解,如果没有,再去类中找。
*/
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)point.getSignature();
DataSource annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(signature.getMethod(), DataSource.class);
if(annotation!=null){
return annotation;
}
return AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(signature.getDeclaringType(),DataSource.class);
}
}@Pointcut("@annotation(org.javatop.dynamic.annotation.DataSource) || " +
"@within(org.javatop.dynamic.annotation.DataSource)")
public void pc() {
}@Pointcut是一个定义在方法上的注解,用来指定一个切点(即在何处进行拦截)。"@annotation(org.javatop.dynamic.annotation.DataSource)"表示拦截所有被@DataSource注解标记的方法。"@within(org.javatop.dynamic.annotation.DataSource)"表示拦截所有在类级别被@DataSource注解标记的类中的方法。pc()方法本身是空的,因为所有的逻辑都将在与这个切点相关的通知(advice)中定义。
e@Around("pc()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) {
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource(point);
if (dataSource != null) {
String value = dataSource.value();
DynamicDataSourceUtil.setDataSourceType(value);
}
try {
return point.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DynamicDataSourceUtil.clear();
}
return null;
}@Around("pc()")表示这是一个环绕通知,它会在pc()方法所定义的切点前后执行。ProceedingJoinPoint point是连接点的信息,它包含了方法的所有相关信息,如方法名、参数等。getDataSource(point)用来获取方法或类上的@DataSource注解。- 如果存在
@DataSource注解,它会从注解中获取数据源的名称,并通过DynamicDataSourceUtil.setDataSourceType(value)设置当前线程的数据源。 point.proceed()是调用原始方法的地方。finally块中的DynamicDataSourceUtil.clear()用于在方法执行完毕后清理数据源设置,确保不会影响其他的数据库操作。
最后获取@DataSource注解
package org.javatop.dynamic.config;
import org.javatop.dynamic.constant.DataSourceType;
import org.javatop.dynamic.utils.DynamicDataSourceUtil;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:18
* @description : 定义动态数据源
*/
@Component
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
public DynamicDataSource(LoadDataSource loadDataSource) {
// 1、设置所有的数据源
Map<String, DataSource> stringDataSourceMap = loadDataSource.loadAllDataSource();
super.setTargetDataSources(new HashMap<>(stringDataSourceMap));
// 2、设置默认的数据源
super.setDefaultTargetDataSource(stringDataSourceMap.get(DataSourceType.default_ds_name));
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
/**
* 这个方法用来返回数据源名称,当系统需要获取数据源的时候,会自动调用该方法获取数据源的名称
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DynamicDataSourceUtil.getDataSourceType();
}
}-
DynamicDataSource类扩展自AbstractRoutingDataSource类,这是Spring框架提供的一个抽象类,用于实现数据源的动态路由。 -
构造函数
public DynamicDataSource(LoadDataSource loadDataSource)接收一个
LoadDataSource类型的参数。这个参数被用于加载所有的数据源配置。
Map<String, DataSource> stringDataSourceMap = loadDataSource.loadAllDataSource();这行代码调用了loadDataSource的loadAllDataSource方法来加载所有数据源配置,并将其存储在一个名为stringDataSourceMap的Map中,其中键是数据源的名称,值是对应的DataSource对象。super.setTargetDataSources(new HashMap<>(stringDataSourceMap));这行代码设置了目标数据源。它将前面加载的所有数据源stringDataSourceMap设置为目标数据源。super.setDefaultTargetDataSource(stringDataSourceMap.get(DataSourceType.default_ds_name));这行代码设置了默认的数据源。它通过DataSourceType.default_ds_name从stringDataSourceMap中获取默认的数据源,并设置为默认数据源。super.afterPropertiesSet();是一个初始化方法,确保所有属性都被正确设置。
-
determineCurrentLookupKey()方法是
AbstractRoutingDataSource的一个抽象方法,必须要实现。这个方法用于决定使用哪个数据源,通常情况下是根据某种条件动态返回数据源名称。
return DynamicDataSourceUtil.getDataSourceType();这行代码返回当前线程所使用的数据源的名称。DynamicDataSourceUtil是一个工具类,可能提供了线程局部变量(ThreadLocal)来存储每个线程所选择的数据源名称。
这样,当应用程序需要与数据库进行交互时,就会通过 DynamicDataSource 获取到当前线程所指定的数据源,并进行相应的数据库操作。这种方式能够在不同业务场景中灵活切换数据源,非常适合多租户、读写分离等复杂的数据库应用场景。
我们编写一个service层
package org.javatop.dynamic.service;
import org.javatop.dynamic.annotation.DataSource;
import org.javatop.dynamic.domain.User;
import org.javatop.dynamic.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:26
* @description :
*/
@Service
public class UserService{
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@DataSource("slave")
// @DataSource
public List<User> getAll(){
List<User> all = userMapper.getAll();
return all;
}
}我们在getAll()方法上加上@DataSource("slave"),并指定slave从数据库。
然后再编写一个mapper,去操作数据库。
package org.javatop.dynamic.mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.javatop.dynamic.domain.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:26
* @description :
*/
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> getAll();
}package org.javatop.dynamic;
import org.javatop.dynamic.domain.User;
import org.javatop.dynamic.service.UserService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author : Leo
* @version 1.0
* @date 2024-01-02 15:32
* @description :
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class DynamicTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* 用于测试:
*/
@Test
public void test() {
List<User> all = userService.getAll();
if(all !=null){
for (User user : all) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
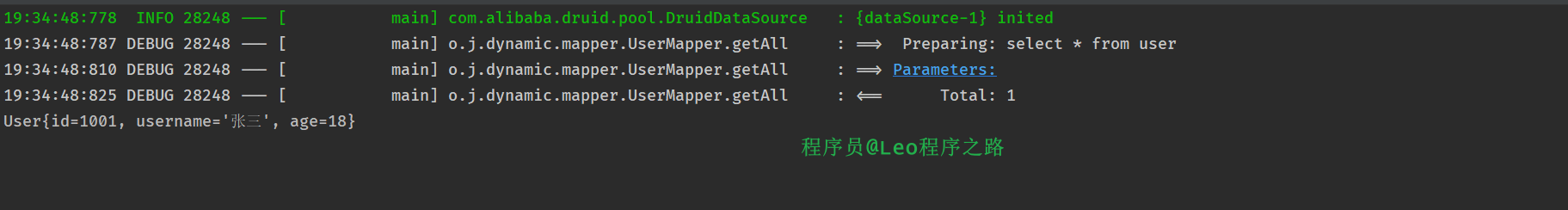
}我们查看控制台。
可以看出来我们去查询的是test02库中的user数据。
大功告成!!!