- 有重复必须先排序,并且在循环中判断是否为第一次出现的数
- 没有重复的数字序列
输入: [1,2,3] 输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [3,2,1] ]
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean st[];
public void dfs(int[] nums, int u) {
if (u == nums.length) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (!st[i]) {
path.add(nums[i]);
st[i] = true;
dfs(nums, u + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
st[i] = false;
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
st = new boolean[nums.length];
dfs(nums, 0);
return ans;
}
}- 可包含重复数字的序列
输入:nums = [1,1,2] 输出: [[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]]
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean st[];
public void dfs(int[] nums, int u) {
if (u == nums.length) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (!st[i]) {
if (i != 0 && nums[i - 1] == nums[i] && !st[i - 1]) continue;
st[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, u + 1);
st[i] = false;
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
st = new boolean[nums.length];
dfs(nums, 0);
return ans;
}
}- 无重复字符串的排列组合
输入:S = "qwe" 输出:["qwe", "qew", "wqe", "weq", "ewq", "eqw"]
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
boolean st[];
public void dfs(char[] str, int u) {
int n = str.length;
if (u == n) {
ans.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!st[i]) {
sb.append(str[i]);
st[i] = true;
dfs(str, u + 1);
st[i] = false;
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
}
}
public String[] permutation(String S) {
st = new boolean[S.length()];
dfs(S.toCharArray(), 0);
String[] res = new String[ans.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i) res[i] = ans.get(i);
return res;
}
}- 有重复字符串的排列组合
输入:S = "qqe" 输出:["eqq","qeq","qqe"]
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
boolean st[];
public void dfs(char[] str, int u) {
int n = str.length;
if (u == n) {
ans.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!st[i]) {
if (i != 0 && str[i] == str[i - 1] && !st[i - 1]) continue;
sb.append(str[i]);
st[i] = true;
dfs(str, u + 1);
st[i] = false;
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
}
}
public String[] permutation(String S) {
char[] str = S.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(str);
st = new boolean[S.length()];
dfs(str, 0);
String[] res = new String[ans.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i) res[i] = ans.get(i);
return res;
}
}- 第k个全排列序列
输入:n = 3, k = 3 输出:"213" _ _ _ 一共三个位置,若第一个位置填1,则后面一共有(n - 1)!种即2种,小于k; 若第一个位置填2,则后面同样有2种,已经超过k,则第一个数字为2。
class Solution {
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
String ans = "";
boolean st[] = new boolean[10];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int fact = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n - i - 1; ++j) fact *= j;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (!st[j]) {
if (fact < k) k -= fact;
else {
ans += Integer.toString(j);
st[j] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}- 大小写转换
输入:S = "a1b2" 输出:["a1b2", "a1B2", "A1b2", "A1B2"]
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String S) {
dfs(S.toCharArray(), 0);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(char s[], int u) {
if (u == s.length) {
ans.add(new String(s));
return;
}
dfs(s, u + 1);
if (Character.isLetter(s[u])) {
s[u] ^= 32;
dfs(s, u + 1);
s[u] ^= 32;
}
}
}class Solution {
Map<Character, String> map = new HashMap<Character, String>() {{
put('2', "abc");
put('3', "def");
put('4', "ghi");
put('5', "jkl");
put('6', "mno");
put('7', "pqrs");
put('8', "tuv");
put('9', "wxyz");
}};
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public void dfs(char[] s, int u) {
int n = s.length;
if (u == n) {
ans.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
String str = map.get(s[u]);
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); ++i) {
sb.append(str.charAt(i));
dfs(s, u + 1);
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
}
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if (digits.equals("")) return new ArrayList<String>();
dfs(digits.toCharArray(), 0);
return ans;
}
}输入: n = 4, k = 2 输出: [ [2,4], [3,4], [2,3], [1,2], [1,3], [1,4], ]
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public void dfs(int n, int k, int u) {
// 剪枝
if (path.size() + (n - u + 1) < k) return;
if (path.size() == k) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
path.add(u);
dfs(n, k, u + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
dfs(n, k, u + 1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
dfs(n, k, 1);
return ans;
}
}- 无重复数字且可以重复使用
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7, 所求解集为: [ [7], [2,2,3] ]
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public void dfs(int[] nums, int target, int u) {
int n = nums.length;
if (target == 0) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
if (u == n) return;
for (int i = 0; nums[u] * i <= target; ++i) {
dfs(nums, target - nums[u] * i, u + 1);
path.add(nums[u]);
}
for (int i = 0; nums[u] * i <= target; ++i) path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
dfs(candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
}- 数字可重复且只能用一次
输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8, 所求解集为: [ [1, 7], [1, 2, 5], [2, 6], [1, 1, 6] ]
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public void dfs(int[] nums, int target, int u) {
int n = nums.length;
if (target == 0) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
if (u == n) return;
int k = u + 1;
while (k < n && nums[k] == nums[u]) k++;
int cnt = k - u;
for (int i = 0; nums[u] * i <= target && i <= cnt; ++i) {
dfs(nums, target - nums[u] * i, k);
path.add(nums[u]);
}
for (int i = 0; nums[u] * i <= target && i <= cnt; ++i) path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
dfs(candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
}- 1-9 九个数字选取k个数,不能重复使用
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
int len = 9;
public void dfs(int k, int target, int u, int sum) {
if (path.size() + (len - u + 1) < k || path.size() > k) return;
if (target == sum && path.size() == k) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
path.add(u);
sum += u;
dfs(k, target, u + 1, sum);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
sum -= u;
dfs(k, target, u + 1, sum);
}
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
dfs(k, n, 1, 0);
return ans;
}
}- 非DFS问题
- f[j] 表示总和为j的所有方案数
class Solution {
public int combinationSum4(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] f = new int[target + 1];
f[0] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j <= target; ++j) {
for (int x: nums) {
if (j >= x) f[j] += f[j - x];
}
}
return f[target];
}
}输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << n; ++i) {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((i >> j & 1) == 1) path.add(nums[j]);
}
ans.add(path);
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public void dfs(int[] nums, int u) {
if (u == nums.length) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
path.add(nums[u]);
dfs(nums, u + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
dfs(nums, u + 1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
dfs(nums, 0);
return ans;
}
}输入:nums = [1,2,2] 输出:[[],[1],[1,2],[1,2,2],[2],[2,2]]
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
private boolean[] st;
public void dfs(int u, int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (u == n) {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (st[i]) path.add(nums[i]);
}
ans.add(path);
return;
}
int k = u;
while (k < n && nums[k]== nums[u]) k++;
dfs(k, nums);
for (int i = u; i < k; ++i) {
st[i] = true;
dfs(k, nums);
}
for (int i = u; i < k; ++i) st[i] = false;
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
st = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.sort(nums);
dfs(0, nums);
return ans;
}
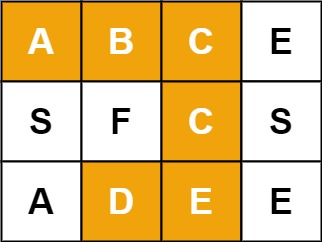
}输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" 输出:true
class Solution {
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
public boolean dfs(char[][] board, String word, int u, int x, int y) {
if (board[x][y] != word.charAt(u)) return false;
if (u == word.length() - 1) return true;
char t = board[x][y];
board[x][y] = '.';
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= board.length || b < 0 || b >= board[0].length || board[a][b] == '.') continue;
if (dfs(board, word, u + 1, a, b)) return true;
}
board[x][y] = t;
return false;
}
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
int n = board.length;
if (n == 0) return false;
int m = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (dfs(board, word, 0, i, j)) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
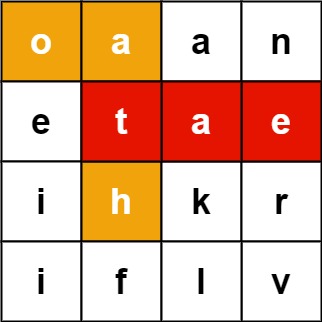
}输入:board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"] 输出:["eat","oath"]
class Solution {
class Node {
Node son[];
int id;
public Node() {
id = -1;
son = new Node[26];
}
}
Node root = new Node();
public void insert(String word, int id) {
Node cur = root;
for (char c: word.toCharArray()) {
int u = c - 'a';
if (cur.son[u] == null) cur.son[u] = new Node();
cur = cur.son[u];
}
cur.id = id;
}
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
Set<Integer> ids = new HashSet<>();
public void dfs(char[][] board, int x, int y, Node cur) {
if (cur.id != -1) ids.add(cur.id);
char t = board[x][y];
board[x][y] = '.';
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= board.length || b < 0 || b >= board[0].length || board[a][b] == '.') continue;
int u = board[a][b] - 'a';
if (cur.son[u] != null) dfs(board, a, b, cur.son[u]);
}
board[x][y] = t;
}
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; ++i) insert(words[i], i);
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[i].length; ++j) {
int u = board[i][j] - 'a';
if (root.son[u] != null) dfs(board, i, j, root.son[u]);
}
}
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer id: ids) ans.add(words[id]);
return ans;
}
}输入: board = [["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","O","X"],["X","X","O","X"],["X","O","X","X"]] 输出:[["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","X","X"]] 解释:被围绕的区间不会存在于边界上,换句话说,任何边界上的 'O' 都不会被填充为 'X'。 任何不在边界上,或不与边界上的 'O' 相连的 'O' 最终都会被填充为 'X'。如果两个元素在水平或垂直方向相邻,则称它们是“相连”的。
class Solution {
public void solve(char[][] board) {
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n = board.length;
if (n == 0) return;
int m = board[0].length;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (board[i][0] == 'O') queue.offer(new int[]{i, 0});
if (board[i][m - 1] == 'O') queue.offer(new int[]{i, m - 1});
}
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; ++i) {
if (board[0][i] == 'O') queue.offer(new int[]{0, i});
if (board[n - 1][i] == 'O') queue.offer(new int[]{n - 1, i});
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = queue.poll();
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
board[x][y] = '.';
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || board[a][b] != 'O') continue;
queue.offer(new int[]{a, b});
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') board[i][j] = 'O';
else if (board[i][j] == 'O') board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}输入:grid = [ ["1","1","1","1","0"], ["1","1","0","1","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","0","0","0"] ] 输出:1
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n = grid.length;
if (n == 0) return 0;
int m = grid[0].length;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
++ans;
grid[i][j] = '0';
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = queue.poll();
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int a = x + dx[k], b = y + dy[k];
if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || grid[a][b] == '0') continue;
queue.offer(new int[]{a, b});
grid[a][b] = '0';
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}输入:[[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0], [0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0], [0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0], [0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]] 输出:6
class Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n = grid.length;
if (n == 0) return 0;
int m = grid[0].length;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
grid[i][j] = 0;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
int tmp = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = queue.poll();
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
tmp++;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int a = x + dx[k], b = y + dy[k];
if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || grid[a][b] == 0) continue;
queue.offer(new int[]{a, b});
grid[a][b] = 0;
}
}
ans = Math.max(ans, tmp);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}输入: [ [0,2,1,0], [0,1,0,1], [1,1,0,1], [0,1,0,1] ] 输出: [1,2,4]
- 此题与上面的题目不同,需要判断周围8个点的坐标,而不是上下左右四个。
class Solution {
public int[] pondSizes(int[][] land) {
int n = land.length;
if (n == 0) return new int[]{};
int m = land[0].length;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (land[i][j] == 0) {
int tmp = 0;
land[i][j] = 1;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = queue.poll();
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
tmp++;
for (int k1 = x - 1; k1 <= x + 1; ++k1) {
for (int k2 = y - 1; k2 <= y + 1; ++k2) {
if (k1 == x && k2 == y) continue;
if (k1 < 0 || k1 >= n || k2 < 0 || k2 >= m || land[k1][k2] != 0) continue;
land[k1][k2] = 1;
queue.offer(new int[]{k1, k2});
}
}
}
ans.add(tmp);
}
}
}
int[] res = ans.stream().mapToInt(Integer::valueOf).toArray();
Arrays.sort(res);
return res;
}
}输入:[[1,0,1], [0,0,0], [1,0,1]] 输出:2 解释: 海洋单元格 (1, 1) 和所有陆地单元格之间的距离都达到最大,最大距离为 2
class Solution {
public int maxDistance(int[][] grid) {
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n = grid.length;
if (n == 0) return 0;
int m = grid[0].length;
int ans = -1;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
if (queue.size() == n * n) return -1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ans++;
int size = queue.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
int[] t = queue.poll();
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || grid[a][b] != 0) continue;
queue.offer(new int[]{a, b});
grid[a][b] = 2;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}输入:[[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]] 输出:4
class Solution {
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
if (n == 0) return 0;
int m = grid[0].length;
int ans = 0, cnt = 0;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
else if (grid[i][j] == 1) cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt == 0) return 0;
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ans++;
int size = queue.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
int[] t = queue.poll();
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a >= 0 && a < n && b >= 0 && b < m && grid[a][b] == 1) {
cnt--;
grid[a][b] = 2;
queue.offer(new int[]{a, b});
}
}
}
}
return cnt == 0 ? ans - 1 : -1;
}
}输入:numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]] 输出:true 解释:总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要完成课程 0 。这是可能的。
class Solution {
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int[] indegrees = new int[numCourses];
List<List<Integer>> adjacency = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) adjacency.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] pre: prerequisites) {
indegrees[pre[0]]++;
adjacency.get(pre[1]).add(pre[0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
if (indegrees[i] == 0) queue.offer(i);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int t = queue.poll();
numCourses--;
for (int cur: adjacency.get(t)) {
if (--indegrees[cur] == 0) queue.offer(cur);
}
}
return numCourses == 0;
}
}输入: 4, [[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2]] 输出: [0,1,2,3] or [0,2,1,3] 解释: 总共有 4 门课程。要学习课程 3,你应该先完成课程 1 和课程 2。并且课程 1 和课程 2 都应该排在课程 0 之后。 因此,一个正确的课程顺序是 [0,1,2,3] 。另一个正确的排序是 [0,2,1,3] 。
class Solution {
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int[] indegrees = new int[numCourses];
for (int[] pre: prerequisites) indegrees[pre[0]]++;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i) {
if (indegrees[i] == 0) queue.offer(i);
}
int cnt = 0;
int[] ans = new int[numCourses];
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int t = queue.poll();
ans[cnt++] = t;
for (int[] cur: prerequisites) {
if (cur[1] == t && --indegrees[cur[0]] == 0) queue.offer(cur[0]);
}
}
if (cnt == numCourses) return ans;
return new int[0];
}
}输入: image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]] sr = 1, sc = 1, newColor = 2 输出: [[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]] 解析: 在图像的正中间,(坐标(sr,sc)=(1,1)), 在路径上所有符合条件的像素点的颜色都被更改成2。 注意,右下角的像素没有更改为2, 因为它不是在上下左右四个方向上与初始点相连的像素点。
class Solution {
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n = image.length;
if (n == 0) return image;
int m = image[0].length;
int c = image[sr][sc];
if (c == newColor) return image;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{sr, sc});
image[sr][sc] = newColor;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = queue.poll();
int x = t[0], y = t[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || image[a][b] != c) continue;
image[a][b] = newColor;
queue.offer(new int[]{a, b});
}
}
return image;
}
}输入:n = 3, paths = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,1]] 输出:[1,2,3] 解释: 花园 1 和 2 花的种类不同。 花园 2 和 3 花的种类不同。 花园 3 和 1 花的种类不同。 因此,[1,2,3] 是一个满足题意的答案。其他满足题意的答案有 [1,2,4]、[1,4,2] 和 [3,2,1]
class Solution {
public int[] gardenNoAdj(int n, int[][] paths) {
int[] ans = new int[n];
List<List<Integer>> adjacency = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) adjacency.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] cur: paths) {
adjacency.get(cur[0]).add(cur[1]);
adjacency.get(cur[1]).add(cur[0]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
boolean[] color = new boolean[5];
for (int id: adjacency.get(i)) color[ans[id - 1]] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; ++j) {
if (!color[j]) {
ans[i - 1] = j;
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {this.val = val; this.next = next;}
} public static ListNode createList(int[] nums) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
for (int num: nums) {
cur = cur.next = new ListNode(num);
}
return dummy.next;
}
public static ListNode createRandomList(int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
Random random = new Random();
while (n-- > 0){
cur = cur.next = new ListNode(random.nextInt() % 1001);
}
return dummy.next;
} public static void printList(ListNode head) {
while (head != null) {
if (head.next != null) System.out.print(head.val + "->");
else System.out.print(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
ListNode cur = this;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (cur != null) {
sb.append(cur.val);
if (cur.next != null) sb.append("->");
cur = cur.next;
}
return sb.toString();
}输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,0,8] 解释:342 + 465 = 807.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
int c = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int a = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int b = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int t = a + b + c;
cur = cur.next = new ListNode(t % 10);
c = t / 10;
if (l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if (l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
}
if (c == 1) cur.next = new ListNode(1);
return dummy.next;
}
}输入:(7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) 输出:7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null) {
s1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
s2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
ListNode cur = null;
int c = 0;
while (!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty() || c != 0) {
int a = s1.isEmpty() ? 0 : s1.pop();
int b = s2.isEmpty() ? 0 : s2.pop();
int t = a + b + c;
c = t / 10;
ListNode tmp = new ListNode(t % 10);
tmp.next = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return cur;
}
}输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head, prev = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
}输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4 输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode a = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; ++i) a = a.next;
ListNode b = a.next, c = b.next;
int k = right - left;
while (k-- > 0) {
ListNode t = c.next;
c.next = b;
b = c;
c = t;
}
a.next.next = c;
a.next = b;
return dummy.next;
}
}输入:head = [1,3,2] 输出:[2,3,1]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return new int[]{};
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode a = dummy;
ListNode b = a.next, c = b.next;
while (c != null && b != null) {
ListNode t = c.next;
c.next = b;
b = c;
c = t;
}
a.next.next = c;
a.next = b;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (ListNode p = dummy.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
ans.add(p.val);
}
return ans.stream().mapToInt(Integer::valueOf).toArray();
}
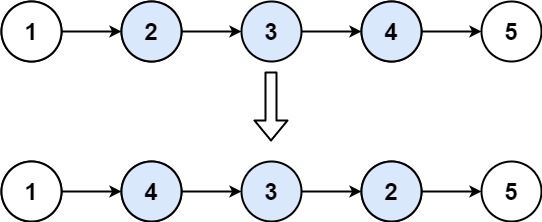
}给定链表 1->2->3->4->5, 重新排列为 1->5->2->4->3.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return;
int n = 0;
for (ListNode p = head; p != null; p = p.next) n++;
ListNode mid = head;
for (int i = 0; i < (n + 1) / 2 - 1; ++i) mid = mid.next;
ListNode a = mid, b = a.next;
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) {
ListNode c = b.next;
b.next = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
ListNode p = head, q = a;
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) {
ListNode o = q.next;
q.next = p.next;
p.next = q;
p = q.next;
q = o;
}
if (n % 2 == 1) mid.next = null;
else mid.next.next = null;
}
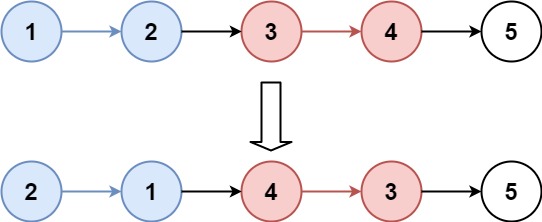
}输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode p = dummy;
while (p != null) {
ListNode q = p;
for (int i = 0; i < k && q != null; ++i) q = q.next;
if (q == null) break;
ListNode a = p.next, b = a.next;
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; ++i) {
ListNode c = b.next;
b.next = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
ListNode t = p.next;
p.next = a;
t.next = b;
p = t;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}输入: 1->2->2->1 输出: true
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
int n = 0;
for (ListNode p = head; p != null; p = p.next) n++;
if (n == 1) return true;
ListNode a = head;
for (int i = 0; i < (n + 1) / 2; ++i) a = a.next;
ListNode b = a.next;
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2 - 1; ++i) {
ListNode c = b.next;
b.next = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
ListNode p = head, q = a;
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) {
if (p.val != q.val) return false;
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
}
return true;
}
}输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Reference of the node with value = 8 输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode A = headA, B = headB;
while (A != B) {
A = A == null ? headB : A.next;
B = B == null ? headA : B.next;
}
return A;
}
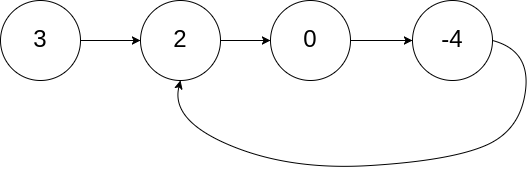
}输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return false;
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return false;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode s = head, f = head.next;
while (s != f) {
if (f == null || f.next == null) return null;
s = s.next;
f = f.next.next;
}
s = head;
f = f.next;
while (s != f) {
s = s.next;
f = f.next;
}
return f;
}
}给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2. 返回链表 4->5.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode l1 = head, l2 = head;
while (k-- > 0) l1 = l1.next;
while (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
return l2;
}
}输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5 输出: [4,1,9] 解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head.val == val) return head.next;
for (ListNode p = head; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (p.next != null && p.next.val == val) {
p.next = p.next.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}输入:head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5 输出:[4,1,9] 解释:给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode l1 = dummy, l2 = dummy;
while (n-- >= 0) l1 = l1.next;
while (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
l2.next = l2.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
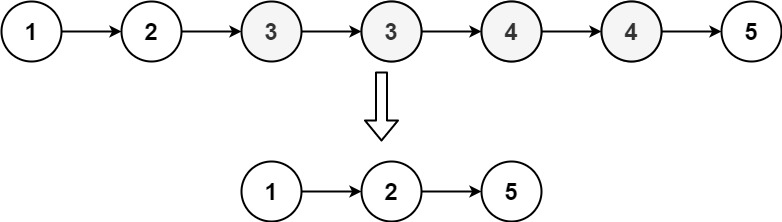
}输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode cur = head;
for (ListNode p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (p.val != cur.val) cur = cur.next = p;
}
cur.next = null;
return head;
}
}输入:head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5] 输出:[1,2,5]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode p = dummy;
while (p.next != null) {
ListNode q = p.next.next;
while (q != null && q.val == p.next.val) q = q.next;
if (p.next.next == q) p = p.next;
else p.next = q;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}输入:[1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1] 输出:[1, 2, 3]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeDuplicateNodes(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(head.val);
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
ListNode p = cur.next;
if (set.add(p.val)) cur = cur.next;
else cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
cur.next = null;
return head;
}
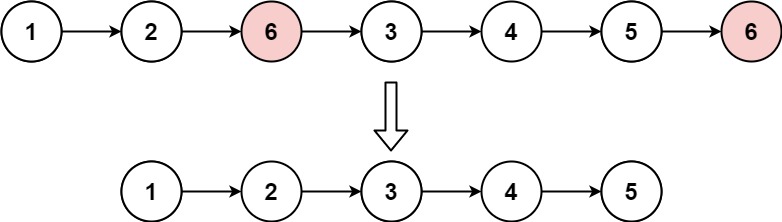
}输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummy, cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) prev.next = cur.next;
else prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}输入: 4->2->1->3 输出: 1->2->3->4
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = head;
while (p != null) {
ListNode cur = dummy, next = p.next;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val <= p.val) cur = cur.next;
p.next = cur.next;
cur.next = p;
p = next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode s = head, f = head;
while (f.next != null && f.next.next != null) {
s = s.next;
f = f.next.next;
}
f = s;
s = s.next;
f.next = null;
return merge(sortList(head), sortList(s));
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1), cur = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (l1 != null) cur.next = l1;
if (l2 != null) cur.next = l2;
return dummy.next;
}
}输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1), cur = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (l1 != null) cur.next = l1;
if (l2 != null) cur.next = l2;
return dummy.next;
}
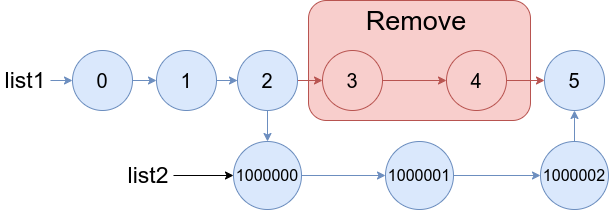
}输入:list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5], a = 3, b = 4, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002] 输出:[0,1,2,1000000,1000001,1000002,5] 解释:我们删除 list1 中第三和第四个节点,并将 list2 接在该位置。上图中蓝色的边和节点为答案链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) {
ListNode cur = list1;
ListNode begin = null, end = null;
int cnt = 0;
while (cur != null) {
if (cnt == a - 1) begin = cur;
else if (cnt == b) {
end = cur;
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
cnt++;
}
begin.next = list2;
cur = list2;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = end.next;
return list1;
}
}输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return lists[l];
if (l > r) return null;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, r));
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (l1 == null) cur.next = l2;
if (l2 == null) cur.next = l1;
return dummy.next;
}
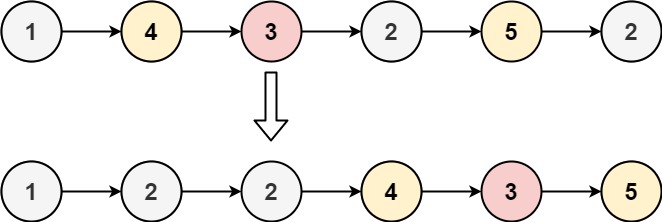
}输入:head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3 输出:[1,2,2,4,3,5]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode l1 = new ListNode(-1), l2 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur1 = l1, cur2 = l2, p = head;
while (p != null) {
if (p.val < x) cur1 = cur1.next = p;
else cur2 = cur2.next = p;
p = p.next;
}
cur2.next = null;
cur1.next = l2.next;
return l1.next;
}
}输入: root = [1, 2, 3], k = 5 输出: [[1],[2],[3],[],[]] 解释: 输入输出各部分都应该是链表,而不是数组。 例如, 输入的结点 root 的 val= 1, root.next.val = 2, \root.next.next.val = 3, 且 root.next.next.next = null。 第一个输出 output[0] 是 output[0].val = 1, output[0].next = null。 最后一个元素 output[4] 为 null, 它代表了最后一个部分为空链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode[] splitListToParts(ListNode root, int k) {
int n = 0;
for (ListNode p = root; p != null; p = p.next) n++;
ListNode cur = root;
int len = n / k, rest = n % k;
ListNode[] ans = new ListNode[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
ans[i] = cur;
ListNode p = new ListNode(-1), q = p;
for (int j = 0; j < len + (i < rest ? 1 : 0) - 1; ++j) {
if (cur != null) cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur == null) break;
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = next;
}
return ans;
}
}输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ans;
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<>();
while (!stk.isEmpty() || root != null) {
while (root != null) {
ans.add(root.val);
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
root = root.right;
}
return ans;
}
}输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ans;
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<>();
while (!stk.isEmpty() || root != null) {
while (root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
ans.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return ans;
}
}输入: [1,null,2,3] 1 \ 2 / 3 输出: [3,2,1]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ans;
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<>();
TreeNode lastNode = null;
while (!stk.isEmpty() || root != null) {
while (root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.peek();
if (root.right == null || root.right == lastNode) {
stk.pop();
ans.add(root.val);
lastNode = root;
root = null;
} else root = root.right;
}
return ans;
}
}输入: [1,6,3,2,5] 输出: false 5 / \ 2 6 / \ 1 3
class Solution {
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
return dfs(postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
public boolean dfs(int[] postorder, int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return true;
int root = postorder[r];
int k = l;
while (postorder[k] < root) k++;
int t = k;
while (postorder[k] > root) k++;
return k == r & dfs(postorder, l, t - 1) && dfs(postorder, t, r - 1);
}
}3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7 [3,9,20,15,7]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return new int[]{};
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
ans.add(t.val);
if (t.left != null) queue.offer(t.left);
if (t.right != null) queue.offer(t.right);
}
return ans.stream().mapToInt(Integer::valueOf).toArray();
}
}3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7 [ [3], [20,9], [15,7] ]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ans;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean flag = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
Deque<Integer> level = new LinkedList<>();
while (size-- > 0) {
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
if (flag) level.offerFirst(t.val);
else level.offerLast(t.val);
if (t.left != null) queue.offer(t.left);
if (t.right != null) queue.offer(t.right);
}
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(level));
flag = !flag;
}
return ans;
}
}输入:前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7] 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 输出: 3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; ++i) map.put(inorder[i], i);
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int pl, int pr, int[] inorder, int il, int ir) {
if (pl > pr) return null;
int k = map.get(preorder[pl]);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pl]);
root.left = build(preorder, pl + 1, pl + k - il , inorder, il, k - 1);
root.right = build(preorder, pl + k - il + 1, pr, inorder, k + 1, ir);
return root;
}
}输入:中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 输出: 3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; ++i) map.put(inorder[i], i);
return build(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] inorder, int il, int ir, int[] postorder, int pl, int pr) {
if (il > ir) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[pr]);
int k = map.get(postorder[pr]);
root.left = build(inorder, il, k - 1, postorder, pl, pl + k - il - 1);
root.right = build(inorder, k + 1, ir, postorder, pl + k - il, pr - 1);
return root;
}
}输入:pre = [1,2,4,5,3,6,7], post = [4,5,2,6,7,3,1] 输出:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode constructFromPrePost(int[] pre, int[] post) {
for (int i = 0; i < post.length; ++i) map.put(post[i], i);
return build(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, post, 0);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] pre, int pl, int pr, int[] post, int ql) {
if (pl > pr) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[pl]);
if (pl < pr) {
int leftv = pre[pl + 1];
int cnt = map.get(leftv) - ql + 1;
root.left = build(pre, pl + 1, pl + cnt, post, ql);
root.right = build(pre, pl + cnt + 1, pr, post, ql + cnt);
}
return root;
}
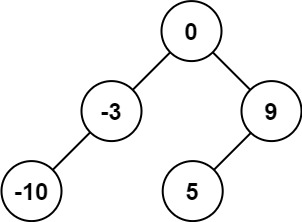
}输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] 输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5] 解释:[0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return dfs(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode dfs(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (l > r) return null;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = dfs(nums, l, mid - 1);
root.right = dfs(nums, mid + 1, r);
return root;
}
}给定的有序链表: [-10, -3, 0, 5, 9], 一个可能的答案是:[0, -3, 9, -10, null, 5], 它可以表示下面这个高度平衡二叉搜索树: 0 / \ -3 9 / / -10 5
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
else if (head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(slow.val);
pre.next = null;
root.left = sortedListToBST(head);
root.right = sortedListToBST(slow.next);
return root;
}
}输入:root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] 输出:[1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<>();
stk.push(root);
TreeNode prev = null;
while (!stk.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = stk.pop();
if (prev != null) {
prev.left = null;
prev.right = cur;
}
if (cur.right != null) stk.push(cur.right);
if (cur.left != null) stk.push(cur.left);
prev = cur;
}
}
}你可以将以下二叉树: 1 / \ 2 3 / \ 4 5 序列化为 "[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]"
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return "[]";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
if (t != null) {
sb.append(t.val + ",");
queue.offer(t.left);
queue.offer(t.right);
} else sb.append("null,");
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if (data.equals("[]")) return null;
String[] val = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1).split(",");
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int idx = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
if (!val[idx].equals("null")) {
t.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val[idx]));
queue.offer(t.left);
}
idx++;
if (!val[idx].equals("null")) {
t.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val[idx]));
queue.offer(t.right);
}
idx++;
}
return root;
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec = new Codec();
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));输入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3] 输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null) return false;
if (p == null && q == null) return true;
if (p.val != q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return isSameTree(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) return true;
if (p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null) return false;
if (p.val != q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.right) && isSameTree(q.left, p.right);
}
}3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7 输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return Math.abs(getDepth(root.left) - getDepth(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
public int getDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(getDepth(root.left), getDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}输入:[1,2,3,4,5,6] 输出:true 解释:最后一层前的每一层都是满的(即,结点值为 {1} 和 {2,3} 的两层),且最后一层中的所有结点({4,5,6})都尽可能地向左。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean flag = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if (cur == null) {
flag = true;
continue;
} else {
if (flag) return false;
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return true;
}
}输入:root = [1,2,3,4], x = 4, y = 3 输出:false
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> depth = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<Integer, TreeNode> parent = new HashMap<>();
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
if (root == null) return true;
dfs(root, null);
return depth.get(x) == depth.get(y) && parent.get(x) != parent.get(y);
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
if (root == null) return;
depth.put(root.val, p == null ? 0 : depth.get(p.val) + 1);
parent.put(root.val, p);
dfs(root.left, root);
dfs(root.right, root);
}
}输入:A = [1,2,3], B = [3,1] 输出:false
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
return A != null && B != null && (dfs(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B));
}
public boolean dfs(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
if (B == null) return true;
if (A == null || A.val != B.val) return false;
return dfs(A.left, B.left) && dfs(A.right, B.right);
}
}s: 3 / \ 4 5 / \ 1 2 t: 4 / \ 1 2 返回 true,因为 t 与 s 的一个子树拥有相同的结构和节点值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (t == null) return true;
if (s == null) return false;
return isSubtree(s.left, t) || isSubtree(s.right, t) || isSameTree(s, t);
}
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) return true;
if (p == null || q == null) return false;
if (p.val != q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7 返回它的最大深度 3
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
depth++;
int size = queue.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) return depth;
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return -1;
}
}1 / \ 2 3 / \ 4 5 返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int ans = 0;
public int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int l = dfs(root.left);
int r = dfs(root.right);
ans = Math.max(ans, l + r + 1);
return Math.max(l, r) + 1;
}
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans - 1;
}
}输入: 1 / \ 2 3 \ 5 输出: ["1->2->5", "1->3"] 解释: 所有根节点到叶子节点的路径为: 1->2->5, 1->3
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public void dfs(TreeNode root, String path) {
if (root == null) return;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(path);
sb.append(Integer.toString(root.val));
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) ans.add(sb.toString());
else {
sb.append("->");
dfs(root.left, sb.toString());
dfs(root.right, sb.toString());
}
}
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, "");
return ans;
}
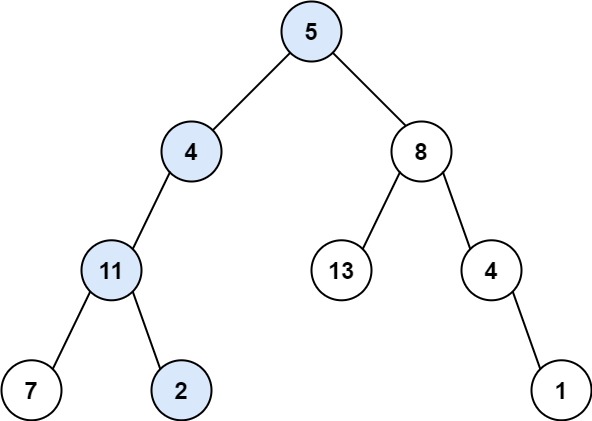
}输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
boolean ans = false;
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) return;
targetSum -= root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == 0) ans = true;
dfs(root.left, targetSum);
dfs(root.right, targetSum);
}
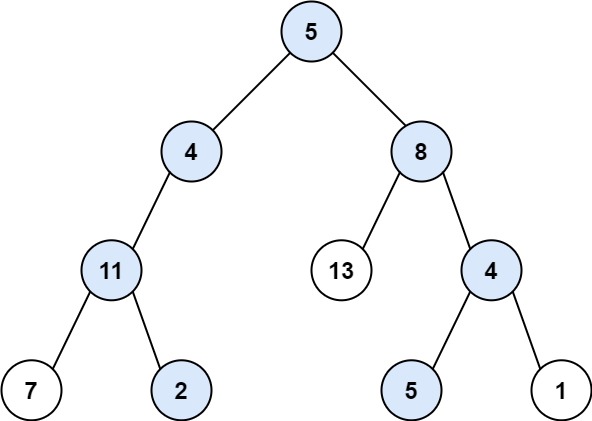
}输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) return;
targetSum -= root.val;
path.add(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == 0) ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
dfs(root.left, targetSum);
dfs(root.right, targetSum);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}- 前缀和
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8 10 / \ 5 -3 / \ \ 3 2 11 / \ \ 3 -2 1 返回 3。和等于 8 的路径有: 1. 5 -> 3 2. 5 -> 2 -> 1 3. -3 -> 11
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
map.put(0, 1);
return dfs(root, 0, targetSum);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, int curSum, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int ans = 0;
curSum += root.val;
ans += map.getOrDefault(curSum - targetSum, 0);
map.put(curSum, map.getOrDefault(curSum, 0) + 1);
int left = dfs(root.left, curSum, targetSum);
int right = dfs(root.right, curSum, targetSum);
ans += left + right;
map.put(curSum, map.get(curSum) - 1);
return ans;
}
}输入: 5 / \ 4 5 / \ \ 1 1 5 输出:2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int ans = 0;
public int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = dfs(root.left);
int right = dfs(root.right);
int tLeft = 0, tRight = 0;
if (root.left != null && root.val == root.left.val) tLeft = left + 1;
if (root.right != null && root.val == root.right.val) tRight = right + 1;
ans = Math.max(ans, tLeft + tRight);
return Math.max(tLeft, tRight);
}
}输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 输出: 6 解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。 输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4 输出: 2 解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
TreeNode cur = root;
while (true) {
if (p.val < cur.val && q.val < cur.val) cur = cur.left;
else if (p.val > cur.val && q.val > cur.val) cur = cur.right;
else break;
}
return cur;
}
}输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出: 3 解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, TreeNode> map = new HashMap<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
dfs(root);
while (p != null) {
visited.add(p.val);
p = map.get(p.val);
}
while (q != null) {
if (visited.contains(q.val)) return q;
q = map.get(q.val);
}
return null;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root.left != null) {
map.put(root.left.val, root);
dfs(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
map.put(root.right.val, root);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left == null && right == null) return null;
if (left == null) return right;
if (right == null) return left;
return root;
}
}输入: s1 = "ab" s2 = "eidbaooo" 输出: True 解释: s2 包含 s1 的排列之一 ("ba").
class Solution {
public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
int n = s1.length(), m = s2.length();
if (n > m) return false;
int[] cnt = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cnt[s1.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
for (int l = 0, r = 0; r < m; ++r) {
int x = s2.charAt(r) - 'a';
cnt[x]++;
while (cnt[x] > 0) --cnt[s2.charAt(l++) - 'a'];
if (r - l + 1 == n) return true;
}
return false;
}
}输入: S = "cba" T = "abcd" 输出: "cbad" 解释: S中出现了字符 "a", "b", "c", 所以 "a", "b", "c" 的顺序应该是 "c", "b", "a". 由于 "d" 没有在S中出现, 它可以放在T的任意位置. "dcba", "cdba", "cbda" 都是合法的输出。
class Solution {
public String customSortString(String S, String T) {
int n = S.length(), m = T.length();
if (n == 0) return T;
int[] cnt = new int[26];
for (char c: T.toCharArray()) cnt[c - 'a']++;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (char c: S.toCharArray()) {
while (cnt[c - 'a'] > 0) {
sb.append(c);
cnt[c - 'a']--;
}
}
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; ++c) {
while (cnt[c - 'a'] > 0) {
sb.append(c);
cnt[c - 'a']--;
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}输入:words = ["word","world","row"], order = "worldabcefghijkmnpqstuvxyz" 输出:false 解释:在该语言的字母表中,'d' 位于 'l' 之后,那么 words[0] > words[1],因此单词序列不是按字典序排列的。
class Solution {
public boolean isAlienSorted(String[] words, String order) {
int[] map = new int[26];
int n = words.length, m = order.length();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) map[order.charAt(i) - 'a'] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
String a = words[i], b = words[i + 1];
boolean flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < Math.min(a.length(), b.length()) && flag; ++j) {
if (a.charAt(j) != b.charAt(j)) {
if (map[a.charAt(j) - 'a'] > map[b.charAt(j) - 'a']) return false;
else flag = false;
}
}
if (a.length() > b.length() && flag) return false;
}
return true;
}
}输入: "tree" 输出: "eert" 解释: 'e'出现两次,'r'和't'都只出现一次。 因此'e'必须出现在'r'和't'之前。此外,"eetr"也是一个有效的答案。
class Solution {
public String frequencySort(String s) {
int[] cnt = new int[128];
for (char c: s.toCharArray()) cnt[c]++;
PriorityQueue<Character> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2)->cnt[o2] - cnt[o1]);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt.length; ++i) {
if (cnt[i] > 0) heap.add((char)i);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
char t = heap.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < cnt[t]; ++i) sb.append(t);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}输入:logs = ["dig1 8 1 5 1","let1 art can","dig2 3 6","let2 own kit dig","let3 art zero"] 输出:["let1 art can","let3 art zero","let2 own kit dig","dig1 8 1 5 1","dig2 3 6"] 解释: 字母日志的内容都不同,所以顺序为 "art can", "art zero", "own kit dig" 。 数字日志保留原来的相对顺序 "dig1 8 1 5 1", "dig2 3 6" 。
class Solution {
public String[] reorderLogFiles(String[] logs) {
Arrays.sort(logs, (a, b)-> {
String[] sa = a.split(" ", 2), sb = b.split(" ", 2);
boolean aisDigit = Character.isDigit(sa[1].charAt(0));
boolean bisDigit = Character.isDigit(sb[1].charAt(0));
if (!aisDigit && !bisDigit) {
if (!sa[1].equals(sb[1])) return sa[1].compareTo(sb[1]);
else return sa[0].compareTo(sb[0]);
}
else if (aisDigit && bisDigit) return 0;
else if (!aisDigit) return -1;
else return 1;
});
return logs;
}
}输入:haystack = "hello", needle = "ll" 输出:2
class Solution {
public int[] getNext(char[] s, int n) {
int[] next = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
while (j > 0 && s[i] != s[j + 1]) j = next[j];
if (s[i] == s[j + 1]) j++;
next[i] = j;
}
return next;
}
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
if (m == 0) return 0;
haystack = " " + haystack;
needle = " " + needle;
char[] p = haystack.toCharArray();
char[] s = needle.toCharArray();
int[] next = getNext(s, m);
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
while (j > 0 && p[i] != s[j + 1]) j = next[j];
if (p[i] == s[j + 1]) j++;
if (j == m) return i - m;
}
return -1;
}
}输入:s = "aa" p = "a" 输出:false 解释:"a" 无法匹配 "aa" 整个字符串。 输入:s = "aab" p = "c*a*b" 输出:true 解释:因为 '*' 表示零个或多个,这里 'c' 为 0 个, 'a' 被重复一次。因此可以匹配字符串 "aab"。 输入:s = "mississippi" p = "mis*is*p*." 输出:false
状态表示:f[i][j]表示所有s[1-i]和p[1-j]的匹配方案,是否存在一个合法方案
状态计算:
p[j] != '*' ==> (s[i] == p[j] || p[j] == '.') && f[i - 1][j - 1]
p[j] == '*' ==> f[i][j] = f[i][j - 2] || f[i - 1][j - 2] && s[i] || f[i - 2][j - 2] && s[i] && s[i - 1] ...
f[i - 1][j] = f[i - 1][j - 2] || f[i - 2][j - 2] && s[i - 1] || f[i - 3][j - 2] && s[i - 1] && s[i -2] ...
==> f[i][j] = f[i][j - 2] || f[i - 1][j] & s[i]
class Solution {
public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
int n = s.length(), m = p.length();
s = " " + s;
p = " " + p;
char[] sa = s.toCharArray();
char[] pa = p.toCharArray();
boolean[][] f = new boolean[n + 1][m + 1];
f[0][0] = true;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
if (j + 1 <= m && pa[j + 1] == '*') continue;
if (i > 0 && pa[j] != '*') f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] && (sa[i] == pa[j] || pa[j] == '.');
else if (pa[j] == '*') {
f[i][j] = f[i][j - 2] || i > 0 && f[i - 1][j] && (sa[i] == pa[j - 1] || pa[j - 1] == '.');
}
}
}
return f[n][m];
}
}输入: pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat dog" 输出: true
class Solution {
public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String s) {
String[] str = s.split(" ");
if (pattern.length() != str.length) return false;
HashMap<Object, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); ++i) {
if (!Objects.equals(map.put(pattern.charAt(i), i), map.put(str[i], i))) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
class Solution {
public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String s) {
String[] str = s.split(" ");
if (pattern.length() != str.length) return false;
HashMap<Character, String> map = new HashMap<>();
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < pattern.length(); ++i) {
char c = pattern.charAt(i);
if (map.containsKey(c)) {
if (!map.get(c).equals(str[i])) return false;
} else {
if (set.contains(str[i])) return false;
map.put(c, str[i]);
set.add(str[i]);
}
}
return true;
}
}输入: big = "mississippi" smalls = ["is","ppi","hi","sis","i","ssippi"] 输出: [[1,4],[8],[],[3],[1,4,7,10],[5]]
class Solution {
class Trie {
class Node {
Node son[];
boolean isEnd;
public Node() {
son = new Node[26];
isEnd = false;
}
}
Node root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (char c: word.toCharArray()) {
int u = c - 'a';
if (cur.son[u] == null) cur.son[u] = new Node();
cur = cur.son[u];
}
cur.isEnd = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (char c: word.toCharArray()) {
int u = c - 'a';
if (cur.son[u] == null) return false;
cur = cur.son[u];
}
return cur.isEnd;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
Node cur = root;
for (char c: prefix.toCharArray()) {
int u = c - 'a';
if (cur.son[u] == null) return false;
cur = cur.son[u];
}
return true;
}
}
public int[][] multiSearch(String big, String[] smalls) {
Map<String, List<Integer>> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
Trie trie = new Trie();
for (int i = 0; i < smalls.length; ++i) {
trie.insert(smalls[i]);
map.put(smalls[i], new LinkedList<>());
}
int n = big.length();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < n) {
String word = big.substring(i, j + 1);
if (!trie.startsWith(word)) j = ++i;
else {
if (map.containsKey(word)) map.get(word).add(i);
j++;
}
if (j > n - 1) j = ++i;
}
int[][] ans = new int[smalls.length][];
i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, List<Integer>> entry: map.entrySet()) {
int size = entry.getValue().size();
int[] t = new int[size];
for (int k = 0; k < size; ++k) t[k] = entry.getValue().get(k);
ans[i++] = t;
}
return ans;
}
}输入:a = "abcd", b = "cdabcdab" 输出:3 解释:a 重复叠加三遍后为 "abcdabcdabcd", 此时 b 是其子串。
class Solution {
public int[] getNext(char[] s, int n) {
int[] next = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
while (j > 0 && s[i] != s[j + 1]) j = next[j];
if (s[i] == s[j + 1]) j++;
next[i] = j;
}
return next;
}
public int repeatedStringMatch(String a, String b) {
int n = a.length(), m = b.length();
b = " " + b;
char[] p = a.toCharArray();
char[] s = b.toCharArray();
int[] next = getNext(s, m);
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i - j < n) {
while (j > 0 && p[i % n] != s[j + 1]) j = next[j];
if (p[i % n] == s[j + 1]) j++;
i++;
if (j == m) return (i % n == 0) ? i / n : i / n + 1;
}
return -1;
}
}输入: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram" 输出: true
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
int n = s.length(), m = t.length();
if (n != m) return false;
int[] cnt1 = new int[26];
int[] cnt2 = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cnt1[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cnt2[t.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (cnt1[i] != cnt2[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
}输入: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"] 输出: [ ["ate","eat","tea"], ["nat","tan"], ["bat"] ]
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str: strs) {
char[] s = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(s);
String key = new String(s);
List<String> list = map.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList<String>());
list.add(str);
map.put(key, list);
}
return new ArrayList<List<String>>(map.values());
}
}输入: s: "cbaebabacd" p: "abc" 输出: [0, 6] 解释: 起始索引等于 0 的子串是 "cba", 它是 "abc" 的字母异位词。 起始索引等于 6 的子串是 "bac", 它是 "abc" 的字母异位词。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
int n = s.length(), m = p.length();
char[] S = s.toCharArray();
char[] P = p.toCharArray();
int[] cnt = new int[128];
for (char c: P) cnt[c]++;
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 128; ++i) if (cnt[i] > 0) t++;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0, j = 0, sum = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (--cnt[S[i]] == 0) sum++;
while (i - j + 1 > m) {
if (cnt[S[j]] == 0) sum--;
cnt[S[j++]]++;
}
if (sum == t) ans.add(j);
}
return ans;
}
}